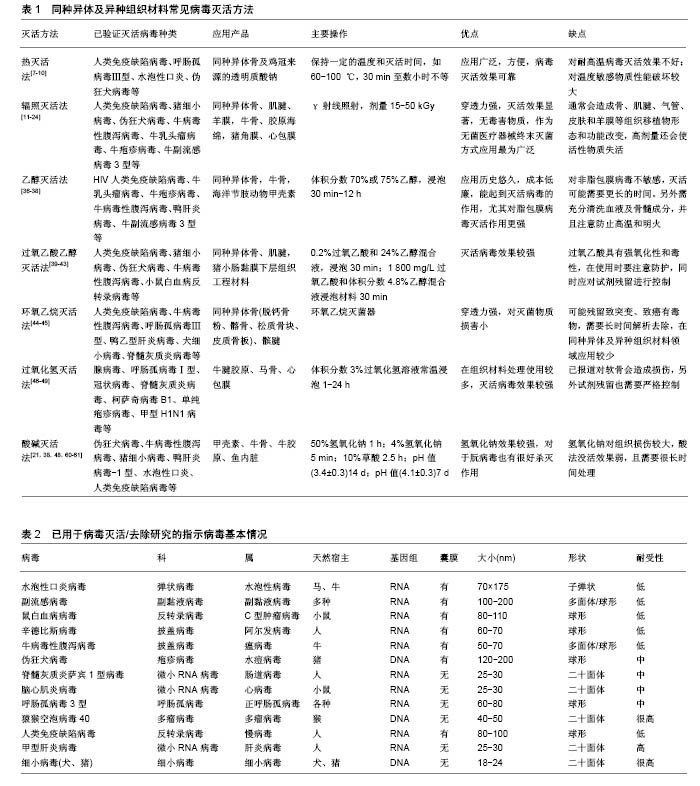
| [1] Wubneh A,Tsekoura EK,Ayranci C,et al. Current state of fabrication technologies and materials for bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomater.2018;80:1-30.[2] Eagle MJ,Rooney P,Kearney JN.Production of an osteoinductive demineralised bone matrix powder without the use of organic solvents.Cell Tissue Bank.2015;16(3):433-441.[3] Su FY,Pang S,Ling Y,et al.Deproteinization of Cortical Bone: Effects of Different Treatments. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;103(5): 554-566.[4] de Girolamo L,Ragni E,Cucchiarini M,et al.Cells, soluble factors and matrix harmonically play the concert of allograft integration.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2018. doi: 10.1007/s00167-018-5182-1.[Epub ahead of print] [5] Chaudhuri R,Ramachandran M,Moharil P,et al.Biomaterials and cells for cardiac tissue engineering: Current choices.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;79:950-957.[6] Dasgupta A,Orgill D,Galiano RD,et al.A Novel Reticular Dermal Graft Leverages Architectural and Biological Properties to Support Wound Repair.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open.2016;4(10):e1065.[7] 朱加亮,刘思扬,衷鸿宾,等.巴氏法对异体骨中HIV病毒灭活效果的研究[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2011,10(3):249-251.[8] Kode J,Taur P,Gulia A,et al.Pasteurization of bone for tumour eradication prior to reimplantation - an in vitro & pre-clinical efficacy study.Indian J Med Res.2014;139(4): 585-597.[9] 任彩霞,范素俊,侯永泰.透明质酸钠原料病毒灭活/去除工艺的研究[J].安徽医药,2010,14 (10):1126-1128.[10] 陈柯君.浅析血液制品病毒灭活的研究进展[A].广东省药学会. 2016年广东省药师周大会论文集[C].广东省药学会:广东省药学会,2015:7.[11] 青莉芳,魏敏,杨平华,等.γ辐照食品灭菌的机理及微生物检测[J].食品研究与开发,2016,37(5):218-220.[12] Singh R,Singh D,Singh A.Radiation sterilization of tissue allografts: A review.World J Radiol. 2016;8(4):355-369.[13] Moore MA.Inactivation of enveloped and non-enveloped viruses on seeded human tissues by gamma irradiation.Cell Tissue Bank.2012;13(3):401-407.[14] Knaepler H,Koch F,Bugany H.Studies on HIV inactivation in allogeneic bone transplants using chemical disinfection and radioactive irradiation.Unfallchirurgie.1992;18(1):1-6.[15] Fideler BM,Vangsness CJ,Moore T,et al.Effects of gamma irradiation on the human immunodeficiency virus. A study in frozen human bone-patellar ligament-bone grafts obtained from infected cadavera.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(7): 1032-1035.[16] Campbell DG, Li P. Sterilization of HIV with irradiation: relevance to infected bone allografts. Aust N Z J Surg. 1999; 69(7):517-521. [17] 刘思扬,庄道民,董如华,等.钴(60)辐照法对生物羊膜中人类免疫缺陷病毒灭活效果的研究[J].中国消毒学杂志, 2015,32(3): 217-218,221.[18] 赵彦涛,刘思扬,尹惠琼,等.γ射线终末辐照对同种异体肌腱病毒灭活效果及生物力学性能影响的研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2018,7(5):389-393.[19] Hernigou P,Gras G,Marinello G,et al.Inactivation of HIV by application of heat and radiation: implication in bone banking with irradiated allograft bone.Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(5): 508-512.[20] Andriola Silva Brun-Graeppi AK, Richard C,Bessodes M,et al. The effect of sterilization methods on the thermo-gelation properties of xyloglucan hydrogels.Polym Degrad Stab. 2010; 95(2):254-259.[21] Lee KI,Lee JS,Jung HH,et al.Inactivation of enveloped and non-enveloped viruses in the process of chemical treatment and gamma irradiation of bovine-derived grafting materials. Xenotransplantation.2012;19(6):365-369.[22] 王剑锋,英志芳,徐康维,等.