中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (35): 5600-5604.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1979
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
川芎嗪干预静态姿势负荷模型大鼠不同时相自由基及酶代谢的变化
肖 凯1,周江红1,高鑫峰1,赵晶晶1,方真华1,杨 林2
- (1武汉市第四医院,华中科技大学同济医学院附属普爱医院,湖北省武汉市 430030;2华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院,湖北省武汉市 430030)
Effects of ligustrazine on free radicals and enzyme metabolism after static postural load in rat models
Xiao Kai1, Zhou Jianghong1, Gao Xinfeng1, Zhao Jingjing1, Fang Zhenhua1, Yang Lin2
- (1Wuhan Fourth Hospital & Puai Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China; 2Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, Hubei Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌肉骨骼疾患:是一类与工作有关疾病,主要有腰背痛、颈肩综合征等,该病的危险因素一般分为职业和个体两类,还可有社会、心理因素,其临床特征为疼痛和活动受限。它影响半数以上的职业人群,成为职工缺勤的主要原因,工业发达国家瑞典、德国、美国及国际劳工组织等已承认它为职业病,且常常因为此病花费过高的医疗及赔偿费用,严重影响了患者的身心健康及工作效率。
钙ATP酶:是存在于组织细胞及细胞器的膜上的一种蛋白酶,由于其离子运转是借助类似泵的机制来完成的,医学上将离子的这种运转方式称为“泵”,钙ATP酶亦称为“钙泵”。它催化质膜内侧的ATP水解,释放出能量,驱动细胞内的钙离子泵出细胞或者泵入内质网腔中储存起来,以维持细胞内低浓度的游离Ca2+。细胞内钙浓度明显增多并导致细胞结构损伤和功能代谢障碍的现象称为钙超载,钙ATP酶对调控钙超载具有积极意义。
文题释义:
肌肉骨骼疾患:是一类与工作有关疾病,主要有腰背痛、颈肩综合征等,该病的危险因素一般分为职业和个体两类,还可有社会、心理因素,其临床特征为疼痛和活动受限。它影响半数以上的职业人群,成为职工缺勤的主要原因,工业发达国家瑞典、德国、美国及国际劳工组织等已承认它为职业病,且常常因为此病花费过高的医疗及赔偿费用,严重影响了患者的身心健康及工作效率。
钙ATP酶:是存在于组织细胞及细胞器的膜上的一种蛋白酶,由于其离子运转是借助类似泵的机制来完成的,医学上将离子的这种运转方式称为“泵”,钙ATP酶亦称为“钙泵”。它催化质膜内侧的ATP水解,释放出能量,驱动细胞内的钙离子泵出细胞或者泵入内质网腔中储存起来,以维持细胞内低浓度的游离Ca2+。细胞内钙浓度明显增多并导致细胞结构损伤和功能代谢障碍的现象称为钙超载,钙ATP酶对调控钙超载具有积极意义。
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌肉骨骼疾患:是一类与工作有关疾病,主要有腰背痛、颈肩综合征等,该病的危险因素一般分为职业和个体两类,还可有社会、心理因素,其临床特征为疼痛和活动受限。它影响半数以上的职业人群,成为职工缺勤的主要原因,工业发达国家瑞典、德国、美国及国际劳工组织等已承认它为职业病,且常常因为此病花费过高的医疗及赔偿费用,严重影响了患者的身心健康及工作效率。
钙ATP酶:是存在于组织细胞及细胞器的膜上的一种蛋白酶,由于其离子运转是借助类似泵的机制来完成的,医学上将离子的这种运转方式称为“泵”,钙ATP酶亦称为“钙泵”。它催化质膜内侧的ATP水解,释放出能量,驱动细胞内的钙离子泵出细胞或者泵入内质网腔中储存起来,以维持细胞内低浓度的游离Ca2+。细胞内钙浓度明显增多并导致细胞结构损伤和功能代谢障碍的现象称为钙超载,钙ATP酶对调控钙超载具有积极意义。
文题释义:
肌肉骨骼疾患:是一类与工作有关疾病,主要有腰背痛、颈肩综合征等,该病的危险因素一般分为职业和个体两类,还可有社会、心理因素,其临床特征为疼痛和活动受限。它影响半数以上的职业人群,成为职工缺勤的主要原因,工业发达国家瑞典、德国、美国及国际劳工组织等已承认它为职业病,且常常因为此病花费过高的医疗及赔偿费用,严重影响了患者的身心健康及工作效率。
