中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (32): 5140-5145.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.32.010
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
腰突颗粒调节腰椎间盘退变模型兔Fas/FasL基因的表达
何升华1,赖居易2,王业广1,孙志涛1,王 建1,冯华龙2,黄飞强2
- (1深圳市中医院,广东省深圳市 518000;2广州中医药大学深圳临床医学院,广东省深圳市 518000)
Yaotu Granules regulate the Fas/FasL expression in a rabbit model of lumbar disc degeneration
He Sheng-hua1, Lai Ju-yi2, Wang Ye-guang1, Sun Zhi-tao1, Wang Jian1, Feng Hua-long2, Huang Fei-qiang2
- (1Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Shenzhen Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
Fas基因:属于细胞凋亡基因,Fas基因的产物Fas蛋白是一种细胞凋亡受体,其与抗Fas单克隆抗体或Fas配体结合后可以传导细胞凋亡信号诱导细胞凋亡。
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。
文题释义:
Fas基因:属于细胞凋亡基因,Fas基因的产物Fas蛋白是一种细胞凋亡受体,其与抗Fas单克隆抗体或Fas配体结合后可以传导细胞凋亡信号诱导细胞凋亡。
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。
.jpg) 文题释义:
Fas基因:属于细胞凋亡基因,Fas基因的产物Fas蛋白是一种细胞凋亡受体,其与抗Fas单克隆抗体或Fas配体结合后可以传导细胞凋亡信号诱导细胞凋亡。
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。
文题释义:
Fas基因:属于细胞凋亡基因,Fas基因的产物Fas蛋白是一种细胞凋亡受体,其与抗Fas单克隆抗体或Fas配体结合后可以传导细胞凋亡信号诱导细胞凋亡。
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。摘要
背景:前期研究发现,腰突颗粒可以通过延缓人髓核细胞的退变,起到保护人髓核细胞的作用。临床发现,其治疗腰椎间盘突出疗效满意。
目的:探讨经验方腰突颗粒对兔腰椎间盘退变模型Fas/FasL基因表达的影响,进一步阐明腰突颗粒防治腰椎间盘退变的作用机制。
方法:将20只新西兰大白兔采用微创针刺旋切法制备兔腰椎间盘退变模型成功后,随机分为生理盐水组、低剂量组、中剂量组、高剂量组(n=5)。生理盐水组予以10 mL生理盐水灌胃,低剂量组、中剂量组、高剂量组分别予以腰突颗粒水煎剂10,20,40 mL灌胃,灌胃次数为2次/d,持续灌胃21 d。所有新西兰大白兔在相同条件下饲养,灌胃干预完成后,对各组大白兔腰椎髓核中的Fas/FasL基因表达水平进行检测。
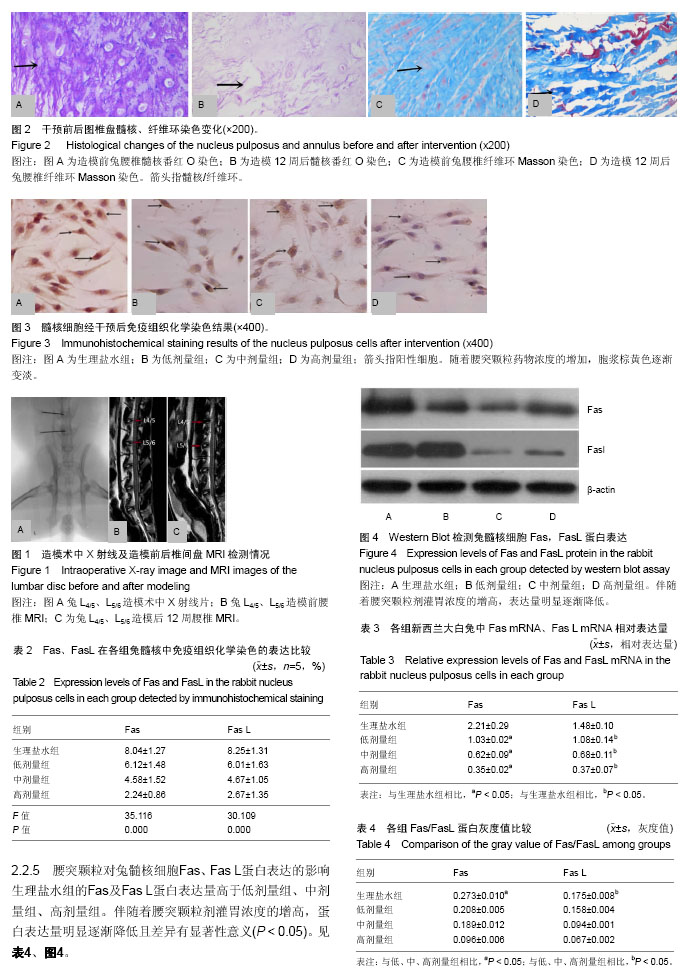
结果与结论:①新西兰大白兔经微创针刺旋切法造模12周后行MRI检查证实椎间盘信号强度减弱,并见纤维环断裂,椎间盘向后突;②Masson染色可见纤维环细胞排列紊乱,甚至断裂,番红O染色见髓核细胞明显减少;③与生理盐水组相比,低剂量组、中剂量组、高剂量组椎间盘组织的Fas mRNA、Fasl mRNA表达均降低,且随着灌服腰突颗粒剂量的增加,Fas mRNA、Fasl mRNA相对表达量逐渐降低(P < 0.05);④结果说明,腰突颗粒可降低兔腰椎兔腰椎间盘退变模型中髓核Fas/FasL基因表达,进而延缓兔腰椎间盘退变。
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
Fas基因:属于细胞凋亡基因,Fas基因的产物Fas蛋白是一种细胞凋亡受体,其与抗Fas单克隆抗体或Fas配体结合后可以传导细胞凋亡信号诱导细胞凋亡。
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。
文题释义:
Fas基因:属于细胞凋亡基因,Fas基因的产物Fas蛋白是一种细胞凋亡受体,其与抗Fas单克隆抗体或Fas配体结合后可以传导细胞凋亡信号诱导细胞凋亡。
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。