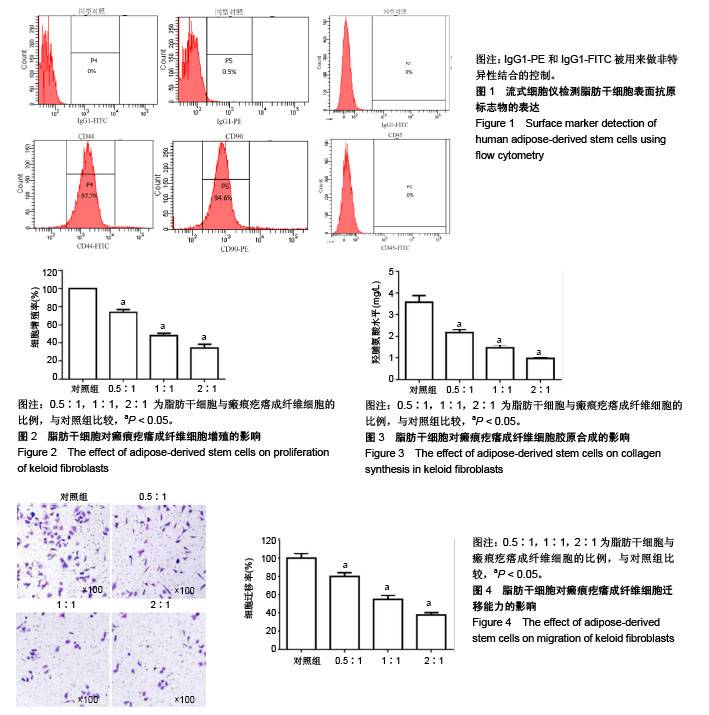
| [1] Rog-Zielinska EA, Norris RA, Kohl P, et al. The Living Scar--Cardiac Fibroblasts and the Injured Heart. Trends Mol Med. 2016;22(2):99-114. [2] Li Y, Shi S, Gao J, et al. Cryptotanshinone downregulates the profibrotic activities of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts and accelerates wound healing: A potential therapy for the reduction of skin scarring. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;80: 80-86. [3] Harris WM, Zhang P, Plastini M, et al. Evaluation of function and recovery of adipose-derived stem cells after exposure to paclitaxel. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(2):211-221. [4] Huang CZ, Yang XN, Liu DC, et al. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide-Induced Calcium Alginate Gel Combined with Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Differentiating to Osteoblasts. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;73(3):609-617. [5] Goh BS, Che Omar SN, Ubaidah MA, et al. Chondrogenesis of human adipose derived stem cells for future microtia repair using co-culture technique. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017;137(4): 432-441. [6] Zhong J, Guo B, Xie J, et al. Crosstalk between adipose-derived stem cells and chondrocytes: when growth factors matter. Bone Res. 2016;4:15036. [7] Wang WZ, Fang XH, Williams SJ, et al. The impact of short-term refrigeration of human lipoaspirate on adipose-derived stem cells and adipocytes. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015;68(1):137-139. [8] Ferng AS, Marsh KM, Fleming JM, et al. Adipose-derived human stem/stromal cells: comparative organ specific mitochondrial bioenergy profiles. Springerplus. 2016;5(1): 2057. [9] Kumai Y, Kobler JB, Park H, et al. Modulation of vocal fold scar fibroblasts by adipose-derived stem/stromal cells. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(2):330-337. [10] Zhang J, Liu Z, Cao W, et al. Amentoflavone inhibits angiogenesis of endothelial cells and stimulates apoptosis in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Burns. 2014;40(5):922-929. [11] He L, Marneros AG. Macrophages are essential for the early wound healing response and the formation of a fibrovascular scar. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(6):2407-2417. [12] Bernabei P, Rigamonti L, Ariotti S, et al. Functional analysis of T lymphocytes infiltrating the dermis and epidermis of post-burn hypertrophic scar tissues. Burns. 1999;25(1):43-48. [13] Gong YF, Zhang XM, Liu F, et al. Inhibitory effect of recombinant human endostatin on the proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts in a rabbit ear model. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;791:647-654. [14] Wang H, Chen Z, Li X, et al. TSG-6 treatment promoted apoptosis in human fibroblasts of pathological scar. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016;62(6):33-37. [15] Li ZJ, Kim SM. The application of the starfish hatching enzyme for the improvement of scar and keloid based on the fibroblast-populated collagen lattice. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014;173(4):989-1002. [16] Liu D, Li G, Liu D, et al. Effects of tetrandrine on the synthesis of collagen and scar-derived fibroblast DNA. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2001;17(4):222-224. [17] Tsagias N, Kouzi-Koliakos K, Koliakos I, et al. Addition of adipose-derived stem cells in cord blood cultures stimulates their pluripotent differentiation. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(10): 4340-4344. [18] Pu CM, Liu CW, Liang CJ, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Protect Skin Flaps against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via IL-6 Expression. