中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (7): 1072-1077.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0119
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
不同剂量微波治疗对骨折术后钛合金植入物毗邻组织的影响
王 刚,徐义明,叶冬梅,付腾飞,邹玉珍,冯宪煊,白跃宏
- 上海交通大学附属第六人民医院康复医学科,上海市 200233
-
出版日期:2018-03-08发布日期:2018-03-08 -
通讯作者:白跃宏,博士,教授,博士生导师,上海交通大学附属第六人民医院,上海市 200023 -
作者简介:王刚,男,1982年生,河南省新郑市人,汉族,2016年上海交通大学毕业,博士,主治医师,研究方向是骨关节疾病康复的基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:上海市科学技术委员会科研计划项目(13231202600)
Effects of different doses of microwave therapy on adjacent tissue of titanium alloy implants after fracture surgery
Wang Gang, Xu Yi-ming, Ye Dong-mei, Fu Teng-fei, Zou Yu-zhen, Feng Xian-xuan, Bai Yue-hong
- Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200233, China
-
Online:2018-03-08Published:2018-03-08 -
Contact:Bai Yue-hong, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200233, China -
About author:Wang Gang, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200233, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Program of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai City, No. 13231202600
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
中图分类号:
引用本文
王 刚,徐义明,叶冬梅,付腾飞,邹玉珍,冯宪煊,白跃宏. 不同剂量微波治疗对骨折术后钛合金植入物毗邻组织的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(7): 1072-1077.
Wang Gang, Xu Yi-ming, Ye Dong-mei, Fu Teng-fei, Zou Yu-zhen, Feng Xian-xuan, Bai Yue-hong. Effects of different doses of microwave therapy on adjacent tissue of titanium alloy implants after fracture surgery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(7): 1072-1077.
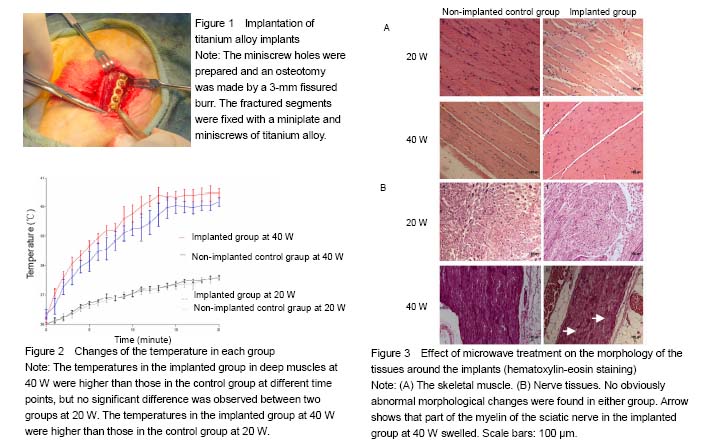
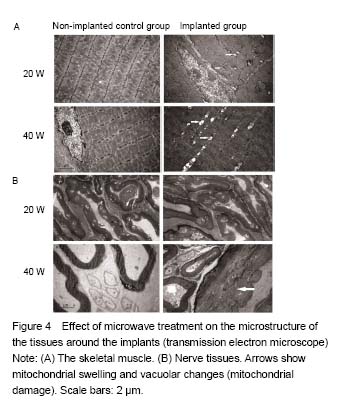
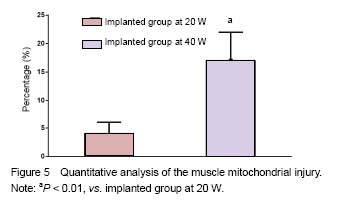
| [1] Perren SM. Fracture healing. The evolution of our understanding. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2008;75(4):241-246.[2] Giombini A, Giovannini V, Di Cesare A, et al. Hyperthermia induced by microwave diathermy in the management of muscle and tendon injuries. Br Med Bull. 2007;83:379-396.[3] Schwan HP, Piersol GM. The absorption of electromagnetic energy in body tissues. Am J Phys Med. 1954;33(6):371-404.[4] Giovanella BC, Mondovi B. Selective heat sensitivity of cancer cells: Introduction. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1977;(59):1-6.[5] Lehmann JF, Guy AW, Stonebridge JB, et al. Temperature distribution produced in models by three microwave applicators at 433.92 megahertz. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1975;56(4):145-151.[6] deLateur BJ, Stonebridge JB, Lehmann JF. Fibrous muscular contractures: treatment with a new direct contact microwave applicator operating at 915 MHz. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1978;59(10):488-499.[7] Goats GC. Microwave diathermy. Br J Sports Med. 1990;24(4):212-218.[8] Chang WH, Sun JS, Chang SP, et al. Study of thermal effects of ultrasound stimulation on fracture healing. Bioelectromagnetics. 2002;23(4):256-263.[9] Leon SA, Asbell SO, Edelstein G, et al. Effects of hyperthermia on bone. I. Heating rate patterns induced by microwave irradiation in bone and muscle phantoms. Int J Hyperthermia. 1993;9(1):69-75.[10] Lubner MG, Brace CL, Hinshaw JL, et al. Microwave tumor ablation: mechanism of action, clinical results, and devices. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(8 Suppl):S192-203.