板层人工角膜辐照法病毒灭活验证方法的建立及灭活效果验证[J].微生物学免疫学进展, 2018,46(4): 40-43.[23] 张伟,潘洁丽,钱垂文,等.钴60-γ射线辐照对动物源性膜材指示病毒灭活效果的验证[J].中国卫生检验杂志, 2015,25(16): 2666-2668.[24] 蒋丽霞.胶原蛋白海绵病毒灭活/去除工艺的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(7):885-888.[25] Harrell CR,Djonov V,Fellabaum C,et al.Risks of Using Sterilization by Gamma Radiation: The Other Side of the Coin.Int J Med Sci.2018;15(3):274-279.[26] Allaveisi F,Mirzaei M.Effects of high-dose gamma irradiation on tensile properties of human cortical bone: Comparison of different radioprotective treatment methods.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;61:475-483.[27] Qiu QQ,Connor J.Effects of gamma-irradiation,storage and hydration on osteoinductivity of DBM and DBM/AM composite. J Biomed Mater Res A.2008;87(2):373-379.[28] Alanay A,Wang JC,Shamie AN,et al.A novel application of high-dose (50kGy) gamma irradiation for demineralized bone matrix: effects on fusion rate in a rat spinal fusion model.Spine J. 2008;8(5):789-795.[29] Hoburg A,Keshlaf S,Schmidt T,et al.High-dose electron beam sterilization of soft-tissue grafts maintains significantly improved biomechanical properties compared to standard gamma treatment. Cell Tissue Bank.2015;16(2):219-226.[30] Baldini T,Caperton K,Hawkins M,et al.Effect of a novel sterilization method on biomechanical properties of soft tissue allografts.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(12): 3971-3975.[31] Hangody G,Szebenyi G,Abonyi B,et al.Does a different dose of gamma irradiation have the same effect on five different types of tendon allografts? - a biomechanical study.Int Orthop. 2017;41(2):357-365.[32] Tian S,Ha C,Wang B,et al.Arthroscopic anatomic double-bundle ACL reconstruction using irradiated versus non-irradiated hamstring tendon allograft.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(1):251-259.[33] Sun K,Zhang J,Wang Y,et al.Arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with at least 2.5 years' follow-up comparing hamstring tendon autograft and irradiated allograft.Arthroscopy. 2011;27(9):1195-1202.[34] DiBartola AC,Everhart JS,Kaeding CC,et al.Maximum load to failure of high dose versus low dose gamma irradiation of anterior cruciate ligament allografts:A meta-analysis. Knee. 2016;23(5):755-762.[35] Mrázová H,Koller J,Kubisova K,et al.Comparison of structural changes in skin and amnion tissue grafts for transplantation induced by gamma and electron beam irradiation for sterilization.Cell Tissue Bank.2016;17(2):255-260.[36] 刘思扬,庄道民,董如华,等.酒精对同种骨植入材料中人类免疫缺陷病毒灭活效果的研究[J].中国消毒学杂志,2009,26(6): 615-617.[37] 衷鸿宾,白玉龙,赵彦涛,等.75%酒精超声清洗工艺对同种脱钙骨基质性能的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,30(12): 1296-1298.[38] 杨倩,宋战昀,张旭光,等.羧甲基壳聚糖病毒灭活/去除工艺验证[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2016,29(5):533-537.[39] Zhou M,Zhang N,Liu X,et al.Tendon allograft sterilized by peracetic acid/ethanol combined with gamma irradiation.J Orthop Sci.2014;19(4):627-636. [40] 刘明,张旗,王蕊.过氧乙酸-乙醇对同种骨植入材料中病毒的灭活效果研究[J].中国消毒学杂志,2010,27(3):241-243.[41] 李雄涛,余国荣,余黎,等.过氧乙酸-乙醇联合辐照灭菌对脱钙骨基质成骨诱导活性的影响[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2018, 15(1):1-4.[42] Rauh J,Despang F,Baas J,et al.Comparative biomechanical and microstructural analysis of native versus peracetic acid-ethanol treated cancellous bone graft.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:784702.[43] Hodde J,Hiles M.Virus safety of a porcine-derived medical device: evaluation of a viral inactivation method.Biotechnol Bioeng.2002;79(2):211-216.