| [1] Berríos-Torres SI,Umscheid CA,Bratzler DW,et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017.JAMA Surg. 2017;152(8): 784-791.[2] Maradit Kremers H,Larson DR,Crowson CS,et al. Prevalence of Total Hip and Knee Replacement in the United States.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2015;97(17):1386-1397.[3] Antoci V,Chen AF, Parvizi J.7.9 Orthopedic Implant Use and Infection.Comprehensive Biomaterials II.2017;7:133-151.[4] Darouiche RO.Treatment of infections associated with surgical implants.N Engl J Med. 2004;350(14):1422-1429.[5] Trampuz A,Zimmerli W.Diagnosis and treatment of infections associated with fracture-fixation devices.Injury.2006;37 Suppl 2:S59-66.[6] Johnson CT,Wroe JA,Agarwal R,et al. Hydrogel delivery of lysostaphin eliminates orthopedic implant infection by Staphylococcus aureus and supports fracture healing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(22):E4960-E4969.[7] Raphel J,Holodniy M,Goodman SB,et al.Multifunctional coatings to simultaneously promote osseointegration and prevent infection of orthopaedic implants.Biomaterials. 2016; 84:301-314.[8] Zhang R,Liu X,Xiong Z,et al.Novel Micro/nanostructured TiO2/ZnO Coating with Antibacterial Capacity and Cytocompatibility. Ceram Int.2018;44:9711-9719.[9] Zhang E,Li F,Wang H,et al.A new antibacterial titanium-copper sintered alloy: preparation and antibacterial property. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(7): 4280-4287.[10] Li Y,Liu L,Wan P,et al.Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloy implants with antibacterial activity for the treatment of osteomyelitis: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. Biomaterials.2016;106:250-263.[11] Sotoudehbagha P,Sheibani S,Khakbiz M,et al.Novel antibacterial biodegradable Fe-Mn-Ag alloys produced by mechanical alloying. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018; 88:88-94.[12] Zhang E,Liu C.A new antibacterial Co-Cr-Mo-Cu alloy: Preparation, biocorrosion, mechanical and antibacterial property. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;69:134-143.[13] 翁文剑,庄均珺,林素雅,等.电化学沉积生物功能涂层的研究进展[J].硅酸盐学报,2017,45(11):1539-1547.[14] Hadidi M,Bigham A,Saebnoori E,et al. Electrophoretic- deposited hydroxyapatite-copper nanocomposite as an antibacterial coating for biomedical applications. Surf Coat Technol.2017;321:171-179.[15] Rasha AA,Sahar AF,Nader E,et al.Improvement of corrosion resistance and antibacterial effect of NiTi orthopedic materials by chitosan and gold nanoparticles.Appl Surf Sci. 2014;292: 390-399.[16] Huang Y,Hao M,Nian X,et al.Strontium and copper co-substituted hydroxyapatite-based coatings with improved antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility fabricated by electrodeposition. Ceram Int.2016;42(10):11876-11888.[17] Weng Y,Liu H,Ji S,et al. A promising orthopedic implant material with enhanced osteogenic and antibacterial activity: Al2O3-coated aluminum alloy.App Surf Sci. 2018;457: 1025-1103.[18] Yao X, Zhang X, Wu H, et al. Microstructure and antibacterial properties of Cu-doped TiO 2, coating on titanium by micro-arc oxidation.Appl Surf Sci.2014;292(1):944-947.[19] 刘亚强,陈青清,李朋.磁控溅射法制备铝掺杂氧化锌薄膜研究进展[J].信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版),2017, 30(4):667-671.[20] Bai L,Hang R,Gao A, et al. Nanostructured titanium–silver coatings with good antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility fabricated by one-step magnetron sputtering.Appl Surf Sci. 2015;355:32-44.[21] Stranak V,Wulff H,Rebl H,et al.Deposition of thin titanium–copper films with antimicrobial effect by advanced magnetron sputtering methods.Mater Sci Eng C. 2011;31(7): 1512-1519.[22] Podporska-Carroll J,Quilty B,Devery R.Non-cytotoxic and antimicrobial plasma sprayed coatings for orthopaedic application. Mater Lett.2013;112(12):54-57.[23] Li D,Gong Y,Chen X,et al.Room-temperature deposition of hydroxyapatite/antibiotic composite coatings by vacuum cold spraying for antibacterial applications.Surf Coat Technol. 2017;330:87-91.[24] Sivaraj D,Vijayalakshmi K.Substantial effect of magnesium incorporation on hydroxyapatite/carbon nanotubes coatings on metallic implant surfaces for better anticorrosive protection and antibacterial ability.J Anal Appl Pyrol.2018;135:15-21.[25] 周游,姚颖悟,吴坚扎西,等.镁合金化学转化膜的研究进展[J].电镀与精饰,2013,35(5):15-18.[26] Hu G,Zeng L,Du H,et al.The formation mechanism and bio-corrosion properties of Ag/HAcomposite conversion coating on the extruded Mg-2Zn-1Mn-0.5Ca alloy for bone implant application.Surf Coat Technol. 2017;325:127-135.[27] Guo YY,Liu B,Hu BB,et al.Antibacterial activity and increased osteoblast cell functions of zinc calcium phosphate chemical conversion on titanium.Surf Coat Technol.2016;294:131-138.