| [1] Bassett CA, Pawluk RJ, Pilla AA. Acceleration of fracture repair by electromagnetic fields. a surgically noninvasive method. Ann N Y Acad Sci.1974;238:242-262.[2] Yang Y, Tao C, Zhao D, et al. Emf acts on rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to promote differentiation to osteoblasts and to inhibit differentiation to adipocytes. Bioelectromagnetics. 2010;31(4): 277-285.[3] Hu J, Zhang T, Xu D, et al. Combined magnetic fields accelerate bone-tendon junction injury healing through osteogenesis. Scand J Med Sci Sports.2015;25(3):398-405.[4] Kim EC, Leesungbok R, Lee SW, et al. Effects of static magnetic fields on bone regeneration of implants in the rabbit: micro-ct, histologic, microarray, and real-time pcr analyses. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(4):396-405.[5] Russo A, Bianchi M, Sartori M, et al. Magnetic forces and magnetized biomaterials provide dynamic flux information during bone regeneration.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2016;27(3):51.[6] Panseri S, Russo A, Giavaresi G, et al. Innovative Magnetic Scaffolds for Orthopedic Tissue Engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A.2012;100(9):2278-2286.[7] Yun HM, Ahn SJ, Park KR, et al. Magnetic nanocomposite scaffolds combined with static magnetic field in the stimulation of osteoblastic differentiation and bone formation. Biomaterials.2016; 85:88-98.[8] Calcagnotto T, Schwengber M M B, De Antoni C C, et al. Magnetic field effects on bone repair after calcium phosphate cement implants: histometric and biochemistry evaluation. Ann Maxillofac Surg.2017;7(1): 18-24.[9] 周围,李月玮,蒋秋冬,等.续骨丹外敷疗法对大鼠胫骨缺损模型血清bmp-2的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2017,36(4):1336-1342.[10] Atalay Y, Gunes N, Guner MD, et al. Pentoxifylline and electromagnetic field improved bone fracture healing in rats. Drug Des Devel Ther.2015;9:5195-5201.[11] Li B, Bi J, Li W, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on histomorphometry and osteocalcin in disuse osteoporosis rats. Technol Health Care.2017;25(S1):13-20.[12] Zhou J, Liao Y, Xie H, et al. Effects of combined treatment with ibandronate and pulsed electromagnetic field on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Bioelectromagnetics. 2017;38(1):31-40.[13] Lei T, Li F, Liang Z, et al. Effects of four kinds of electromagnetic fields (emf) with different frequency spectrum bands on ovariectomized osteoporosis in mice. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):553.[14] Aksoy MÇ, Topal O, Özkavak HV, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field on mineral density, biomechanical properties, and metabolism of bone tissue in heparin-induced osteoporosis in male rats. Biomed Res Int.2017;28(6):2724-2729.[15] Zhou J, Liao Y, Zeng Y, et al. Effect of intervention initiation timing of pulsed electromagnetic field on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Bioelectromagnetics. 2017;38(6):456-465.[16] Zhang H, Gan L, Zhu X, et al. Moderate-intensity 4mt static magnetic fields prevent bone architectural deterioration and strength reduction by stimulating bone formation in streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Bone. 2018;107: 36-44.[17] Liu C, Zhang Y, Fu T, et al. Effects of electromagnetic fields on bone loss in hyperthyroidism rat model. Bioelectromagnetics. 2017,38(2):137-150.[18] 周建,马小妮,陈克明,等.电磁场不同处理时间对人脐带间充质干细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].解放军医药杂志, 2015,3:11-15+19.[19] Jing D, Cai J, Wu Y, et al. Moderate-intensity rotating magnetic fields do not affect bone quality and bone remodeling in hindlimb suspended rats. Plos One. 2014;9(7): e102956.[20] Zhou J, Ming LG, Ge BF, et al. Effects of 50 Hz sinusoidal electromagnetic fields of different intensities on proliferation, differentiation and mineralization potentials of rat osteoblasts. Bone.2011;49(4):753-761.[21] Li K, Ma S, Li Y, et al. Effects of pemf exposure at different pulses on osteogenesis of mc3t3-e1 cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59(9): 921-927.[22] Yang J, Zhang J, Ding C, et al. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation and iron content in mc3t3-e1 cells by static magnetic field with different intensities. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s12011-017-1161-5. [23] Tschon M, Veronesi F, Contartese D, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields and platelet rich plasma in preventing osteoclastogenesis in an in vitro model of osteolysis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(3): 2645-2656.[24] He J, Zhang Y, Chen J, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on the expression of nfatc1 and caii in mouse osteoclast-like cells. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2015;27(1): 13-19.[25] Zhang J, Meng X, Ding C, et al. Regulation of osteoclast differentiation by static magnetic fields. Electromagn Biol Med. 2017;36(1): 8-19.