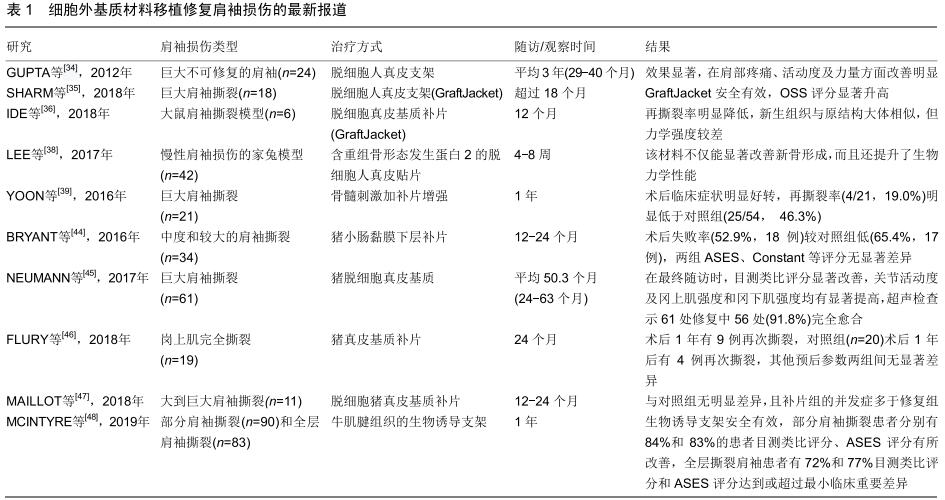
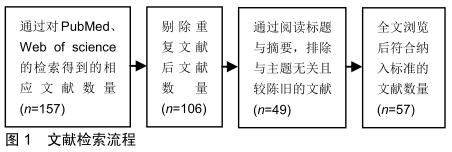
|
[1] HASHIMOTO T, NOBUHARA K, HAMADA T. Pathologic evidence of degeneration as a primary cause of rotator cuff tear. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;(415):111-120.
[2] FEHRINGER EV, SUN J, VANOEVEREN LS, et al. Full-thickness rotator cuff tear prevalence and correlation with function and co-morbidities in patients sixty-five years and older.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(6):881-885.
[3] KIM M, TEEFEY SA, ZELIG A, et al. Shoulder Strength in Asymptomatic Individuals with Intact Compared with Torn Rotator Cuffs .J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91a(2):289-296.
[4] 冉北航,张芬,尹文芳.羽毛球运动中发生手腕和肩袖损伤的相关因素调查[J].中国临床康复, 2006,10(44):41-43.
[5] COLVIN AC, EGOROVA N, HARRISON AK, et al. National Trends in Rotator Cuff Repair.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2012;94a(3):227-233.
[6] JUDGE A, MURPHY RJ, MAXWELL R, et al. Temporal trends and geographical variation in the use of subacromial decompression and rotator cuff repair of the shoulder in England.Bone Joint J. 2014;96b(1): 70-74.
[7] PALONEVA J, LEPOLA V, AARIMAA V, et al. Increasing incidence of rotator cuff repairs--A nationwide registry study in Finland.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2015;16:189.
[8] ELLMAN H. Diagnosis and treatment of incomplete rotator cuff tears. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1990;254:64-74.
[9] THON SG, O'MALLEY L 2ND, O'BRIEN MJ, et al. Evaluation of Healing Rates and Safety With a Bioinductive Collagen Patch for Large and Massive Rotator Cuff Tears:2-Year Safety and Clinical Outcomes.Am J Sports Med.2019;47(8):1901-1908.
[10] ALLEN GM. The diagnosis and management of shoulder pain.J Ultrason.2018;18(74): 234-239.
[11] BUNKER DL, ILIE V, ILIE V, et al. Tendon to bone healing and its implications for surgery . Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4(3): 343-350.
[12] GALATZ L M, SANDELL L J, ROTHERMICH S Y, et al. Characteristics of the rat supraspinatus tendon during tendon-to-bone healing after acute injury.J Orthop Res.2006;24(3):541-550.
[13] CARPENTER JE, WENING JD, MELL AG, et al. Changes in the long head of the biceps tendon in rotator cuff tear shoulders.Clin Biomech. 2005;20(2):162-165.
[14] SANO H, KUMAGAI J, SAWAI T. Experimental fascial autografting for the supraspinatus tendon defect:Remodeling process of the grafted fascia and the insertion into bone.J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2002;11(2): 166-173.
[15] KIRCHER J, SCHMIDT F, HAWELLEK T, et al. Autologous bridging of rotator cuff tears with a hamstring tendon patch. A cadaver feasibility study and biomechanical testing.Clin Biomech. 2018;56(36-39.
