中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (35): 5587-5591.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1973
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
Klotho基因多态性与60岁以上老年原发性骨质疏松症的相关性
马秋华,王云文,马 慧,齐 杰,张清潭
- (滨州医学院附属医院,山东省滨州市 256600)
Association of polymorphisms of klotho gene with primary osteoporosis in the elderly aging above 60 years old
Ma Qiuhua, Wang Yunwen, Ma Hui, Qi Jie, Zhang Qingtan
- (Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
SNP:全称Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms,是指在基因组上单个核苷酸的变异,包括转换、颠换、缺失和插入,形成的遗传标记,其数量很多,多态性丰富。从理论上来看每一个SNP位点都可以有4 种不同的变异形式,但实际上发生的只有2种,即转换和颠换,二者之比为2∶1,而且多是C转换为T。
Klotho基因:是一种新发现的抗衰老基因,与人类多种疾病如骨质疏松、肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化、血糖异常等均有关,但不同国家、地区、民族间的研究结果不尽相同,仅国内关于该基因与骨质疏松症的相关性在南北不同区域间就为不同。
文题释义:
SNP:全称Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms,是指在基因组上单个核苷酸的变异,包括转换、颠换、缺失和插入,形成的遗传标记,其数量很多,多态性丰富。从理论上来看每一个SNP位点都可以有4 种不同的变异形式,但实际上发生的只有2种,即转换和颠换,二者之比为2∶1,而且多是C转换为T。
Klotho基因:是一种新发现的抗衰老基因,与人类多种疾病如骨质疏松、肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化、血糖异常等均有关,但不同国家、地区、民族间的研究结果不尽相同,仅国内关于该基因与骨质疏松症的相关性在南北不同区域间就为不同。
.jpg) 文题释义:
SNP:全称Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms,是指在基因组上单个核苷酸的变异,包括转换、颠换、缺失和插入,形成的遗传标记,其数量很多,多态性丰富。从理论上来看每一个SNP位点都可以有4 种不同的变异形式,但实际上发生的只有2种,即转换和颠换,二者之比为2∶1,而且多是C转换为T。
Klotho基因:是一种新发现的抗衰老基因,与人类多种疾病如骨质疏松、肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化、血糖异常等均有关,但不同国家、地区、民族间的研究结果不尽相同,仅国内关于该基因与骨质疏松症的相关性在南北不同区域间就为不同。
文题释义:
SNP:全称Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms,是指在基因组上单个核苷酸的变异,包括转换、颠换、缺失和插入,形成的遗传标记,其数量很多,多态性丰富。从理论上来看每一个SNP位点都可以有4 种不同的变异形式,但实际上发生的只有2种,即转换和颠换,二者之比为2∶1,而且多是C转换为T。
Klotho基因:是一种新发现的抗衰老基因,与人类多种疾病如骨质疏松、肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化、血糖异常等均有关,但不同国家、地区、民族间的研究结果不尽相同,仅国内关于该基因与骨质疏松症的相关性在南北不同区域间就为不同。摘要
背景:研究发现,Klotho基因与人类多种疾病如骨质疏松、肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化、血糖异常等均有关。
目的:进一步验证klotho基因多态性与老年人(≥60岁)原发性骨质疏松症的相关性。
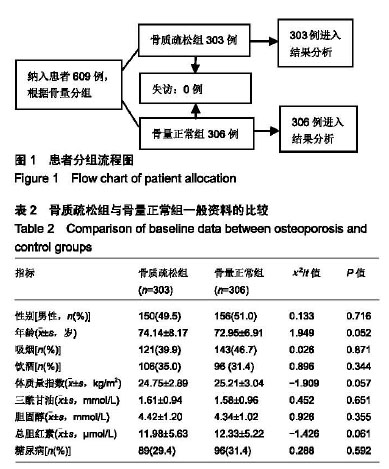
方法:研究方案的实施符合滨州医学院附属医院医院对研究的相关伦理要求。受试者对试验过程完全知情同意。收集于滨州医学院附属医院体检中心、老年医学科就诊的,长期居住鲁西北地区的汉族老年患者609例,其中骨质疏松者303例,骨量正常者306例,利用SNaPshot SNP分型技术对klotho基因G395A、F352V位点进行基因分型。
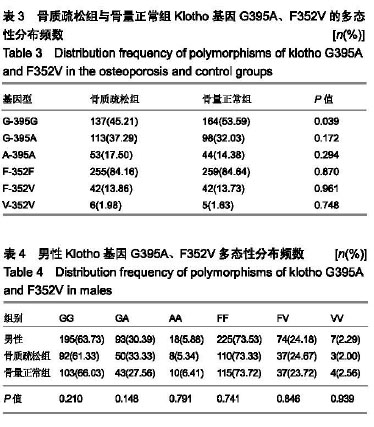
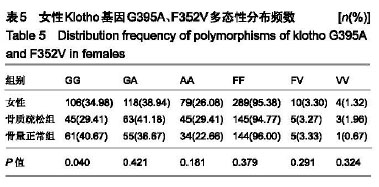
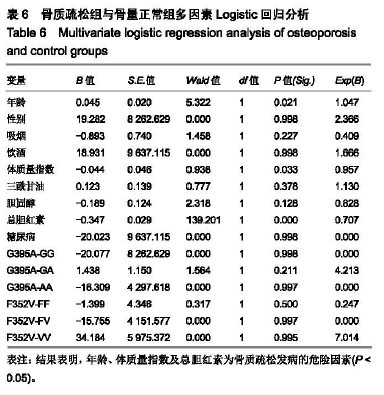
结果与结论:①Klotho基因G395A基因型GG在骨量正常组中分布频率显著高于骨质疏松组(P < 0.05);②女性骨质疏松组患者GG基因型分布频率显著低于骨量正常组(P < 0.05);③多因素Logistic回归分析表明,总胆红素、年龄及体质量指数为原发性骨质疏松症发病的危险因素;④结果说明,Klotho基因G395A、F352V位点多态性可能不是该地区汉族老年人群骨质疏松症发生的危险因子,总胆红素、年龄及体质量指数可能与骨质疏松症的发生有关。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
SNP:全称Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms,是指在基因组上单个核苷酸的变异,包括转换、颠换、缺失和插入,形成的遗传标记,其数量很多,多态性丰富。从理论上来看每一个SNP位点都可以有4 种不同的变异形式,但实际上发生的只有2种,即转换和颠换,二者之比为2∶1,而且多是C转换为T。
Klotho基因:是一种新发现的抗衰老基因,与人类多种疾病如骨质疏松、肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化、血糖异常等均有关,但不同国家、地区、民族间的研究结果不尽相同,仅国内关于该基因与骨质疏松症的相关性在南北不同区域间就为不同。
文题释义:
SNP:全称Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms,是指在基因组上单个核苷酸的变异,包括转换、颠换、缺失和插入,形成的遗传标记,其数量很多,多态性丰富。从理论上来看每一个SNP位点都可以有4 种不同的变异形式,但实际上发生的只有2种,即转换和颠换,二者之比为2∶1,而且多是C转换为T。
Klotho基因:是一种新发现的抗衰老基因,与人类多种疾病如骨质疏松、肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化、血糖异常等均有关,但不同国家、地区、民族间的研究结果不尽相同,仅国内关于该基因与骨质疏松症的相关性在南北不同区域间就为不同。