中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 1773-1778.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3083
• 组织构建相关数据分析 Date analysis of organization construction • 上一篇 下一篇
肩袖损伤后脂肪浸润基因表达谱及关键通路的生物信息学分析
刘沛东1,2,冯江峰1,2,徐文杰1,许晓栋1,杨自权1,2
- 山西医科大学第二医院,1运动医学科,2骨与软组织损伤修复省重点实验室,山西省太原市 030000
Bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profile and key pathways related to fatty infiltration after rotator cuff injury
Liu Peidong1, 2, Feng Jiangfeng1, 2, Xu Wenjie1, Xu Xiaodong1, Yang Ziquan1, 2
- 1Department of Sports Medicine, 2Shanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Damage Repair, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
 文题释义:
文题释义:
肩袖损伤后脂肪浸润:是肩袖修补术后失败的关键因素之一,其与再撕裂率和功能预后密切相关。脂肪浸润多发生在肩袖撕裂后1年内,萎缩的肌肉组织被脂肪组织替代,并向邻近组织侵袭,影响肌肉及肌腱的质量及力学特性。
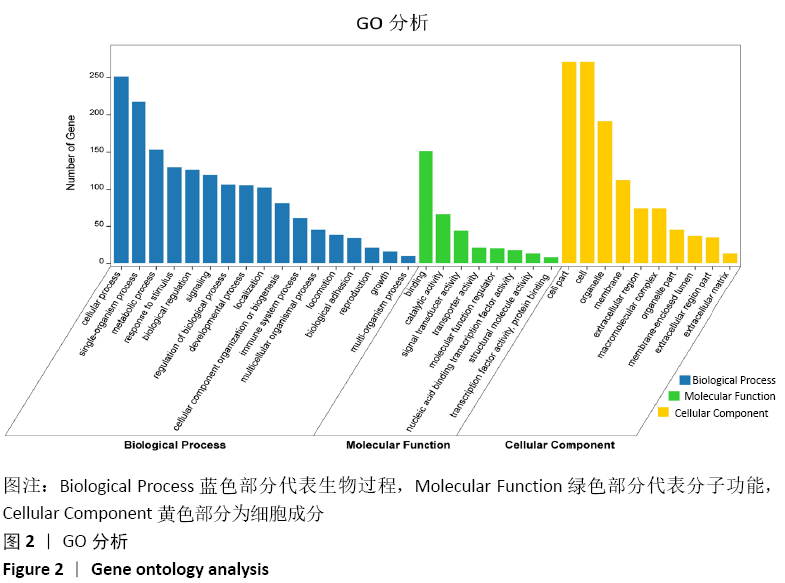
基因本体分析(Gene ontology,GO):是通过对生物学的3个方面——细胞组分(cellular component)、分子功能(molecular function)、生物过程(biological process),将差异基因从功能、参与的生物途径及细胞中的定位进行了标准化描述,即对基因产物进行了简单注释。
背景:脂肪浸润是肩袖修补术后失败的关键因素,然而肩袖损伤后脂肪浸润的病理变化机制尚不清楚。
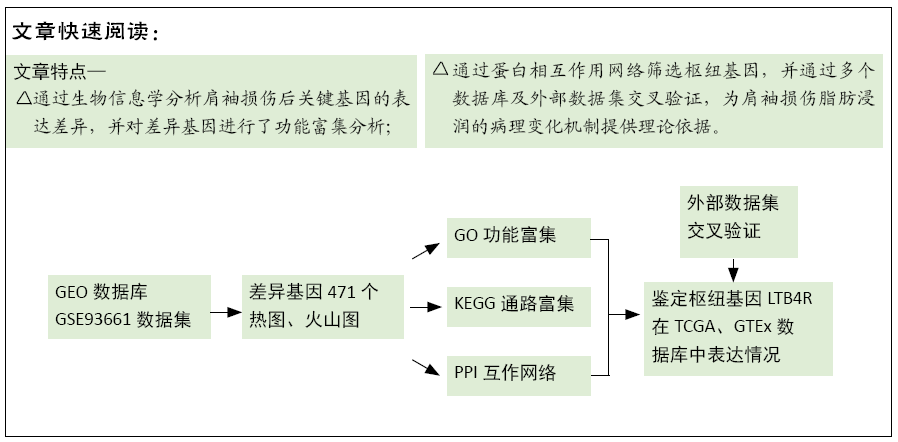
目的:旨在探索肩袖损伤后关键基因的表达差异,确定其功能和机制通路,为肩袖损伤脂肪浸润的病理变化机制提供理论依据。
方法:通过GEO数据库获取GSE93661芯片筛选差异表达基因,采用GO、KEGG分析脂肪浸润的潜在机制。通过构建PPI网络获取枢纽基因,分析潜在致病靶点。