[16] MIHARA S, FUJITA T, ONO T, et al. Rotator cuff repair using an original iliotibial ligament with a bone block patch: preliminary results with a 24-month follow-up period.J Shoulder Elb Surg.2016;25(7):1155-1162.
[17] ROSALES-VARO AP, GARCIA-ESPONA MA, RODA-MURILLO O. Outcomes of rotator cuff augmentation surgery with autologous fascia lata.Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol.2018;62(3):157-167.
[18] RHEE SM, OH JH. Bridging Graft in Irreparable Massive Rotator Cuff Tears:Autogenic Biceps Graft versus Allogenic Dermal Patch Graft.Clin Orthop Surg.2017;9(4):497-505.
[19] CHUNG SW, KIM JY, KIM MH, et al. Arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears: outcome and analysis of factors associated with healing failure or poor postoperative function.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(7):1674-1683.
[20] MORI D, FUNAKOSHI N, YAMASHITA F.Arthroscopic surgery of irreparable large or massive rotator cuff tears with low-grade fatty degeneration of the infraspinatus:patch autograft procedure versus partial repair procedure.Arthroscopy.2013;29(12):1911-1921.
[21] MORI D, FUNAKOSHI N, YAMASHITA F, et al. Effect of Fatty degeneration of the infraspinatus on the efficacy of arthroscopic patch autograft procedure for large to massive rotator cuff tears.Am J Sports Med.2015;43(5):1108-1117.
[22] KEW SJ, GWYNNE JH, ENEA D, et al. Synthetic collagen fascicles for the regeneration of tendon tissue.Acta Biomater.2012;8(10):3723-3731.
[23] BADYLAK SF, FREYTES DO, GILBERT TW. Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material:Structure and function.Acta Biomater. 2009; 5(1):1-13.
[24] SHEA KP, OBOPILWE E, SPERLING JW, et al.A biomechanical analysis of gap formation and failure mechanics of a xenograft-reinforced rotator cuff repair in a cadaveric model.J Shoulder Elb Surg.2012;21(8):1072-1079.
[25] CAI YZ, ZHANG C, JIN R L, et al. Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair With Graft Augmentation of 3-Dimensional Biological Collagen for Moderate to Large Tears:A Randomized Controlled Study.Am J Sports Med.2018;46(6):1424-1431.
[26] SCHLEGEL TF, ABRAMS JS, BUSHNELL BD, et al. Radiologic and clinical evaluation of a bioabsorbable collagen implant to treat partial-thickness tears: a prospective multicenter study.J Shoulder Elb Surg.2018;27(2):242-251.
[27] BOKOR DJ, SONNABEND D, DEADY L, et al. Evidence of healing of partial-thickness rotator cuff tears following arthroscopic augmentation with a collagen implant:a 2-year MRI follow-up.Muscles Ligaments Tendons J.2016;6(1):16-25.
[28] ARNOCZKY SP, BISHAI SK, SCHOFIELD B, et al. Histologic Evaluation of Biopsy Specimens Obtained After Rotator Cuff Repair Augmented With a Highly Porous Collagen Implant. Arthroscopy.2017;33(2):278-283.
[29] CHAUDHURY S, HOLLAND C, THOMPSON MS, et al. Tensile and shear mechanical properties of rotator cuff repair patches.J Shoulder Elb Surg.2012;21(9):1168-1176.
[30] RICCHETTI E T, AURORA A, IANNOTTI J P, et al. Scaffold devices for rotator cuff repair. J Shoulder Elb Surg.2012;21(2):251-265.
[31] PAN J, LIU GM, NING LJ, et al. Rotator cuff repair using a decellularized tendon slices graft: an in vivo study in a rabbit model. Knee Surg Sport Tr A.2015;23(5):1524-1535.
[32] SMITH RDJ, CARR A, DAKIN SG, et al. The Response Of Tenocytes To Commercial Scaffolds Used for Rotator Cuff Repair.Eur Cells Mater.2016;31:107-118.
[33] ZHENG Z, RAN J, CHEN W, et al. Alignment of collagen fiber in knitted silk scaffold for functional massive rotator cuff repair.Acta Biomater. 2017;51:317-329.
[34] GUPTA AK, HUG K, BERKOFF DJ, et al. Dermal tissue allograft for the repair of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears.Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(1):141-147.
[35] SHARMA N, EL REFAIY A, SIBLY TF. Short-term results of rotator cuff repair using GraftJacket as an interpositional tissue-matched thickness graft.J Orthop. 2018;15(2):732-735.
[36] IDE J, TOKUNAGA T.Rotator cuff tendon-to-bone healing at 12 months after patch grafting of acellular dermal matrix in an animal model.J Orthop Sci.2018;23(2):207-212.
