| [1] Consensus development conference: prophylaxis and treatment of osteoporosis.Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA.1991;1(2):114-117.[2] Watts NB,GLOW investigators. Insights from the Global Longitudinal Study of Osteoporosis in Women( GLOW).Nat Rev Endocrinol.2014;10(7):412-422.[3] Budhia S,Mikyas Y,Tang M,et al.Osteoporotic fractures: asystematic review of U.S.healthcare costs and resourceutilization.Pharmacoeconomics.2012;30(2):147-170.[4] 中国健康促进基金会骨质疏松防治中国白皮书编委会.骨质疏松症中国白皮书[J].中国健康管理学杂志,2009,3(3):148-154.[5] 朱卫红,宋阳.机关工作人员骨密度调查分析[J].体育科技文献通报,2016,24(5):86-87. [6] Valimaki MJ, Karkkainen M,Lamberg -Allardt C,et al.Exercise,smoking and calcium intake during adolescence and earlyadulthood as determinants of peak bone mass.BMJ. 1994;309(23):230-235.[7] Welten DC,Kemper HC,Post GB,et al.Weight -bearing activity during youth is a more important factor for peak bone mass than calcium intake.J Bone Miner Res.1994;9(7):1089 -1096.[8] Nickols-richardson SM,Modlesky CM,O' Connor PJ, et al. Premenarcheal gymnasts possess higher bone mineral density than controls.Med Sci Sports Exerc.2000;32(1):63-69.[9] Blimkie CJ,Rice S,Webber CE,et al.Effects of resistance training on BMC and density in adolescent females.J PhysiolPharmacol.1996;74(19):1025-1033.[10] Morris FL,Naughton GA,Gibbs JL, et al.Prospective 10-month exercise intervention in premenarcheal girls:positive effects on bone and lean mass.J Bone Miner Res.1997;12(9):1453 -1462.[11] 张军,陆大江.有氧运动结合抗阻力量训练对中年女性身体成分和骨密度的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2016,36(18): 4553-4556.[12] 邱惠晶,杨阳,周丽云,等.福建省老年人骨密度与体质现状研究[J].福建体育科技,2017,36(3):7-8.[13] 黄中华.弹力带抗阻健身操和广场舞对绝经后女性骨密度影响的实验研究[J].浙江体育科学,2016,38(5): 92-96.[14] 林若崴,林立.大学生跟骨骨密度与跑步能力关系的研究-以北京体育大学非体育专业大学生为例[J].闽江学院学报, 2017,2: 90-97.[15] 李世昌.运动解剖学[M].3版北京:高等教育出版社, 2015:72, 110,119.[16] 谭克理.不同专项运动训练对男大学生运动员骨密度的影响[J].西安体育学院学报,2011,28(6):721-724.[17] 李在军,邹晓丽.羽毛球运动对女大学生骨密度的影响[J].当代体育科技,2012,2(34):12-14. [18] 赵立君,李凤丽,陈琼,等.篮球专业和非篮球专业男性大学生身体不同部位骨密度对比分析[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2007,33(6): 1077-1079. [19] 席磊.健身操和瑜伽交替练习对女大学生体成分、骨密度及心肺功能等的影响研究[D].曲阜:曲阜师范大学,2011.[20] 张丽,王美月.武术套路运动对女大学生骨密度和基本体质指标的影响[J].体育科技文献通报,2008,16(12):91-92. [21] 杨洪涛.