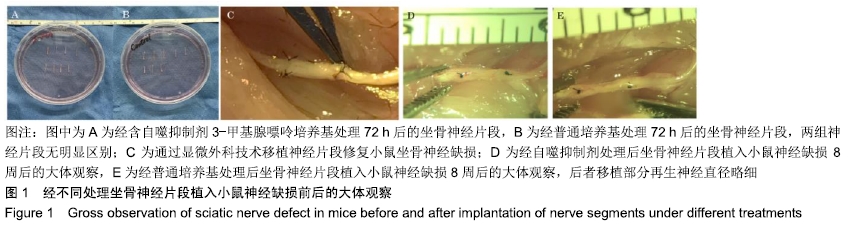
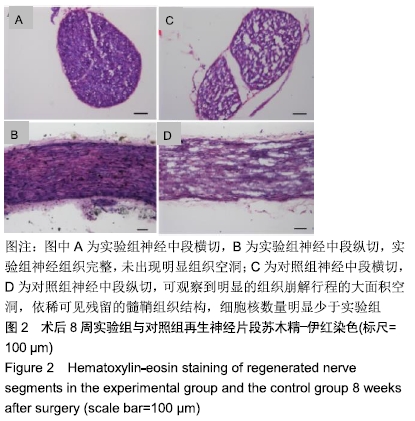
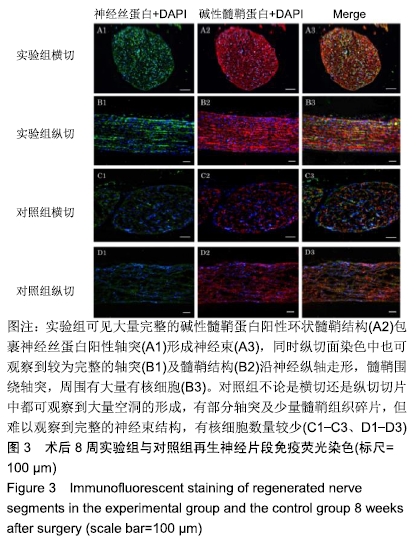
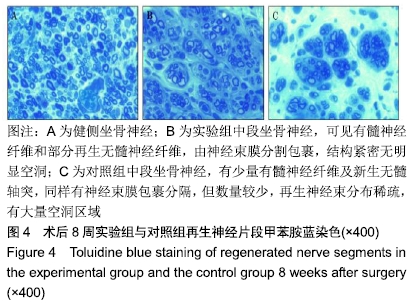
[1] RIVLIN M, SHEIKH E, ISAAC R, et al.The role of nerve allografts and conduits for nerve injuries. Hand Clin.2010; 26(3):435-446.
[2] RAY WZ, MACKINNON SE.Management of nerve gaps: autografts, allografts, nerve transfers, and end-to-side neurorrhaphy.Exp Neurol.2010;223(1):77-85.
[3] GRINSELL D, KEATING CP. Peripheral nerve reconstruction after injury: a review of clinical and experimental therapies. Biomed Res Int.2014;2014:698256.
[4] CASTILLO-GALVAN ML, MARTINEZ-RUIZ FM, DE LA GARZA-CASTRO O, et al.[Study of peripheral nerve injury in trauma patients].Gac Med Mex.2014;150(6):527-532.
[5] SCHMID AB, COPPIETERS MW, RUITENBERG MJ, et al. Local and remote immune-mediated inflammation after mild peripheral nerve compression in rats.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.2013;72(7):662-680.
[6] CONFORTI L, GILLEY J, COLEMAN MP. Wallerian degeneration: an emerging axon death pathway linking injury and disease.Nat Rev Neurosci.2014;15(6):394-409.
[7] GOMEZ-SANCHEZ JA, CARTY L, IRUARRIZAGA-LEJARRETA M, et al.Schwann cell autophagy, myelinophagy, initiates myelin clearance from injured nerves.J Cell Biol.2015;210(1):153-168.
[8] HUANG HC, CHEN L, ZHANG HX, et al.Autophagy Promotes Peripheral Nerve Regeneration and Motor Recovery Following Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury in Rats.J Mol Neurosci. 2016;58(4):416-423.
