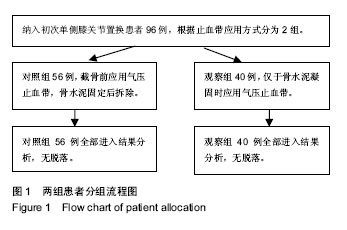
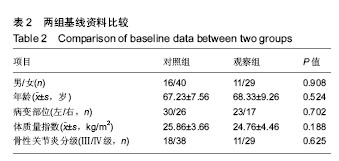
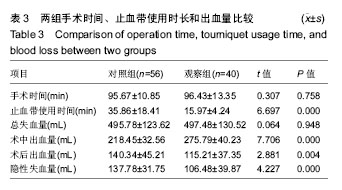
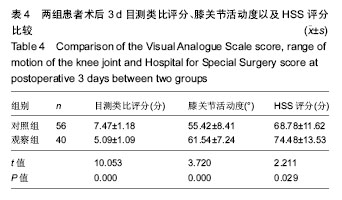
| [1] Smith TO, Hing CB. Is a tourniquet benef icial in total knee replacement surgery? A meta-analysis and systematic review. Knee. 2010;17(2):141-147.[2] Tai TW, Lin CJ, Jou IM,et al. Tourniquet use in totaI kn ee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(7):1121-1130.[3] 马卫华,张树栋,王诗军,等. 止血带的使用方式对膝关节置换术失血量和手术时间的影响[J].中华关节外科(电子版),2011, 5(6):33-36.[4] Kvederas G, Porvaneckas N, Andrijauskas A, et al. A randomized double-blind clinical trial of tourniquet application strategies for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(12):2790-2799.[5] 孙啸,王浩洋,康鹏德. TKA术中不同时机使用止血带对患者造成的损伤比较[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2016, 47(1):135-137.[6] Dennis DA , Kittelson AJ , Yang CC, et al. Does tourniquet use in tka affect recovery of lower extremity strength and function? a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016; 474(1):69-77.[7] Jawhar A , Hermanns S , Ponelies N, et al. Tourniquet-induced ischaemia during total knee arthroplasty results in higher proteolytic activities within vastus medialis cells: a randomized clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(10):3313-3321.[8] León-Muñoz VJ, Lisón-Almagro AJ, Hernández-García CH, et al. Silicone ring tourniquet versus pneumatic cuff tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty surgery: A randomised comparative study. J Orthop. 2018;15(2):545-548.[9] Hasanain S, Apostu D, Alrefaee A, et al. Comparing the effect of tourniquet vs. tourniquet-less in simultaneous bilateral total knee replacements. J Arthroplasty. 2018: S0883540318301426.[10] Yang G, Huang W, Xie W. Patellar non-eversion in primary TKA reduces the complication rate. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(3):921-930.[11] Si HB, Yang TM, Zeng Y, et al. No clear benefit or drawback to the use of closed drainage after primary total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):183.[12] Zhou K, Ling T, Wang H, et al. Influence of tourniquet use in primary total knee arthroplasty with drainage: a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1): 172.[13] 杜哲. TKA中止血带应对围手术期失血量及近期疗效的影响研究[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2014.[14] Tsunoda K , Sonohata M , Kugisaki H , et al. The effect of air tourniquet on interleukin-6 levels in total knee arthroplasty. Open Orthop J. 2017;11(1):20-28.[15] Matsui Y , Shintani K , Okajima Y, et al. The effect of tourniquets on patellofemoral joint congruity during total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21(5):630-634.[16] Jiang FZ , Zhong HM , Hong YC, et al. Use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(1):110-123.[17] Mayer C , Franz A , Harmsen JF , et al. Soft-tissue damage during total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop. 2017;14(3):347-353.[18] Li Z , Liu D , Long G , et al. Association of tourniquet utilization with blood loss, rehabilitation, and complications in Chinese obese patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Medicine. 2017;96(49):e9030.[19] Lee O, Lee MC, Han HS. Efficacy and safety of a new elastic tourniquet cuff in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study. Biomed Eng Online. 2017;16(1): 102.[20] 张炜,陈思锋,李宁,等.止血带对初次全膝关节表面置换作用的Meta分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014, 8(2):215-221.[21] 张元凯,李德强,刘培来,等. 气囊止血带的三种应用方法在TKA的影响分析[C]//中华骨科杂志论坛, 2013.[22] Ozkunt O, Sariyilmaz K, Gemalmaz HC, et al. The effect of tourniquet usage on cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty. Medicine. 2018; 97(4):e9668.[23] Ryu KJ. CORR, Insights®: does tourniquet use in tka affect recovery of lower extremity strength and function? A randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(1):78-80.[24] Tie K , Hu D , Qi Y , et al. Effects of tourniquet release on total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2016;39(4):e642-e650.[25] 徐莉莉,林丽娜. TKA术中气囊止血带不同应用时机对出血量、皮肤并发症的影响[J]. 中国现代医生, 2015, 53(31):1-4.[26] Barker T, Rogers VE, Brown KB, et al. Tourniquet use during total knee arthroplasty does not modulate the neutrophil-to- lymphocyte ratio, pain, or activity. J Orthop Traumatol. 2016; 18(3):1-5.[27] Numkanisorn S, Chareancholvanich K, Pornrattanamaneewong C. Intravenous tranexamic acid before and after tourniquet use can reduce blood loss and blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016;99(11):1220-1225.[28] Dreyer HC. Tourniquet use during knee replacement surgery may contribute to muscle atrophy in older adults. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2016;44(2):61-70.[29] Zhang P, Liang Y, He J, et al. Timing of tourniquet release in total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Orthop J China. 2017;96(17):445-451.[30] 曹学伟,杨伟毅,梁比记,等. 不同止血带使用方法对TKA围手术期失血量影响的临床研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2011, 4(6):455-459.[31] Chen S, Li JP, Peng H ,et al. The influence of a half-course tourniquet strategy on peri-operative blood loss and early functional recovery in primary total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):355-359.[32] Ejaz A, Laursen AC, Kappel A, et al. Faster recovery without the use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthopaedica. 2014;85(4):422-426. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)