核心力量训练对大学生骨密度及躯干屈伸肌力量影响的实证研究[J].体育世界(学术),2015(3):71-74. [22] 赵晓虎.黑龙江省不同运动训练水平大学生身体成分和骨密度的比较研究[J].哈尔滨体育学院学报,2013,31(5):93-96.[23] Bellew JW,Gehrig L.A comparison of bone mineral density in adolescent female swimmer,soccer players,and weight lifters.Pediatric Physical Therapy.2006;18(1):19-22.[24] Mudd L M,Fornetti W,Pivarnik J M.Bone mineral density in collegiate female athletes: comparisons among spores.J Athl Train.2007;42(3):403-448.[25] 郭见平,尹海滨,牛英群.体育与非体育专业大学生骨密度和体成分比较[J].中国学校卫生,2012,33(11):1338-1340.[26] 张国海.运动对大学生骨密度和体成分的影响及相互关系的研究[J].中国体育科技,2008,44(5):56-61. [27] 李勇,张凯.投掷项目运动损伤的预防[J].湖北体育科技,2016, 35(12):1050-1053.[28] 陈兵.再析投掷项目最后用力的发力顺序[J].韶关学院学报:自然科学,2010,31(6):105-108. [29] 陈洁敏.不同投掷项目最后用力阶段右腿技术特征的比较分析[J].北京体育大学学报,2005,28(5):703-705.[30] 曲绵域.高水平与动员训练中的运动创伤适应[J].中国运动医学杂志,2000,19(1):84-85.[31] 任玉衡,田得详,史和福,等.优秀运动员的运动受伤流行病学调查[J].中国运动医学杂志,2000,19(4):377-386.[32] 杨淑萍.田径投掷项目最后用力技术分析[J].青海师范大学学报:自然科学版,2005(3): 99-100.[33] 叶永延,郑亦华.起跳时摆动动作的生物力学分析[J].体育与科学:学术版,1995,18(2):31-36.[34] 袁春华,陈佩杰,陈敏雄.男性青少年骨密度与下肢跳跃能力的关系及运动训练对其影响[J].体育学利,2004,11(6):39-42. [35] 房东梅.不同模式的跑台运动对生长期大鼠长骨骨矿含量和力学特性的影响[J].体育科学,2009,29(6):73-76. [36] 袁春华,陈佩杰.男性青少年骨密度与身体形态学指标的关系及运动训练对其影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2003,22(5):499-502. [37] 刘保华.纵跳对悬吊大鼠骨密度、生物力学指标及股骨表达的影响[D].上海:华东师范大学,2010.[38] 黄何平,王国祥,张林.纵跳和闭目单足站立对跟骨骨密度的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(41):8324-8326.[39] Boudignon BM,Bikle DD,Kurimoto P,et al.Insulin like growth factor I stimulates recovery of bone lost after a period of skeletal unloading.J Appl Physiol.2007;103(1):125-131.[40] Giangregoria L,Blimkie CJR.Skeletal adaptations to alteratrons in weight bearing activity a comparison of models of disuse osteoporosis.Sports Med.2002;32(7):459-476.[41] 刘海山,马莉.篮球运动员不同类型损伤的性别差异研究[J].河南教育学院学报:自然科学版,2017,26(2):81-84.[42] Attenborough AS, Hiller CE, Smith RM, et al.Chronic ankle instability in sporting populations.Sports Med.2014;44(11) : 1545-1556.[43] 王成,李勇杰,史儒林.藏族、汉族大学生体质状况的比较研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2008,31(7): 946-953.[44] 兰宝森,尹小俭,李世昌,等.藏汉大学生生活习惯和体质健康的比较分析[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报,2010,29(4) : 85-89.[45] 张世威,郝文亭,张雅玲.我国藏族与塔吉克族学生身体素质比较研究[J].中国体育科技,2012,48(5) : 92-99.