[9] CAI Y, ARIKKATH J, YANG L, et al.Interplay of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in neurodegenerative disorders.Autophagy.2016;12(2):225-244.
[10] 徐筑秋,杨晓楠,祁佐良.细胞自噬在周围神经损伤及再生中研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017,31(1):122-125.
[11] INSERRA MM, BLOCH DA, TERRIS DJ.Functional indices for sciatic, peroneal, and posterior tibial nerve lesions in the mouse.Microsurgery.1998;18(2):119-124.
[12] GAUDET AD, POPOVICH PG, RAMER MS.Wallerian degeneration: gaining perspective on inflammatory events after peripheral nerve injury.J Neuroinflammation.2011;8:110.
[13] LIU JH, TANG Q, LIU XX, et al.Analysis of transcriptome sequencing of sciatic nerves in Sprague-Dawley rats of different ages.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(12):2182-2190.
[14] CASTANO A, BELL MD, PERRY VH.Unusual aspects of inflammation in the nervous system: Wallerian degeneration. Neurobiol Aging.1996;17(5):745-751.
[15] RUSSELL RC, YUAN HX, GUAN KL.Autophagy regulation by nutrient signaling.Cell Res.2014;24(1):42-57.
[16] MIZUSHIMA N, YOSHIMORI T, OHSUMI Y.The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.2011;27:107-132.
[17] XIAO X, ZHU Y, BU J, et al.The autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine restores sevoflurane anesthesiainduced cognitive dysfunction and neurons apoptosis. Pharmazie. 2017;72(4):214-218.
[18] BUTTEMEYER R, RAO U, JONES NF. Peripheral nerve allograft transplantation with FK506: functional, histological, and immunological results before and after discontinuation of immunosuppression.Ann Plast Surg.1995;35(4):396-401.
[19] ZALEWSKI AAGULATI AK. Evaluation of histocompatibility as a factor in the repair of nerve with a frozen nerve allograft.J Neurosurg.1982;56(4):550-554.
[20] PATEL NP, LYON KA, HUANG JH.An update-tissue engineered nerve grafts for the repair of peripheral nerve injuries.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(5):764-774.
[21] KARANTH S, YANG G, YEH J, et al.Nature of signals that initiate the immune response during Wallerian degeneration of peripheral nerves.Exp Neurol.2006;202(1):161-166.
[22] DEFRANCESCO-LISOWITZ A, LINDBORG JA, NIEMI JP, et al.The neuroimmunology of degeneration and regeneration in the peripheral nervous system.Neuroscience. 2015;302: 174-203.
[23] RAIMONDO S, FORNARO M, TOS P, et al.Perspectives in regeneration and tissue engineering of peripheral nerves.Ann Anat.2011;193(4):334-340.
[24] MASAKI T, MATSUMURA K, SAITO F, et al.Expression of dystroglycan and laminin-2 in peripheral nerve under axonal degeneration and regeneration.Acta Neuropathol. 2000;99(3): 289-295.
[25] CHEN P, PIAO X, BONALDO P. Role of macrophages in Wallerian degeneration and axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury.Acta Neuropathol. 2015;130(5): 605-618.
[26] PULESTON DJ, SIMON AK. Autophagy in the immune system. Immunology.2014;141(1): 1-8.
[27] CHOI SH, GONEN A, DIEHL CJ, et al.SYK regulates macrophage MHC-II expression via activation of autophagy in response to oxidized LDL.Autophagy.2015;11(5):785-795.
[28] OKANO M, SAKATA N, UEDA S, et al.Appropriate modulation of autophagy sensitizes malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor cells to treatment with imatinib mesylate. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014;36(3):200-211.
[29] 范洪伟,殷钢,马玉林,.枸杞多糖对大鼠坐骨神经离断后创伤性神经瘤形成及其疼痛影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2010,24(1): 1298-1301.
[30] MARINELLI S, NAZIO F, TINARI A, et al.Schwann cell autophagy counteracts the onset and chronification of neuropathic pain.Pain.2014;155(1):93-107.
|