[37] SMITH RDJ, ZARGAR N, BROWN CP, et al. Characterizing the macro and micro mechanical properties of scaffolds for rotator cuff repair. J Shoulder Elb Surg.2017;26(11):2038-2046.
[38] LEE KW, LEE JS, KIM YS, et al. Effective healing of chronic rotator cuff injury using recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 coated dermal patch in vivo.J Biomed Mater Res B.2017;105(7):1840-1846.
[39] YOON JP, CHUNG SW, KIM JY, et al. Outcomes of Combined Bone Marrow Stimulation and Patch Augmentation for Massive Rotator Cuff Tears.Am J Sport Med.2016;44(4):963-971.
[40] STEINHAUS ME, MAKHNI EC, COLE BJ, et al. Outcomes After Patch Use in Rotator Cuff Repair . Arthroscopy.2016;32(8):1676-1690.
[41] IANNOTTI JP, CODSI MJ, KWON YW, et al. Porcine small intestine submucosa augmentation of surgical repair of chronic two-tendon rotator cuff tears - A randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006;88a(6):1238-1244.
[42] WALTON JR, BOWMAN NK, KHATIB Y, et al. Restore orthobiologic implant: not recommended for augmentation of rotator cuff repairs.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2007;89(4):786-791.
[43] GILBERT TW, FREUND JM, BADYLAK SF. Quantification of DNA in biologic scaffold materials.J Surg Res.2009;152(1):135-139.
[44] BRYANT D, HOLTBY R, WILLITS K, et al. A randomized clinical trial to compare the effectiveness of rotator cuff repair with or without augmentation using porcine small intestine submucosa for patients with moderate to large rotator cuff tears:a pilot study. J Shoulder Elb Surg.2016;25(10):1623-1633.
[45] NEUMANN JA, ZGONIS MH, RICKERT KD, et al. Interposition Dermal Matrix Xenografts: A Successful Alternative to Traditional Treatment of Massive Rotator Cuff Tears.Am J Sports Med.2017;45(6):1261-1268.
[46] FLURY M, RICKENBACHER D, JUNG C, et al. Porcine Dermis Patch Augmentation of Supraspinatus Tendon Repairs: A Pilot Study Assessing Tendon Integrity and Shoulder Function 2 Years After Arthroscopic Repair in Patients Aged 60 Years or Older.Arthroscopy. 2018;34(1):24-37.
[47] MAILLOT C, HARLY E, DEMEZON H, et al. Surgical repair of large-to-massive rotator cuff tears seems to be a better option than patch augmentation or debridement and biceps tenotomy: a prospective comparative study.J Shoulder Elb Surg.2018,27(9):1545-1552.
[48] MCINTYRE LF, BISHAI SK, BROWN PB, 3RD, et al. Patient-Reported Outcomes After Use of a Bioabsorbable Collagen Implant to Treat Partial and Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(8): 2262-2271.
[49] MCCORMACK RA, SHREVE M, STRAUSS EJ.Biologic augmentation in rotator cuff repair--should we do it, who should get it, and has it worked? Bull Hosp Jt Dis.2014;72(1):89-96.
[50] CIAMPI P, SCOTTI C, NONIS A, et al. The Benefit of Synthetic Versus Biological Patch Augmentation in the Repair of Posterosuperior Massive Rotator Cuff Tears A 3-Year Follow-up Study.Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(5):1169-1175.
[51] VITALI M, CUSUMANO A, PEDRETTI A, et al. Employment of synthetic patch with augmentation of the long head of the biceps tendon in irreparable lesions of the rotator cuff: our technique applied to 60 patients.Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg.2015;19(1):32-39.
[52] SHEPHERD HM, LAM PH, MURRELL GA. Synthetic Patch Rotator Cuff Repair:A 10-year Follow-Up.Shoulder Elbow.2014;6(1):35-39.
[53] GAO C, LI C, XU Y, et al. Electrospun polycaprolactone/collagen type Ⅰnanofibers oriented patch for rotator cuff repairing.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2019; 33(5):628-633.
[54] ZHAO S, XIE X, PAN G, et al. Healing improvement after rotator cuff repair using gelatin-grafted poly(L-lactide) electrospun fibrous membranes. J Surg Res.2015;193(1): 33-42.
[55] GUO JS, SU W, JIANG J, et al. Enhanced tendon to bone healing in rotator cuff tear by PLLA/CPS composite films prepared by a simple melt-pressing method: An in vitro and in vivo study.Compos Part B-Eng.2019;165(526-536.
[56] HURLEY ET, FAT DU, MORAN CJ, et al. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair:A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(3):753-761.
[57] KIM YS, SUNG CH, CHUNG SH, et al. Does an Injection of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Loaded in Fibrin Glue Influence Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes? A Clinical and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study.Am J Sports Med.2017;45(9):2010-2018.
|