[46] 高升.1985—2010 年藏族学生体质变化趋势的性别差异分析[J].吉林体育学院学报,2017,33(3):53-56.[47] 程华.专业和性别差异在体育大学生人格特质中的影响[J].岭南师范学院学报,2016,37(6):123-130.[48] 杜子明,梁姗,黄颂民.青春期体质指数及腰臀比的性别差异[J].广东微量元素科学,2017,24(1):64-68.[49] 马生霞,马福海,陆一帆,等.世居高、平原运动员血液流变性的性别差异及与运动能力的关系[J].体育科研,2012,33(3):74-77.[50] 梁芝栋.大学生篮球运动员和普系学生的指长比均值比较[J].体育学刊, 2017,24(2):135-139.[51] 陈金鳌,相建华,陈琉.年龄和性别因素对力量训练后肌肉量变化的影响[J].体育科学,2011,31(9):57-62,84. [52] 郝思哲,邵华.大学生速度滑冰课性别及心理素质差异分析与研究[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2007,28(1):85-86. [53] 徐勇,时孝荣.学生运动参与、运动享受及自我知觉的性别差异[J].杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版,2015,14(3):333-336.[54] 宋新民,袁平,刘琳.不同性别年龄钙骨密度测定分析[J].微量元素与健康研究,2000,17(4):22-23.[55] 陈金标,秦林林,马海波,等.桡骨超远端体积骨密度的测量及性别间的比较[J].中日友好医院学报,2000,14(3):125-128.[56] 谢志丹.体育舞蹈运动对女大学生骨密度和身体成分的影响[D].西安:西安体育学院,2013.[57] 汪六六,沈彤,游丽琴,等.成人骨密度随年龄变化趋势分析[J].中国公共卫生,2001,17(2):157.[58] 张京鲁,盖凌,刘淑敏,等.女子足球运动员与无运动训练女大学生腰椎、股骨颈骨密度比较[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(2): 167-169.[59] 黄陈恕,吴景全,朱艳琳.重庆地区中老年男性骨质疏松症患者骨密度与年龄、身高、体质量、体质量指数关系研究[J].四川医学,2016,37(7):717-720. [60] Watts NB,GLOW investigators. Insights from the Global Longitudinal Study of Osteoporosis in Women( GLOW).Nat Rev Endocrinol.2014;10(7):412-22.[61] 叶美婷,黄抒佳,王保兵,等.骨密度测量部位选择分析[J].中国辐射卫生,2012,21(1):90-91. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨密度:全称是骨骼矿物质密度,是骨强度和骨质量的一个重要指标,也是反映骨质疏松程度、预测骨折危险性的重要依据。在国际单位制中以g/cm2表示,是一个绝对值。在临床使用骨密度值时由于不同的骨密度检测仪的绝对值不同,通常使用T值判断骨密度是否正常。T值是一个相对值,正常参考值在-1和+1之间,当T值低于-2.5时为不正常。
峰值骨量:是指一个个体在正常状态下发育成熟后达到的最高骨量。一个根本的思路就是在骨骼的生长发育期尽可能使骨量增加,使之达到一个较高的峰值,即峰值骨量。 它与先天的遗传因素、后天的合理营养、户外活动以及适度的身体锻炼息息相关。
田径运动员:田径是田赛、径赛和全能比赛的统称。以高度和距离长度计算成绩的跳跃、投掷类项目叫“田赛”;以时间计算成绩的竞走和跑的项目叫“径赛”。由部分田赛和径赛项目组成的项目叫“十项全能”。在中国,根据从事田径运动的人的运动成绩国家会颁发运动员等级证书,总共为六个等级,分别为国际级运动健将、运动健将、一级运动员、二级运动员、三级运动员和少年级运动员。在本研究中,大学生田径运动员指是具有田径二级运动员及以上运动等级证书的在校大学生。
文题释义:
骨密度:全称是骨骼矿物质密度,是骨强度和骨质量的一个重要指标,也是反映骨质疏松程度、预测骨折危险性的重要依据。在国际单位制中以g/cm2表示,是一个绝对值。在临床使用骨密度值时由于不同的骨密度检测仪的绝对值不同,通常使用T值判断骨密度是否正常。T值是一个相对值,正常参考值在-1和+1之间,当T值低于-2.5时为不正常。
峰值骨量:是指一个个体在正常状态下发育成熟后达到的最高骨量。一个根本的思路就是在骨骼的生长发育期尽可能使骨量增加,使之达到一个较高的峰值,即峰值骨量。 它与先天的遗传因素、后天的合理营养、户外活动以及适度的身体锻炼息息相关。
田径运动员:田径是田赛、径赛和全能比赛的统称。以高度和距离长度计算成绩的跳跃、投掷类项目叫“田赛”;以时间计算成绩的竞走和跑的项目叫“径赛”。由部分田赛和径赛项目组成的项目叫“十项全能”。在中国,根据从事田径运动的人的运动成绩国家会颁发运动员等级证书,总共为六个等级,分别为国际级运动健将、运动健将、一级运动员、二级运动员、三级运动员和少年级运动员。在本研究中,大学生田径运动员指是具有田径二级运动员及以上运动等级证书的在校大学生。.jpg) 文题释义:
骨密度:全称是骨骼矿物质密度,是骨强度和骨质量的一个重要指标,也是反映骨质疏松程度、预测骨折危险性的重要依据。在国际单位制中以g/cm2表示,是一个绝对值。在临床使用骨密度值时由于不同的骨密度检测仪的绝对值不同,通常使用T值判断骨密度是否正常。T值是一个相对值,正常参考值在-1和+1之间,当T值低于-2.5时为不正常。
峰值骨量:是指一个个体在正常状态下发育成熟后达到的最高骨量。一个根本的思路就是在骨骼的生长发育期尽可能使骨量增加,使之达到一个较高的峰值,即峰值骨量。 它与先天的遗传因素、后天的合理营养、户外活动以及适度的身体锻炼息息相关。
田径运动员:田径是田赛、径赛和全能比赛的统称。以高度和距离长度计算成绩的跳跃、投掷类项目叫“田赛”;以时间计算成绩的竞走和跑的项目叫“径赛”。由部分田赛和径赛项目组成的项目叫“十项全能”。在中国,根据从事田径运动的人的运动成绩国家会颁发运动员等级证书,总共为六个等级,分别为国际级运动健将、运动健将、一级运动员、二级运动员、三级运动员和少年级运动员。在本研究中,大学生田径运动员指是具有田径二级运动员及以上运动等级证书的在校大学生。
文题释义:
骨密度:全称是骨骼矿物质密度,是骨强度和骨质量的一个重要指标,也是反映骨质疏松程度、预测骨折危险性的重要依据。在国际单位制中以g/cm2表示,是一个绝对值。在临床使用骨密度值时由于不同的骨密度检测仪的绝对值不同,通常使用T值判断骨密度是否正常。T值是一个相对值,正常参考值在-1和+1之间,当T值低于-2.5时为不正常。
峰值骨量:是指一个个体在正常状态下发育成熟后达到的最高骨量。一个根本的思路就是在骨骼的生长发育期尽可能使骨量增加,使之达到一个较高的峰值,即峰值骨量。 它与先天的遗传因素、后天的合理营养、户外活动以及适度的身体锻炼息息相关。
田径运动员:田径是田赛、径赛和全能比赛的统称。以高度和距离长度计算成绩的跳跃、投掷类项目叫“田赛”;以时间计算成绩的竞走和跑的项目叫“径赛”。由部分田赛和径赛项目组成的项目叫“十项全能”。在中国,根据从事田径运动的人的运动成绩国家会颁发运动员等级证书,总共为六个等级,分别为国际级运动健将、运动健将、一级运动员、二级运动员、三级运动员和少年级运动员。在本研究中,大学生田径运动员指是具有田径二级运动员及以上运动等级证书的在校大学生。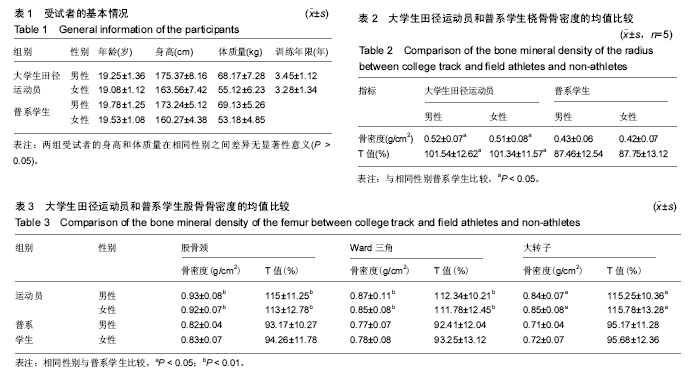
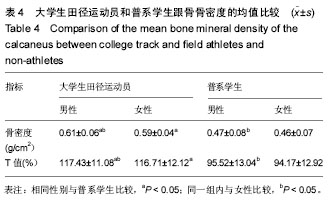
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨密度:全称是骨骼矿物质密度,是骨强度和骨质量的一个重要指标,也是反映骨质疏松程度、预测骨折危险性的重要依据。在国际单位制中以g/cm2表示,是一个绝对值。在临床使用骨密度值时由于不同的骨密度检测仪的绝对值不同,通常使用T值判断骨密度是否正常。T值是一个相对值,正常参考值在-1和+1之间,当T值低于-2.5时为不正常。
峰值骨量:是指一个个体在正常状态下发育成熟后达到的最高骨量。一个根本的思路就是在骨骼的生长发育期尽可能使骨量增加,使之达到一个较高的峰值,即峰值骨量。 它与先天的遗传因素、后天的合理营养、户外活动以及适度的身体锻炼息息相关。
田径运动员:田径是田赛、径赛和全能比赛的统称。以高度和距离长度计算成绩的跳跃、投掷类项目叫“田赛”;以时间计算成绩的竞走和跑的项目叫“径赛”。由部分田赛和径赛项目组成的项目叫“十项全能”。在中国,根据从事田径运动的人的运动成绩国家会颁发运动员等级证书,总共为六个等级,分别为国际级运动健将、运动健将、一级运动员、二级运动员、三级运动员和少年级运动员。在本研究中,大学生田径运动员指是具有田径二级运动员及以上运动等级证书的在校大学生。
文题释义:
骨密度:全称是骨骼矿物质密度,是骨强度和骨质量的一个重要指标,也是反映骨质疏松程度、预测骨折危险性的重要依据。在国际单位制中以g/cm2表示,是一个绝对值。在临床使用骨密度值时由于不同的骨密度检测仪的绝对值不同,通常使用T值判断骨密度是否正常。T值是一个相对值,正常参考值在-1和+1之间,当T值低于-2.5时为不正常。
峰值骨量:是指一个个体在正常状态下发育成熟后达到的最高骨量。一个根本的思路就是在骨骼的生长发育期尽可能使骨量增加,使之达到一个较高的峰值,即峰值骨量。 它与先天的遗传因素、后天的合理营养、户外活动以及适度的身体锻炼息息相关。
田径运动员:田径是田赛、径赛和全能比赛的统称。以高度和距离长度计算成绩的跳跃、投掷类项目叫“田赛”;以时间计算成绩的竞走和跑的项目叫“径赛”。由部分田赛和径赛项目组成的项目叫“十项全能”。在中国,根据从事田径运动的人的运动成绩国家会颁发运动员等级证书,总共为六个等级,分别为国际级运动健将、运动健将、一级运动员、二级运动员、三级运动员和少年级运动员。在本研究中,大学生田径运动员指是具有田径二级运动员及以上运动等级证书的在校大学生。