[26] Du L, Fan H, Miao H, et al. Extremely low frequency magnetic fields inhibit adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics.2014;35(7): 519-530.[27] Kim EC, Leesungbok R, Lee SW, et al. Effects of moderate intensity static magnetic fields on human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 2015;36(4): 267-276.[28] Son B, Kim H D, Kim M, et al. Physical stimuli-induced chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells using magnetic nanoparticles. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(9):1339-1347.[29] Kavand H, Haghighipour N, Zeynali B, et al. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic field in mesenchymal stem cells gene regulation: chondrogenic markers evaluation. Artif Organs. 2016; 40(10): 929-937.[30] Kim EC, Park J, Kwon IK, et al. Static magnetic fields promote osteoblastic/cementoblastic differentiation in osteoblasts, cementoblasts, and periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2017;47(5): 273-291.[31] Du S, Li J, Du C, et al. Overendocytosis of superparamagnetic iron oxide particles increases apoptosis and triggers autophagic cell death in human osteosarcoma cell under a spinning magnetic field. Oncotarget.2017;8(6): 9410-9424.[32] Zhou J, He H, Yang L, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone mass and wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Arch Med Res. 2012;43(4): 274-282.[33] Jing D, Li F, Jiang M, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields improve bone microstructure and strength in ovariectomized rats through a wnt/lrp5/beta-catenin signaling-associated mechanism. PLoS One. 2013;8(11): e79377.[34] Lei T, Liang Z, Li F, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields (pemf) attenuate changes in vertebral bone mass, architecture and strength in ovariectomized mice. Bone. 2018;108:10-19.[35] Fathi E, Farahzadi R. Enhancement of osteogenic differentiation of rat adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by zinc sulphate under electromagnetic field via the pka, erk1/2 and wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. PLoS One.2017;12(3): e0173877.[36] Rotherham M, Henstock J R, Qutachi O, et al. Remote regulation of magnetic particle targeted wnt signaling for bone tissue engineering. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(1):173-184.[37] Zhou J, Chen S, Guo H, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field stimulates osteoprotegerin and reduces rankl expression in ovariectomized rats. Rheumatol Int.2013;33(5): 1135-1141.[38] Yong Y, Ming Z D, Feng L, et al. Electromagnetic fields promote osteogenesis of rat mesenchymal stem cells through the pka and erk1/2 pathways. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(10): e537-e545.[39] Elsisi H F, Mousa G S, Mt E L. Electromagnetic field versus circuit weight training on bone mineral density in elderly women. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10: 539-547.[40] 杜迅,郝建凤.低频脉冲磁场对绝经后骨质疏松症患者骨代谢标志物水平的影响[J].中国临床研究.2016;9: 1216-1218.[41] Meszaros S, Tabak AG, Horvath C, et al. Influence of local exposure to static magnetic field on pain perception and bone turnover of osteoporotic patients with vertebral deformity - a randomized controlled trial. Int J Radiat Biol.2013;89(10): 877-885.[42] 张展翅,李晓强,马隽,等.鲑鱼降钙素结合脉冲电磁场治疗脊髓损伤致骨质疏松症的临床效果[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2017(09): 1191-1194+1260.[43] 王鑫,白倩,王斌,等.运动、药物联合物理因子治疗对脊髓损伤后骨质疏松症疗效的观察[J].中国疗养医学, 2017,11: 1121-1124.[44] Gajjar B, Sheth M, Sharma S, et al. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic energy therapy on pain and function in subjects with knee osteoarthritis. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 2014;3(6): 1.[45] Dundar U, Asik G, Ulasli AM, et al. Assessment of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy with serum ykl-40 and ultrasonography in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Int J Rheum Dis.2016;19(3):287-293.[46] 尹萍.超短波电疗法联合脉冲磁疗治疗骨折效果研究[J].中国疗养医学,2018,1: 41-42.[47] Phillips M, Baumhauer J, Sprague S, et al. Use of combined magnetic field treatment for fracture nonunion. J Long Term Eff Med Implants.2016;26(3): 277-284.[48] Gujjalapudi M, Anam C, Mamidi P, et al. Effect of magnetic field on bone healing around endosseous implants -an in-vivo study. J Clin Diagn Res.2016;10(10): Zf01-zf04.[49] Jung JG, Park JH, Kim SC, et al. Effectiveness of pulsed electromagnetic field for pain caused by placement of initial orthodontic wire in female orthodontic patients: a preliminary single-blind randomized clinical trial. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2017;152(5): 582-591.[50] 覃宗见.康复训练联合脉冲磁疗对膝关节骨性关节炎患者膝关节功能恢复的影响[J].医药前沿, 2017,7(14):386-387.[51] Wuschech H, Von Hehn U, Mikus E, et al. Effects of pemf on patients with osteoarthritis: results of a prospective, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Bioelectromagnetics. 2015;36(8):576-585. |
.jpg)
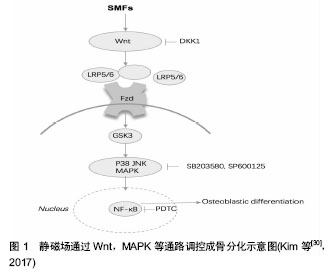
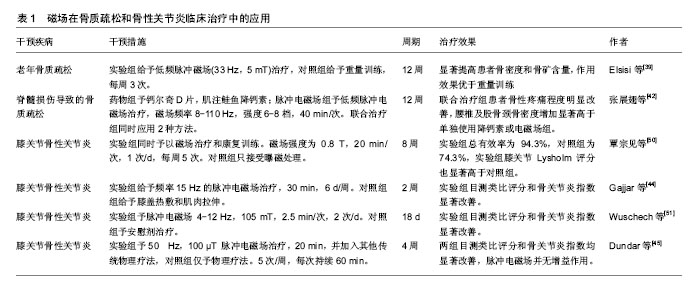
.jpg)