[28] Cunha A,Elie AM,Plawinski L,et al.Femtosecond laser surface texturing of titanium as a method to reduce the adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and biofilm formation.Appl Surf Sci. 2016;360:485-493.[29] Chan CW,Carson L,Smith GC,et al.Enhancing the antibacterial performance of orthopaedic implant materials by fibre laser surface engineering.Appl Surf Sci.2017;404:67-81.[30] Weng F,Chen C,Yu H.Research statusof laser cladding on titanium and it alloys:A review.Mater Design.2014(58): 412-425.[31] Boutinguiza M,Fernández-Arias M,del Val J,et al.Synthesis and deposition of silver nanoparticles on cp Ti by laser ablation in open air for antibacterial effect in dental implants. Mater Lett. 2018;231:126-129.[32] Hidalgo-Robatto BM,Aguilera-Correa JJ,López-Álvarez M,et al. Fluor carbonated hydroxyapatite coatings by pulsed laser deposition to promote cell viability and antibacterial properties. Surf Coat Technol.2018;349:736-744.[33] Vaithilingam J,Kilsby S,Goodridge RD,et al.Immobilisation of an antibacterial drug to Ti6Al4V components fabricated using selective laser melting.Appl Surf Sci.2014;314(24):642-654.[34] Gao A,Hang R,Chu PK.Recent advances in anti-infection surfaces fabricated on biomedical implants by plasma-based technology.Surf Coat Technol.2017;312:2-6.[35] Yeung K,Wu S,Zhao Y, et al. Antimicrobial effects of oxygen plasma modified medical grade Tie6Ale4V alloy.Vacuum. 2013;89(1):271-279.[36] Huang HH,Shiau DK,Chen CS,et al.Nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation treatment to enhance corrosion resistance, bone cell growth, and antibacterial adhesion of Ti-6Al-4V alloy in dental applications.Surf Coat Technol.2018. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.06.023[37] Yu L,Tian Y,Qiao Y,et al.Mn-containing titanium surface with favorable osteogenic and antimicrobial functions synthesized by PIII&D. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2017;152:376-384.[38] Tian Y,Cao H,Qiao Y,et al.Antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility of titanium oxide coating modified by iron ion implantation.Acta Biomaterialia.2014;10(10):4505-4517.[39] Echeverrigaray FG,Echeverrigaray S,Delamare APL.Antibacterial properties obtained by low-energy silver implantation in stainless steel surfaces.Surf Coat Technol. 2016;307:345-351.[40] Jin G,Cao H,Qiao Y,et al.Osteogenic activity and antibacterial effect of zinc ion implanted titanium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2014;117:158-165.[41] Jaggessar A,Yarlagadda P,Qiu TF,et al.Fabrication of Nano Pyramid Texture on Ti-6Al-4V Using Nanosphere Lithography. Mater Today: Proceedings. 2018;5(5): 11593-11600.[42] Palla-Rubio B,Araújo-Gomes N,Fernández-Gutiérrez M,et al.Synthesis and characterization of silica-chitosan hybrid materials as antibacterial coatings for titanium implants. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;203:331-341.[43] Keynoosh B,Abbasi KB,Abdollah A.Characterization of sol-gel derived silver/fluor-hydroxyapatite composite coatings on titanium substrate.Surf Coat Technol.2018;352:522-528.[44] Meng LY,Wang B,Ma MG,et al.The progress of microwave-assisted hydrothermal method in the synthesis of functional nanomaterials.Mater Today Chem.2016;1-2:63-83.[45] Xiang Y,Li J,Liu X,et al.Construction of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/ZnO nanorods/Ag nanoparticles hybrid coating on Ti implants for enhanced antibacterial activity and biocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;79:629-637.[46] Mohandas A,Krishnan AG,Biswas R,et al.Antibacterial and cytocompatible nanotextured Ti surface incorporating silver via single step hydrothermal processing.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;75:115-124.[47] 王海侨,文芳岱,李效玉.分子自组装技术及其在发光器件制备上的应用[J].高分子通报,2006,19(4):35-41.[48] Zeng RC,Liu LJ,Luo KJ,et al.In vitro corrosion and antibacterial properties of layer-by-layer assembled GS/PSS coating on AZ31 magnesium alloys.Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2015; 25(12):4028-4039.[49] Tao B,Shen X,Yuan Z,et al.N-halamine-based multilayers on titanium substrates for antibacterial application. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;170:382-392.[50] Zhao Y,Shi L,Ji X,et al.Corrosion resistance and antibacterial properties of polysiloxane modified layer-by-layer assembled self-healing coating on magnesium alloy.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;526:43-50.[51] Hatada R,Flege S,Bobrich A,et al.Preparation of Ag-containing diamond-like carbon films on the interior surface of tubes by a combined method of plasma source ion implantation and DC sputtering. Appl Surf Sci. 2014;310(9): 257-261.[52] 刘振,张腾,尚剑.载银氧化锌涂层抗菌机制的研究进展[J].中华实验外科杂志,2018,35(7):1383-1387. |
.jpg)
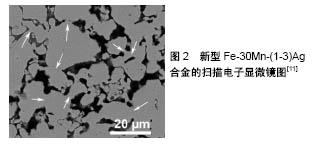
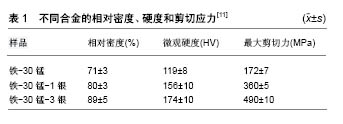
.jpg)
.jpg)