| [1] Kearon C, Akl EA, Ornelas J, et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest. 2016; 149(2):315-352. [2] Dyer MR, Chen Q, Haldeman S, et al. Deep vein thrombosis in mice is regulated by platelet HMGB1 through release of neutrophil-extracellular traps and DNA. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2068. [3] Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303(5663): 1532-1535. [4] Fuchs TA, Abed U, Goosmann C, et al. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol. 2007;176(2): 231-241. [5] Urban CF, Ermert D, Schmid M, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contain calprotectin, a cytosolic protein complex involved in host defense against Candida albicans. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5(10): e1000639. [6] Seeley EJ, Matthay MA, Wolters PJ. Inflection points in sepsis biology: from local defense to systemic organ injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;303(5):L355-363. [7] Saitoh T, Komano J, Saitoh Y, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate a host defense response to human immunodeficiency virus-1. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12(1):109-116. [8] von Köckritz-Blickwede M, Chow O, Ghochani M, et al. 7 - Visualization and Functional Evaluation of Phagocyte Extracellular Traps. Method Microbiol. 2010;37:139-160. [9] Leshner M, Wang S, Lewis C, et al. PAD4 mediated histone hypercitrullination induces heterochromatin decondensation and chromatin unfolding to form neutrophil extracellular trap-like structures. Front Immunol. 2012 4; 3:307. [10] Brinkmann V, Laube B, Abu Abed U, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps: how to generate and visualize them. J Vis Exp. 2010;(36): 1724. [11] Martinod K, Demers M, Fuchs TA, et al. Neutrophil histone modification by peptidylarginine deiminase 4 is critical for deep vein thrombosis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(21): 8674-8679. [12] Keshari RS, Jyoti A, Dubey M, et al. Cytokines induced neutrophil extracellular traps formation: implication for the inflammatory disease condition. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48111. [13] Martinelli S, Urosevic M, Daryadel A, et al. Induction of genes mediating interferon-dependent extracellular trap formation during neutrophil differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(42): 44123-44132. [14] Marin-Esteban V, Turbica I, Dufour G, et al. Afa/Dr diffusely adhering Escherichia coli strain C1845 induces neutrophil extracellular traps that kill bacteria and damage human enterocyte-like cells. Infect Immun. 2012;80(5):1891-1899. [15] Hasan R, Rink L, Haase H. Zinc signals in neutrophil granulocytes are required for the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. Innate Immun. 2013;19(3):253-264. [16] Papayannopoulos V, Metzler KD, Hakkim A, et al. Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase regulate the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol. 2010;191(3):677-691. [17] McInturff AM, Cody MJ, Elliott EA, et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation via induction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α. Blood. 2012; 120(15): 3118-3125. [18] Zhang S, Yuan J, Yu M, et al. IL-17A facilitates platelet function through the ERK2 signaling pathway in patients with acute coronary syndrome. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40641. [19] Ding P, Zhang S1, Yu M1, et al. IL-17A promotes the formation of deep vein thrombosis in a mouse model. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;57:132-138. [20] Fuchs TA, Brill A, Duerschmied D, et al. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(36): 15880-15885. [21] Pereira LF, Marco FM, Boimorto R, et al. Histones interact with anionic phospholipids with high avidity; its relevance for the binding of histone-antihistone immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994;97(2):175-180. [22] Saffarzadeh M, Juenemann C, Queisser MA, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps directly induce epithelial and endothelial cell death: a predominant role of histones. PLoS One. 2012;7(2): e32366. [23] Brill A, Fuchs TA, Savchenko AS, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote deep vein thrombosis in mice. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10(1):136-144. [24] Carmona-Rivera C, Zhao W, Yalavarthi S, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps induce endothelial dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus through the activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(7):1417-1424. [25] Xu J, Zhang X, Pelayo R, et al. Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nat Med. 2009;15(11):1318-1321. [26] Ammollo CT, Semeraro F, Xu J, et al. Extracellular histones increase plasma thrombin generation by impairing thrombomodulin-dependent protein C activation. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9(9):1795-1803. [27] Blair P, Rex S, Vitseva O, et al. Stimulation of Toll-like receptor 2 in human platelets induces a thromboinflammatory response through activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Circ Res. 2009; 104(3): 346-354. [28] Semeraro F, Ammollo CT, Morrissey JH, et al. Extracellular histones promote thrombin generation through platelet-dependent mechanisms: involvement of platelet TLR2 and TLR4. Blood. 2011;118(7): 1952-1961. [29] Cognasse F, Hamzeh H, Chavarin P, et al. Evidence of Toll-like receptor molecules on human platelets. Immunol Cell Biol. 2005; 83(2):196-198. [30] Esmon CT. Extracellular histones zap platelets. Blood. 2011; 118(13): 3456-3457. [31] Zhang G, Han J, Welch EJ, et al. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates platelet secretion and potentiates platelet aggregation via TLR4/MyD88 and the cGMP-dependent protein kinase pathway. J Immunol. 2009;182(12):7997-8004. [32] Xu J, Zhang X, Monestier M, et al. Extracellular histones are mediators of death through TLR2 and TLR4 in mouse fatal liver injury. J Immunol. 2011;187(5):2626-2631. [33] Ruiz FA, Lea CR, Oldfield E, et al. Human platelet dense granules contain polyphosphate and are similar to acidocalcisomes of bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(43): 44250-44257. [34] Smith SA, Mutch NJ, Baskar D, et al. Polyphosphate modulates blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103(4): 903-908. [35] Stark K, Philippi V, Stockhausen S, et al. Disulfide HMGB1 derived from platelets coordinates venous thrombosis in mice. Blood. 2016;128(20):2435-2449. [36] Kambas K, Chrysanthopoulou A, Vassilopoulos D, et al. Tissue factor expression in neutrophil extracellular traps and neutrophil derived microparticles in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated vasculitis may promote thromboinflammation and the thrombophilic state associated with the disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(10): 1854-1863. [37] Higuchi DA, Wun TC, Likert KM, et al. The effect of leukocyte elastase on tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood. 1992;79(7): 1712-1719. [38] von Brühl ML, Stark K, Steinhart A, et al. Monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in mice in vivo. J Exp Med. 2012;209(4):819-835. [39] Gould TJ, Vu TT, Swystun LL, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote thrombin generation through platelet-dependent and platelet-independent mechanisms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(9):1977-1984. [40] Müller F, Mutch NJ, Schenk WA, et al. Platelet polyphosphates are proinflammatory and procoagulant mediators in vivo. Cell. 2009;139(6):1143-1156. [41] Grasso S, Neumann A, Lang IM, et al. Interaction of factor VII activating protease (FSAP) with neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Thromb Res. 2018;161:36-42. [42] Noubouossie DF, Whelihan MF, Yu YB, et al. In vitro activation of coagulation by human neutrophil DNA and histone proteins but not neutrophil extracellular traps. Blood. 2017;129(8):1021-1029. [43] Jiménez-Alcázar M, Napirei M, Panda R, et al. Impaired DNase1-mediated degradation of neutrophil extracellular traps is associated with acute thrombotic microangiopathies. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(5):732-742. [44] Jiménez-Alcázar M, Kim N, Fuchs TA. Circulating Extracellular DNA: Cause or Consequence of Thrombosis? Semin Thromb Hemost. 2017;43(6):553-561. [45] Meng W, Paunel-Görgülü A, Flohé S, et al. Deoxyribonuclease is a potential counter regulator of aberrant neutrophil extracellular traps formation after major trauma. Mediators Inflamm. 2012; 2012:149560. [46] Storisteanu DM, Pocock JM, Cowburn AS, et al. Evasion of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps by Respiratory Pathogens. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017;56(4):423-431. [47] Chang Z, Jiang N, Zhang Y, et al. The TatD-like DNase of Plasmodium is a virulence factor and a potential malaria vaccine candidate. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11537. [48] Gondaira S, Higuchi H, Nishi K, et al. Mycoplasma bovis escapes bovine neutrophil extracellular traps. Vet Microbiol. 2017;199: 68-73. [49] 张凯,陈虹宇,李娇,等.中性粒细胞细胞外诱捕网的研究进展[J].中国畜牧兽医,2018,45(1):206-211.[50] Johnson CJ, Cabezas-Olcoz J, Kernien JF, et al. The Extracellular Matrix of Candida albicans Biofilms Impairs Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12(9): e1005884. |
.jpg)
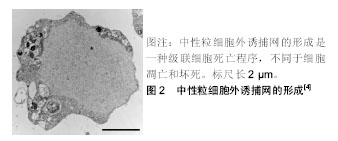

.jpg)