[11] Shields N, Gormley J, O'Hare N. Short-wave diathermy: current clinical and safety practices. Physiother Res Int. 2002;7(4):191-202.[12] Guy AW. Dosimetry associated with exposure to non-ionizing radiation: very low frequency to microwaves. Health Phys. 1987;53(6):569-584.[13] Ruggera PS, Witters DM, von Maltzahn G, et al. In vitro assessment of tissue heating near metallic medical implants by exposure to pulsed radio frequency diathermy. Phys Med Biol. 2003;48(17):2919-2928.[14] Virtanen H, Keshvari J, Lappalainen R. The effect of authentic metallic implants on the SAR distribution of the head exposed to 900, 1800 and 2450 MHz dipole near field. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52(5):1221-1236. [15] McIntosh RL, Anderson V, McKenzie RJ. A numerical evaluation of SAR distribution and temperature changes around a metallic plate in the head of a RF exposed worker. Bioelectromagnetics. 2005;26(5):377-388.[16] Virtanen H, Huttunen J, Toropainen A, et al. Interaction of mobile phones with superficial passive metallic implants. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50(11):2689-2700.[17] Seiger C, Draper DO. Use of pulsed shortwave diathermy and joint mobilization to increase ankle range of motion in the presence of surgical implanted metal: A case series. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36(9):669-677.[18] Wen CE, Yamada Y, Shimojima K, et al. Processing and mechanical properties of autogenous titanium implant materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2002;13(4):397-401.[19] Muranaka H, Horiguchi T, Ueda Y, et al. Evaluation of RF heating on hip joint implant in phantom during MRI examinations. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2010;66(7):725-733.[20] Huidobro C, Larson B, Mynderse S, et al. Characterizing Prostiva RF treatments of the prostate for BPH with gadolinium-enhanced MRI. ScientificWorldJournal. 2009;9:10-16.[21] Ye D, Xu Y, Zhang H, et al. Effects of low-dose microwave on healing of fractures with titanium alloy internal fixation: an experimental study in a rabbit model. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75756.[22] Danilov RK. Ultrastructure of skeletal muscle tissue of microwave damaged chick embryos. Arkh Anat Gistol Embriol. 1980;78(1):83-88.[23] Dwivedi RS, Dwivedi U, Chiang B. Low intensity microwave radiation effects on the ultrastructure of Chang liver cells. Exp Cell Res. 1989;180(1):253-265.[24] Zhao L, Peng RY, Wang SM, et al. Relationship between cognition function and hippocampus structure after long-term microwave exposure. Biomed Environ Sci. 2012;25(2):182-188.[25] Mileva K, Georgieva B, Radicheva N. About the biological effects of high and extremely high frequency electromagnetic fields. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Bulg. 2003;27(2-3):89-100.[26] Green DR, Reed JC. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science. 1998;281(5381):1309-1312.[27] Mehdizadeh M, Kermanian F, Farjah G. Schwann cell injuries of radial nerve after lead (Pb) exposure in rats. Pathophysiology. 2008;15(1):13-17.[28] Barroso-Moguel R, Villeda Hernández J. Experimental neuropathy produced in rats with industrial solvents (thinner). Arch Invest Med (Mex). 1989;20(1):53-60.[29] Can B, Saray A, Caglikulekçi M, et al. Effects of obstructive jaundice on the peripheral nerve: an ultrastructural study in rats. Eur Surg Res. 2004;36(4):226-233.