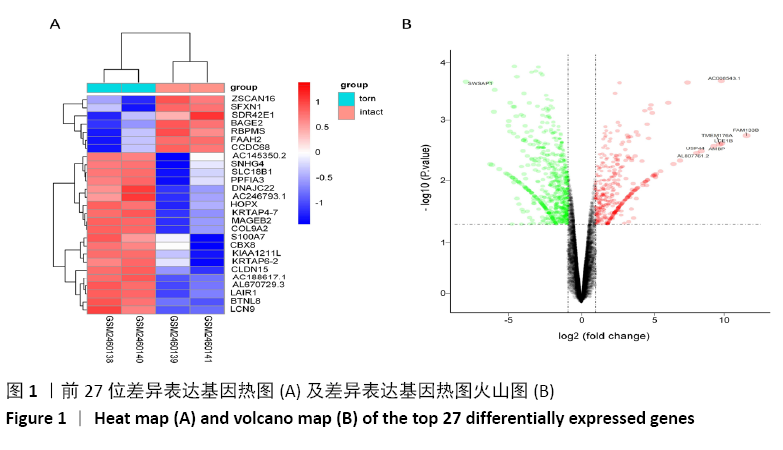
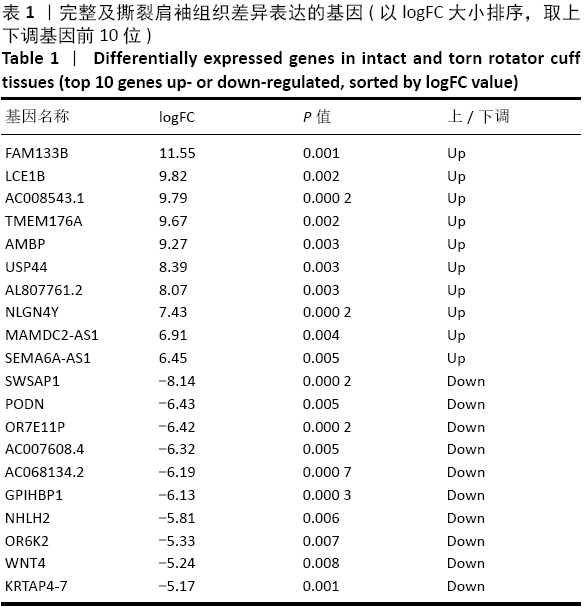
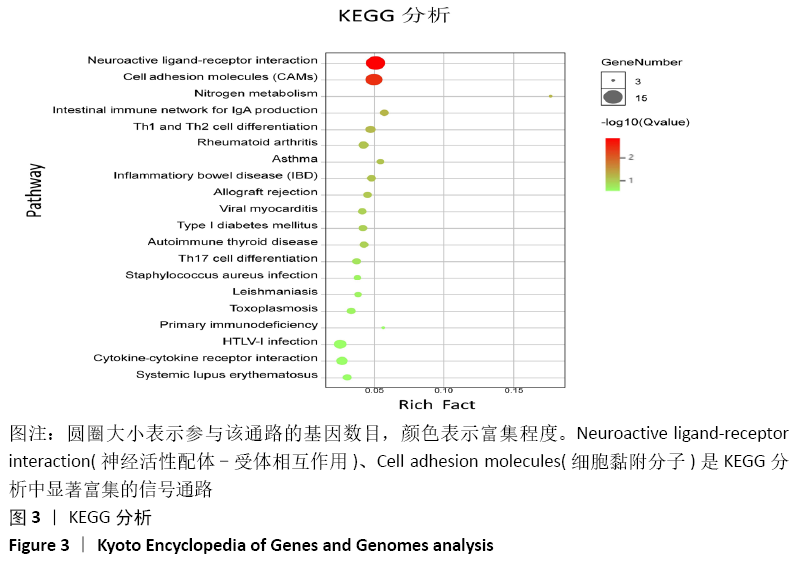
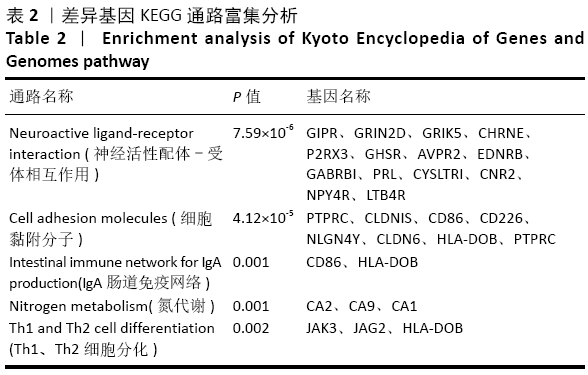
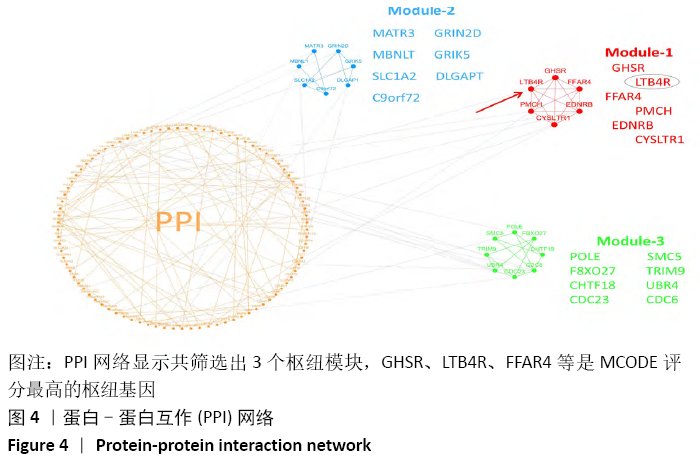
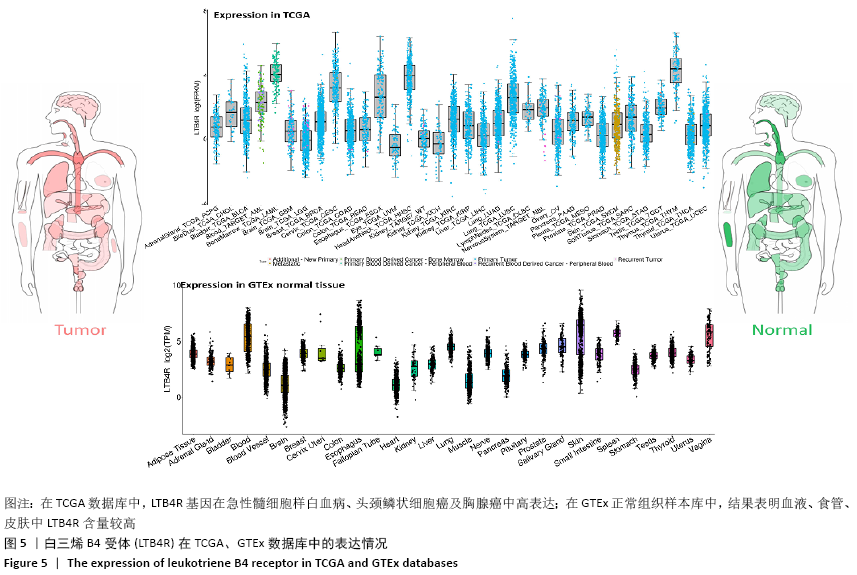
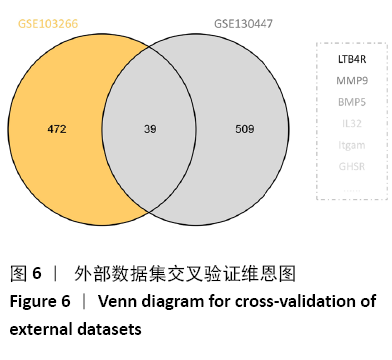
结果与结论:共鉴定差异表达基因471个。GO和KEGG分析表明神经活性配体-受体相互作用、细胞黏附分子通路是肩袖损伤脂肪浸润的潜在机制。白三烯B4受体(LTB4R)作为PPI网络中的枢纽基因,可能是肩袖损伤脂肪浸润的关键靶标。提示:文章发现了肩袖损伤后脂肪浸润病理发展中潜在的关键基因和通路,为今后的治疗提供了参考方向。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1261-6120(刘沛东)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: