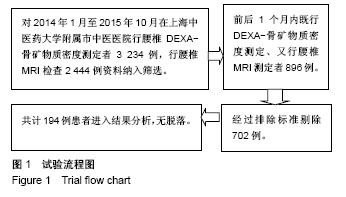
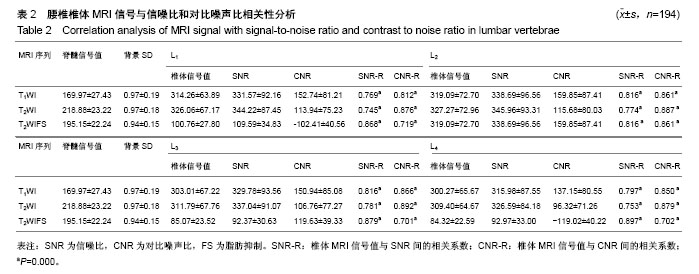
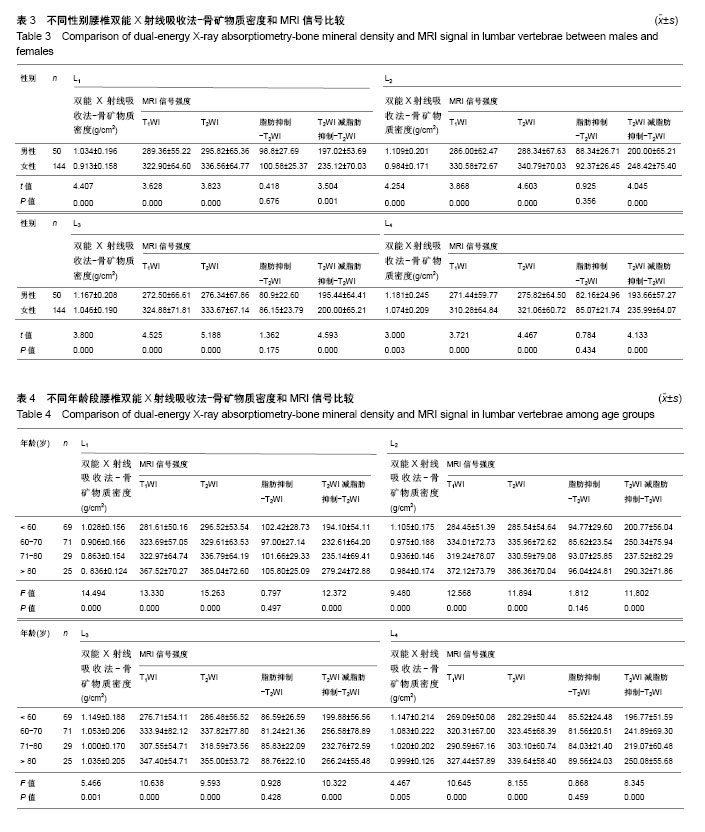
| [1] Ralston SH, Fraser J. Diagnosis and management of osteoporosis. Practitioner. 2015;259(1788):15-19. [2] 毛文晴,田甜.原发性骨质疏松的原因及发病机制[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(10):937-940.[3] 陈刚,俞茂华.男性骨质疏松的原因[J].中华老年医学杂志, 2007, 26(12):955-956.[4] Kanis JA, McCloskey EV, Johansson H, et al. European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(1): 23-57. [5] World Health Organization. Prevention and management of osteoporosis. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2003;921: 1-164. [6] Weaver CM, Gordon CM, Janz KF, et al. The National osteoporosis foundation's position statement on peak bone mass development and lifestyle factors: a systematic review and implementation recommendations. Osteoporos Int. 2016; 27(4):1281-1386. [7] Baum T, Rohrmeier A, Syväri J, et al. Anatomical variation of age-related changes in vertebral bone marrow composition using chemical shift encoding-based water-fat magnetic resonance imaging. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9: 141. [8] 雷立存,何丽,刘斋,等.磁共振化学位移成像对骨质疏松的诊断价值[J].中国临床医学影像学杂志,2014,25(9):648-651.[9] Schwartz AV. Marrow fat and bone: review of clinical findings. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015;6(40):40. [10] Messina C, Maffi G, Vitale JA, et al. Diagnostic imaging of osteoporosis and sarcopenia: a narrative review. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2018;8(1):86-99. [11] 程晓光,杨定焯,周琦,等.中国女性的年龄相关骨密度、骨丢失率、骨质疏松发生率及参考数据库——多中心合作项目[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2008,14(4):221-228.[12] Brennan O, Kennedy OD, Lee TC, et al. The effects of estrogen deficiency and bisphosphonate treatment on tissue mineralisation and stiffness in an ovine model of osteoporosis. J Biomech. 2011;44(3):386-390. [13] Koh LK, Sedrine WB, Torralba TP, et al. A simple tool to identify asian women at increased risk of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2001;12(8):699-705. [14] Muslim D, Mohd E, Sallehudin A, et al. Performance of osteoporosis self-assessment tool for asian (osta) for primary osteoporosis in post-menopausal malay women. Malays Orthop J. 2012;6(1):35-39. [15] 景彩霞,李二乐,薛亚娟.OSTA指数与体重指数对于绝经后妇女骨质疏松的预测效果评价[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(9): 1083-1086.[16] Oh SM, Song BM, Nam BH, et al. Development and validation of osteoporosis risk-assessment model for korean men. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(1):187-196. [17] Mistry SD, Woods GN, Sigurdsson S, et al. Sex hormones are negatively associated with vertebral bone marrow fat. Bone. 2018;108(1):20-24. [18] Lewiecki EM. Clinical applications of bone density testing for osteoporosis. Minerva Med. 2005;96(5):317-330. [19] Winzenberg T, Jones G. Dual energy X-ray absorptionmetry. Aust Fam Physician. 2011;40(1-2):43-44. [20] 吴丹,孔西建,叶进,等.女性骨质疏松性骨折骨密度阈值冀中国人群骨质疏松诊断标准探讨[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2011,17(5): 382-385.[21] 查小云,庞晓娜,李锂,等.中老年男性骨质疏松(OP)危险分层与定量超声骨密度(QUS-BMD)及双能X线骨密度(DXA-BMD)的相关性[J].复旦学报(医学版),2014,41(4):504-510.[22] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011,4(1):2-17.[23] 张智海,刘忠厚,李娜,等.中国人骨质疏松症诊断标准专家共识(第三稿•2014版)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(9):1007-1010.[24] 刘中银,陈涛.48例双能X线骨密度检测假阴性结果分析[J].西南国防医学,2013,23(4):414-415.[25] 何涛,杨定焯,刘忠厚.骨质疏松症诊断标准的探讨[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(2):151-156,104.[26] 张昕,王峻,苏晋生,等.定量CT与双能X线吸收测定仪测量腰椎各椎体间骨密度差异性研究[J].中国医学影像学杂志, 2011,19(12): 884-886.[27] Link TM. Radiology of Osteoporosis. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2016;67(1):28-40. [28] 宋飞鹏,张进,郜璐璐,等.骨质疏松症影像学诊断的研究现状[J].中国现代医生,2014,52(11):158-160.[29] Balzano RF, Mattera M, Cheng X, et al. Osteoporosis: what the clinician needs to know? Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2018; 8(1):39-46. [30] Chou SH, LeBoff MS. Vertebral imaging in the diagnosis of osteoporosis: a clinician's perspective. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017;15(6):509-520. [31] 李冠武,常时新,鲍虹,等.骨髓脂肪含量对预测骨质疏松性椎体骨折风险的初步应用[J].实用放射学杂志,2012,28(1):74-77.[32] 张灵艳,李绍林,郝帅.比较氢质子磁共振波谱和正反相位MRI成像在骨髓脂肪沉积中的价值[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(6): 691-696.[33] 雷立存,何丽,刘斋,等.磁共振化学位移成像对骨质疏松的诊断价值[J].中国临床医学影像学杂志,2014,25(9):648-651.[34] Zhang L, Li S, Hao S, et al. Quantification of fat deposition in bone marrow in the lumbar vertebra by proton MRS and in-phase and out-of-phase MRI for the diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Xray Sci Technol. 2016;24(2):257-266. [35] 柯祺,许灼新,曹海伟,等.腰椎骨质疏松双能X线吸收法骨密度测定与MRI对照分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2003,19(3):236-240.[36] Paccou J, Hardouin P, Cotten A, et al. The role of bone marrow fat in skeletal health: usefulness and perspectives for clinicians. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(10):3613-3621.[37] 常飞霞,黄刚,樊敦徽,等.磁共振水-脂分离成像技术对椎体脂肪含量的测量[J].磁共振成像,2016,7(12):902-908.[38] 顾晨琦,陈广东,顾云斌.核磁共振对骨质疏松性骨折疼痛责任椎体的诊断价值研究[J].中国血液流变学杂志, 2016,26(2): 259-261.[39] 张恒,黄刚,毛泽庆,等.3.0T磁共振腹部DWI序列定量评价腰椎骨质疏松的价值[J].医学影像学杂志,2016,26(6):1083-1087.[40] Oei L, Koromani F, Rivadeneira F, et al. Quantitative imaging methods in osteoporosis. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2016; 6(6):680-698. |
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)