[30] Berry EM. Dietary fatty acids in the management of diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;66(4 Suppl):991S-997S.[31] Chen Y, Yi Q, Liu G, et al. Cerebral white matter injury and damage to myelin sheath following whole-brain ischemia. Brain Res. 2013;1495:11-17.[32] Hoogeveen JF, Troost D, Wondergem J, et al. Hyperthermic injury versus crush injury in the rat sciatic nerve: a comparative functional, histopathological and morphometrical study. J Neurol Sci. 1992;108(1):55-64.[33] Vujaskovic Z, McChesney Gillette S, Powers BE, et al. Effects of intraoperative hyperthermia on canine sciatic nerve: histopathologic and morphometric studies. Int J Hyperthermia. 1994;10(6):845-855.[34] Dewey WC. Arrhenius relationships from the molecule and cell to the clinic. Int J Hyperthermia. 2009;25(1):3-20.[35] Ginzburg EL, Mashanski? VF, Krylenkov VA, et al. Correlation of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase activity with their size following exposure of cells to higher temperatures. Tsitologiia. 1976;18(5):600-604.[36] Funk RH, Nagel F, Wonka F, et al. Effects of heat shock on the functional morphology of cell organelles observed by video-enhanced microscopy. Anat Rec. 1999;255(4):458-464. |
| [1] | 张 超, 吕 欣. 髋臼骨折固定后的异位骨化:危险因素、预防及其治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [2] | 吴 刚, 陈建文, 王世隆, 段笑然, 刘海军, 董建峰. 单纯HyProCure跗骨螺钉治疗青少年柔韧性平足合并痛性副舟骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| [3] | 孔令宝, 吕 欣. 胫骨后外侧平台骨折手术治疗中植入物选择与入路对支撑作用的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 942-947. |
| [4] | 刘正蓬, 王雅辉, 张义龙, 明 颖, 孙志杰, 孙 贺. 3D打印椎间融合器置入治疗脊髓型颈椎病:颈椎曲度及椎间高度恢复的半年随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [5] | 李兴平, 肖东琴, 赵 桥, 陈 硕, 白亦光, 刘 康, 冯 刚, 段 可. 钛表面载铜抗菌功能膜的制备及性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [6] | 石晓岫, 毛世龙, 刘 洋, 马幸双, 罗彦凤. 钽与钛(合金)骨科材料的差异比较:理化指标及抗菌和成骨能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | 吕家兴, 白磊鹏, 杨朝昕, 苗岳松, 金 宇, 李哲宏, 孙广普, 徐 莹, 张擎柱. 膝关节骨性关节炎老年股骨转子间骨折行股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [8] | 刘 畅, 韩树峰. 股骨近端联合拉力交锁髓内钉与股骨近端防旋髓内钉、亚洲型股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗老年转子间骨折的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| [9] | 吕泽祥, 吴居泰, 蒋 健, 冯 骁, 李腾飞, 王业华. 氨甲环酸联合卡络磺钠干预全膝关节置换的失血及安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 386-390. |
| [10] | 张德刚, 刘 栋, 李 朋, 王兆林, 张 锴, 张新军. 弹性髓内钉与钢板置入治疗移位锁骨中段B型骨折的短期随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3860-3864. |
| [11] | 白胜超, 高 扬, 王 博, 李俊平, 王瑞元. 针刺干预大负荷运动损伤模型大鼠骨骼肌线粒体功能的动态变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(23): 3648-3653. |
| [12] | 张振华, 刘姿辰, 禹宝庆. 聚己内酯及其复合材料在组织工程骨构建中的地位与问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3571-3577. |
| [13] | 闻志靖, 顾鹏真, 贺西京, 李家良, 王一斌, 王逸群. 高分子聚合物聚醚酮酮的发展及其医学应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3603-3608. |
| [14] | 吴世桐, 宁仁德, 方 闰, 毕程浩. 桡骨远端骨折尺背侧骨折块不同固定方法的疗效比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(21): 3343-3348. |
| [15] | 黄辰宇, 唐 成, 魏 波, 李佳怡, 李旭祥, 张惠康, 徐 燕, 姚庆强, 王黎明. 3D打印手术导板在膝关节内外翻畸形患者全膝关节置换中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(18): 2789-2793. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
Design
Statistical analysis
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
.jpg)
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||