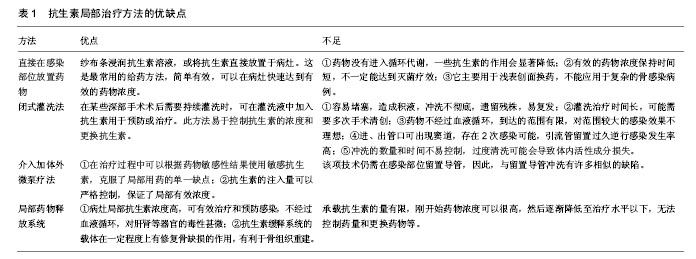
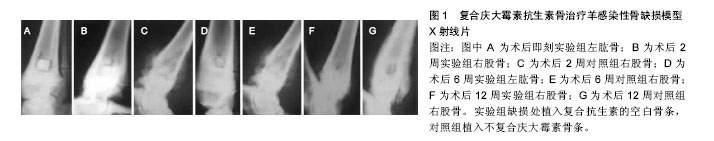
| [1] 任高宏.临床骨科诊断与治疗[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2015.[2] Beris AE, Lykissas MG, Korompilias AV, et al. Vascularized fibula transfer for lower limb reconstruction. Microsurgery. 2011;31(3): 205-211.[3] 黄雷,李兵,刘沂,等. 开放植骨治疗感染性骨折不愈合[J].中华骨科杂志, 2005, 25(1):30-34.[4] Stewart PS, Costerton JW. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet. 2001;358(9276):135-138.[5] 李军,毕龙,薛宝宝,等.下肢大段感染性骨缺损的治疗[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(23):4477-4480.[6] 任高宏,蒋桂勇,王钢,等.静脉移植桥接血管蒂的游离腓骨瓣移植治疗长骨感染性骨缺损[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(8):833-841.[7] 杨建平,王黎明,徐燕,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗早期股骨头坏死的实验研究[J].医学研究生学报,2008,21(12):1263-1266.[8] Bakhshalian N, Jalayer T, Shahoon H, et al. Osteopromotive property of allogenic demineralized dentin matrix: a pilot study. J West Soc Periodontol Periodontal Abstr. 2013;61(2):35-38.[9] Roberts TT, Rosenbaum AJ. Bone grafts, bone substitutes and orthobiologics: the bridge between basic science and clinical advancements in fracture healing. Organogenesis. 2012;8(4): 114-124.[10] Won YH, Kim SG, Oh JS, et al. Clinical evaluation of demineralized bone allograft for sinus lifts in humans: a clinical and histologic study. Implant Dent. 2011;20(6):460-464.[11] Lima CE, Calixto JC, Anbinder AL. Influence of the association between simvastatin and demineralized bovine bone matrix on bone repair in rats. Braz Oral Res. 2011;25(1):42-48.[12] Zhang HY, Luo JB, Zhou M,et al. Biotribological properties at the stem-cement interface lubricated with different media. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013;20:209-216.[13] Zhang H. Investigation of protein adsorption mechanism and biotribological properties at simulated stem–cement interface. J Tribology. 2013; 135(3):928-931.[14] Ketonis C, Barr S, Shapiro IM, et al. Antibacterial activity of bone allografts: comparison of a new vancomycin-tethered allograft with allograft loaded with adsorbed vancomycin. Bone. 2011; 48(3):631-638.[15] 任高宏,蒋桂勇,王钢,等. 静脉移植桥接血管蒂的游离腓骨瓣移植治疗长骨感染性骨缺损[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(8):833-841.[16] 丛海波,王晓科,丁英杰,等. 组织瓣移植结合骨搬运修复重建小腿大范围复合组织缺损[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014, 16(6):461-464.[17] 汪银锋,阮洪江,范存义,等.慢性创伤后骨髓炎诊治进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2008,29(2):100-101.[18] 鲁玉来.全面看待慢性骨髓炎的治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008, 16(11):872-874.[19] 任一,胡建山,唐广应,等.CCD联合VSD治疗远期复发性骨髓炎的分析[J].国外医药:抗生素分册,2013,34(5):208-211.[20] 付志明.慢性骨髓炎的介入治疗[J].中国医药导报,2008,5(24): 242-243.[21] 王燕萍,陈娅,武新安,等. 慢性骨髓炎的病原学特点及抗菌药物治疗进展[J].中国药房,2015,26(20):2867-2870.[22] 樊晓海,刘兴炎,甄平.介入治疗在慢性骨髓炎治疗中作用的实验研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志, 2001,16(2):111-114.[23] 郑磊,王前,裴国献.骨组织工程中细胞外基质材料的选择[J].中华外科杂志,2000, 38(10):745-748.[24] 薛德挺. 间充质干细胞复合多孔支架修复骨与软骨缺损的实验性研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2015.[25] 任广铁. 组织工程骨膜修复兔桡骨大段骨缺损的早期观察及BMP-2对组织工程骨膜体外成骨能力的影响[D]. 兰州:兰州大学,2014.[26] 陈伟良,藕小平,王建广,等.人颌骨骨膜成骨细胞复合异体部分脱钙骨的成骨实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2004,14(2):112-114.[27] 邢自宝,刘永刚,苏佳灿,等.骨组织工程种子细胞研究进展[J].临床医学工程,2010,17(10):152-154.[28] 朱付平,熊光仲,王万春,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞在骨科中应用的研究进展[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2005,13(5):78-81.[29] Wang T, Yang X, Qi X, et al. Osteoinduction and proliferation of bone-marrow stromal cells in three-dimensional poly (ε-caprolactone)/ hydroxyapatite/collagen scaffolds. J Transl Med. 2015;13:152.[30] Perut F, Filardo G, Mariani E, et al. Preparation method and growth factor content of platelet concentrate influence the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(7):830-839.[31] Subbiah R, Hwang MP, Van SY, et al. Osteogenic/angiogenic dual growth factor delivery microcapsules for regeneration of vascularized bone tissue. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(13): 1982-1992. [32] 王磊,黄远亮.BMP/FGF对骨髓基质细胞生长作用的研究进展[J].