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137(6):1353-1362. [19] Payne NL, Sun G, McDonald C, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells engineered to secrete IL-10 inhibit APC function and limit CNS autoimmunity. Brain Behav Immun. 2013;30:103-114. [20] Razmkhah M, Jaberipour M, Erfani N, et al. Adipose derived stem cells (ASCs) isolated from breast cancer tissue express IL-4, IL-10 and TGF-β1 and upregulate expression of regulatory molecules on T cells: do they protect breast cancer cells from the immune response. Cell Immunol. 2011;266(2): 116-122. [21] Razmkhah M, Jaberipour M, Hosseini A, et al. Expression profile of IL-8 and growth factors in breast cancer cells and adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) isolated from breast carcinoma. Cell Immunol. 2010;265(1):80-85. [22] Cao JQ, Liang YY, Li YQ, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells enhance myogenic differentiation in the mdx mouse model of muscular dystrophy via paracrine signaling. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(10):1638-1643. [23] Harn HJ, Lin SZ, Hung SH, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells can abrogate chemical-induced liver fibrosis and facilitate recovery of liver function. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(12): 2753-2764. [24] Rivera-Valdés JJ, García-Bañuelos J, Salazar-Montes A, et al. Human adipose derived stem cells regress fibrosis in a chronic renal fibrotic model induced by adenine. PLoS One. 2017;12(12):e0187907. [25] Zhao J, Shu B, Chen L, et al. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits collagen synthesis in dermal fibroblasts and prevents hypertrophic scar formation in vivo. Exp Dermatol. 2016; 25(8):604-610. [26] Tejiram S, Zhang J, Travis TE, et al. Compression therapy affects collagen type balance in hypertrophic scar. J Surg Res. 2016;201(2):299-305. [27] 武艳,张春雷,刘阳,等.骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养液对瘢痕成纤维细胞生物活性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(7): 1009-1014.[28] Chun Q, ZhiYong W, Fei S, et al. Dynamic biological changes in fibroblasts during hypertrophic scar formation and regression. Int Wound J. 2016;13(2):257-262. [29] 张鹏,纪亮,张翠香,等.基质金属蛋白酶促进瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞迁移及其意义[J].中国现代医学杂志,2013,23(3):11-14.[30] 余州,宋雅娟,苏映军,等.KU-0063794抑制增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖及迁移的研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2017,28(6): 328-331.[31] Lin TY, Fan CW, Maa MC, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-promoted proliferation of Caco-2 cells is mediated by c-Src induction and ERK activation. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2015;5(1):5. [32] Sapkota M, Li L, Choi H, et al. Bromo-honaucin A inhibits osteoclastogenic differentiation in RAW 264. 7 cells via Akt and ERK signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;769: 100-109. [33] Zhang Z, Liu P, Wang J, et al. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C regulates apoptosis-dependent tumor progression of non-small cell lung cancer via ERK pathway. Med Oncol. 2015;32(5):149. [34] Zuo H, Lin T, Wang D, et al. RKIP Regulates Neural Cell Apoptosis Induced by Exposure to Microwave Radiation Partly Through the MEK/ERK/CREB Pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(3):1520-1529. [35] 沈利,余扬,马少林.A型肉毒毒素对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖、凋亡及对ERK/MAPK信号通路的影响[J].医学研究杂志, 2017, 46(7):26-29.[36] 刘宏伟,程飚,付小兵,等.血管紧张素Ⅱ对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞细胞外信号调节激酶活性的影响[J].中国美容医学杂志, 2007, 16(7):874-877.[37] 吴江群,聂兴举,秦泽莲.氧化苦参碱对病理性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖凋亡的影响[J].中国微创外科杂志,2011,11(3):259-263.[38] 唐世杰,胡素銮,王玉银.Bcl-2 对病理性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖活性及细胞凋亡的影响[J].汕头大学医学院学报, 2002,15(4): 211-212.[39] 李响,刘宏伟,梁杰,等.异泽兰黄素抑制瘢痕组织成纤维细胞增殖的机制[J].中国老年学杂,2017,37(22):5495-5498. |
.jpg)

.jpg)