钙ATP酶:是存在于组织细胞及细胞器的膜上的一种蛋白酶,由于其离子运转是借助类似泵的机制来完成的,医学上将离子的这种运转方式称为“泵”,钙ATP酶亦称为“钙泵”。它催化质膜内侧的ATP水解,释放出能量,驱动细胞内的钙离子泵出细胞或者泵入内质网腔中储存起来,以维持细胞内低浓度的游离Ca2+。细胞内钙浓度明显增多并导致细胞结构损伤和功能代谢障碍的现象称为钙超载,钙ATP酶对调控钙超载具有积极意义。摘要
背景:研究发现,川芎嗪能有效保护失用状态下大鼠骨骼肌细胞、对抗失神经大鼠骨骼肌萎缩。
目的:探究川芎嗪对大鼠静态姿势负荷后不同时相自由基及酶代谢的影响。
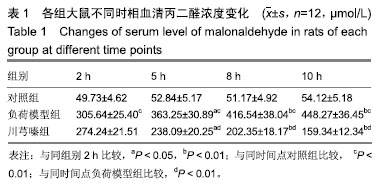
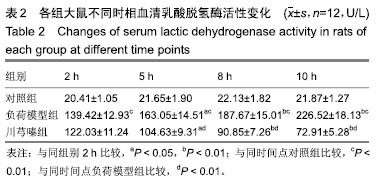
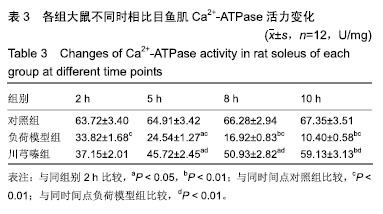
方法:实验方案经华中科技大学附属同济医院实验动物实验伦理委员会批准。36只SPF级雄性SD大鼠随机被分为对照组、负荷模型组、川芎嗪组。实验开始前0.5 h,对照组、负荷模型组大鼠灌胃2 mL溶媒,川芎嗪组大鼠灌胃川芎嗪溶液2 mL。实验过程中对照组大鼠不施加任何负荷;负荷模型组、川芎嗪组大鼠以夹板固定四肢持续实施静态姿势负荷,且躯干部分固定在预先制作好的木盒中保持伸直状态10 h,建立静态姿势负荷大鼠模型。检测川芎嗪干预不同时相(2,5,8和10 h)大鼠血清丙二醛水平、血清乳酸脱氢酶活性及比目鱼肌钙ATP酶(Ca2+-ATPase)活力变化。
结果与结论:①对照组大鼠血清丙二醛浓度、血清乳酸脱氢酶活性及比目鱼肌Ca2+-ATPase活力不随时间变化而改变;与负荷模型组2 h比较,同组5, 8和10 h的丙二醛浓度、血清乳酸脱氢酶活性均显著升高,Ca2+-ATPase活力均显著降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);与川芎嗪组2 h比较,同组5,8和10 h的丙二醛浓度、血清乳酸脱氢酶活性均显著降低,Ca2+-ATPase活力均显著升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);与对照组同时相比较,负荷模型组大鼠血清中丙二醛自由基水平、乳酸脱氢酶活性均显著增加,Ca2+-ATPase活力显著降低(P < 0.01);与负荷模型组同时相比较(2 h除外),川芎嗪组大鼠丙二醛自由基水平、乳酸脱氢酶活性均显著降低,Ca2+-ATPase活力显著增加(P < 0.01);②结果说明,川芎嗪能显著降低不同时相静态姿势负荷引起的血清丙二醛浓度及血清乳酸脱氢酶活性,显著升高目鱼肌Ca2+-ATPase活力,以达到缓解长时间静态姿势负荷引起的机体损伤。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌肉骨骼疾患:是一类与工作有关疾病,主要有腰背痛、颈肩综合征等,该病的危险因素一般分为职业和个体两类,还可有社会、心理因素,其临床特征为疼痛和活动受限。它影响半数以上的职业人群,成为职工缺勤的主要原因,工业发达国家瑞典、德国、美国及国际劳工组织等已承认它为职业病,且常常因为此病花费过高的医疗及赔偿费用,严重影响了患者的身心健康及工作效率。
钙ATP酶:是存在于组织细胞及细胞器的膜上的一种蛋白酶,由于其离子运转是借助类似泵的机制来完成的,医学上将离子的这种运转方式称为“泵”,钙ATP酶亦称为“钙泵”。它催化质膜内侧的ATP水解,释放出能量,驱动细胞内的钙离子泵出细胞或者泵入内质网腔中储存起来,以维持细胞内低浓度的游离Ca2+。细胞内钙浓度明显增多并导致细胞结构损伤和功能代谢障碍的现象称为钙超载,钙ATP酶对调控钙超载具有积极意义。
文题释义:
肌肉骨骼疾患:是一类与工作有关疾病,主要有腰背痛、颈肩综合征等,该病的危险因素一般分为职业和个体两类,还可有社会、心理因素,其临床特征为疼痛和活动受限。它影响半数以上的职业人群,成为职工缺勤的主要原因,工业发达国家瑞典、德国、美国及国际劳工组织等已承认它为职业病,且常常因为此病花费过高的医疗及赔偿费用,严重影响了患者的身心健康及工作效率。
钙ATP酶:是存在于组织细胞及细胞器的膜上的一种蛋白酶,由于其离子运转是借助类似泵的机制来完成的,医学上将离子的这种运转方式称为“泵”,钙ATP酶亦称为“钙泵”。它催化质膜内侧的ATP水解,释放出能量,驱动细胞内的钙离子泵出细胞或者泵入内质网腔中储存起来,以维持细胞内低浓度的游离Ca2+。细胞内钙浓度明显增多并导致细胞结构损伤和功能代谢障碍的现象称为钙超载,钙ATP酶对调控钙超载具有积极意义。