医学综述,2008,14(8):1140-1142.[33] 宋会平,李琪佳,李宝兴,等. 组织工程骨促进大鼠骨缺损修复的实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009,23(10):1250-1253.[34] 温叶飞,胡帼颖,张志雄,等. 组织工程技术系列专题(二)——种子细胞与组织工程的研究[J]. 透析与人工器官, 2009, 20(2):16-33.[35] 朱丹华, 舒晓春. 骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的潜能和影响因素[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2009, 25(15):2596-2598.[36] Ng F, Boucher S, Koh S, et al. PDGF, TGF-beta, and FGF signaling is important for differentiation and growth of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): transcriptional profiling can identify markers and signaling pathways important in differentiation of MSCs into adipogenic, chondrogenic, and osteogenic lineages. Blood. 2008;112(2):295-307.[37] Reijnders CM, Bravenboer N, Tromp AM, et al. Effect of mechanical loading on insulin-like growth factor-I gene expression in rat tibia. J Endocrinol. 2007;192(1):131-140.[38] Tielens S, Declercq H, Gorski T, et al. Gelatin-based microcarriers as embryonic stem cell delivery system in bone tissue engineering: an in-vitro study. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8(3):825-832.[39] Han NR, Park YH, Yun JI, et al. Determination of feeder cell-based cellular niches supporting the colonization and maintenance of spermatogonial stem cells from prepubertal domestic cat testes.Reprod Domest Anim. 2014;49(5):705-710.[40] King NM, Perrin J. Ethical issues in stem cell research and therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(4):85.[41] Jiang XQ, Zhang ZY, Chang Q, et al. Effects of transient transfection of human BMP-4 gene on rabbit bone marrow stromal cells. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2003;25(1):13-16.[42] Gao X, Usas A, Lu A, et al. BMP2 is superior to BMP4 for promoting human muscle-derived stem cell-mediated bone regeneration in a critical-sized calvarial defect model. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(12):2393-2408.[43] Shen HC, Peng H, Usas A, et al. Ex vivo gene therapy-induced endochondral bone formation: comparison of muscle-derived stem cells and different subpopulations of primary muscle-derived cells. Bone. 2004;34(6):982-992.[44] Bar-On E, Weigl DM, Bor N, et al. Chronic osteomyelitis in children: treatment by intramedullary reaming and antibiotic-impregnated cement rods. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010; 30(5):508-513.[45] 范卫民,陈曦,李翔.抗生素骨水泥物理和力学性能及洗提特性的实验研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2003, 23(6):361-364.[46] Yan RJ, Zhang C, Guo QF, et al. One-stage compound grafting of antibiotic-impregnated calcium sulfate and autogenous cancellous bone for the treatment of chronic calcaneal osteomyelitis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(10):854-857.[47] 陈红卫,赵钢生,鲍丰,等.载药自固化磷酸钙人工骨治疗慢性骨髓炎[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2005, 20(10):673-675.[48] 颜翼,崔华,徐永清.抗生素载体及缓释系统治疗慢性骨髓炎的研究进展[J].西南国防医药, 2010, 20(2):211-212.[49] Hendriks JG, Neut D, van Horn JR, et al. Bacterial survival in the interfacial gap in gentamicin-loaded acrylic bone cements. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(2):272-276.[50] 李宝兴,张育敏,赵亚平,等.复合庆大霉素抗生素骨制备及其治疗感染性骨缺损的实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2006, 20(9):920-924.[51] 袁志,胡蕴玉,孙梁,等.抗感染重组合异种骨系列实验研究[J].中华医学杂志,2003, 83(2):128-132.[52] 高秋明,刘兴炎,董晓萍,等.纤维蛋白凝胶复合骨形态发生蛋白和庆大霉素缓释药物治疗感染性骨缺损的实验研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2003, 18(6):384-387.[53] Hanssen AD. Local antibiotic delivery vehicles in the treatment of musculoskeletal infection. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(437):91-96.[54] Ishimoto K, Arimoto M, Okuda T, et al. Biobased polymers: synthesis of graft copolymers and comb polymers using lactic acid macromonomer and properties of the product polymers. Biomacromolecules. 2012;13(11):3757-3768.[55] Ambrose CG, Clyburn TA, Louden K, et al. Effective treatment of osteomyelitis with biodegradable microspheres in a rabbit model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(421):293-299. |
.jpg)
.jpg)