[44] Moore TM,Gendler E,Gendler E.Viruses adsorbed on musculoskeletal allografts are inactivated by terminal ethylene oxide disinfection.J Orthop Res. 2004;22(6): 1358-1361.[45] 周宗科,裴福兴,屠重棋,等.环氧乙烷处理同种异体皮质骨板移植组织学研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2004,1(4):1-4.[46] 施坚.双氧水灭活病毒[J].国外医学.生物制品分册, 1979,2(1): 45-46.[47] 陆烨,陆龙喜,李晔,等.汽化过氧化氢对不同空间消毒效果观察[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2015,25(11):2626-2628.[48] 方哲翔,王建华,袁平,等.医用胶原修复膜病毒灭活/去除工艺的验证和评价[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2016,29(12):1341-1345.[49] Cusinato R,Pacenti M,Martello T,et al.Effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide and electron-beam irradiation treatment for removal and inactivation of viruses in equine-derived xenografts. J Virol Methods.2016;232:39-46.[50] 杨朋,胡晓青,傅欣,等.过氧化氢体外诱导人关节软骨细胞外基质降解研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(4):306-311.[51] 王超.双氧水对关节软骨损害的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2012.[52] Cicek E.Hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative damage on mechanical properties of the articular cartilage.Acta Biol Hung. 2017;68(4):368-375.[53] Ouyang X,Wei B,Hong SD,et al.Study on the Mechanisms of Cartilage Tissue Damage Caused by Hydrogen Peroxide.Cell Biochem Biophys.2015;72(2):343-348.[54] Gardner EM,VonderHeide N,Fisher R,et al.Effect of hydrogen peroxide on human tendon allograft.Cell Tissue Bank.2013; 14(4):667-671.[55] Leow-Dyke SF,Rooney P,Kearney JN.The efficacy and sterilisation of human decellularised dermal allografts with combinations of cupric ions and hydrogen peroxide.Cell Tissue Bank. 2017;18(4):561-572.[56] WHO.Decontamination methods for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Report of a WHO consultation, Geneva,Switzerland,23-26 march 1999.In: WHO infection control guidelines for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies.WHO/CDS/CSR/APH/2000.3;2009:29-32.[57] van Steenberghe M,Schubert T,Guiot Y,et al.Enhanced vascular biocompatibility of decellularized xeno-/allogeneic matrices in a rodent model.Cell Tissue Bank. 2017;18(2): 249-262.[58] van Steenberghe M,Schubert T,Xhema D,et al.Enhanced vascular regeneration with chemically/physically treated bovine/human pericardium in rodents.J Surg Res. 2018;222: 167-179.[59] Fawzi-Grancher S,Goebbels RM,Bigare E,et al.Human tissue allograft processing: impact on in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20(8): 1709-1720.[60] 王春雨,徐琳凯,李超,等.工艺处理过程中病毒的灭活效果研究[J].实验动物科学,2015,32(2):15-17.[61] 梁婧,张潇文,李策生,等.低pH孵放病毒灭活效果回顾性验证评价[J].中国输血杂志,2016,29(9):915-917.[62] Squillace DM,Zhao Z,Call GM,et al.Viral Inactivation of Human Osteochondral Grafts with Methylene Blue and Light. Cartilage.2014;5(1):28-36.[63] Shirasaki N,Matsushita T,Matsui Y,et al.Assessment of the efficacy of membrane filtration processes to remove human enteric viruses and the suitability of bacteriophages and a plant virus as surrogates for those viruses.Water Res. 2017; 115:29-39.[64] Huang Q,Ingham E,Rooney P,et al.Production of a sterilised decellularised tendon allograft for clinical use.Cell Tissue Bank.2013;14(4):645-654.[65] Bui D,Lovric V,Oliver R,et al.Meniscal allograft sterilisation: effect on biomechanical and histological properties.Cell Tissue Bank.2015;16(3):467-475.[66] 国家食品药品监督管理总局.动物源性医疗器械注册技术审查指导原则(2017年修订版)[S],2017年第224号. |
.jpg)
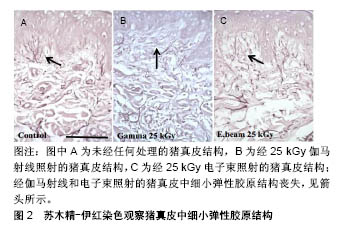
.jpg)
.jpg)