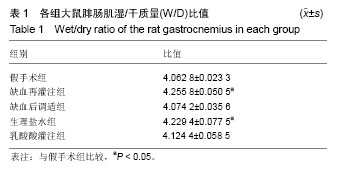
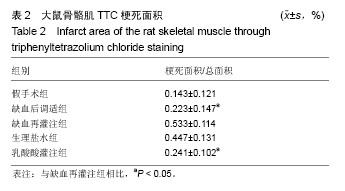
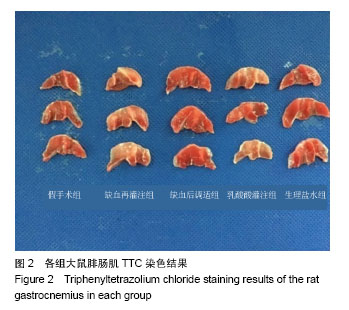
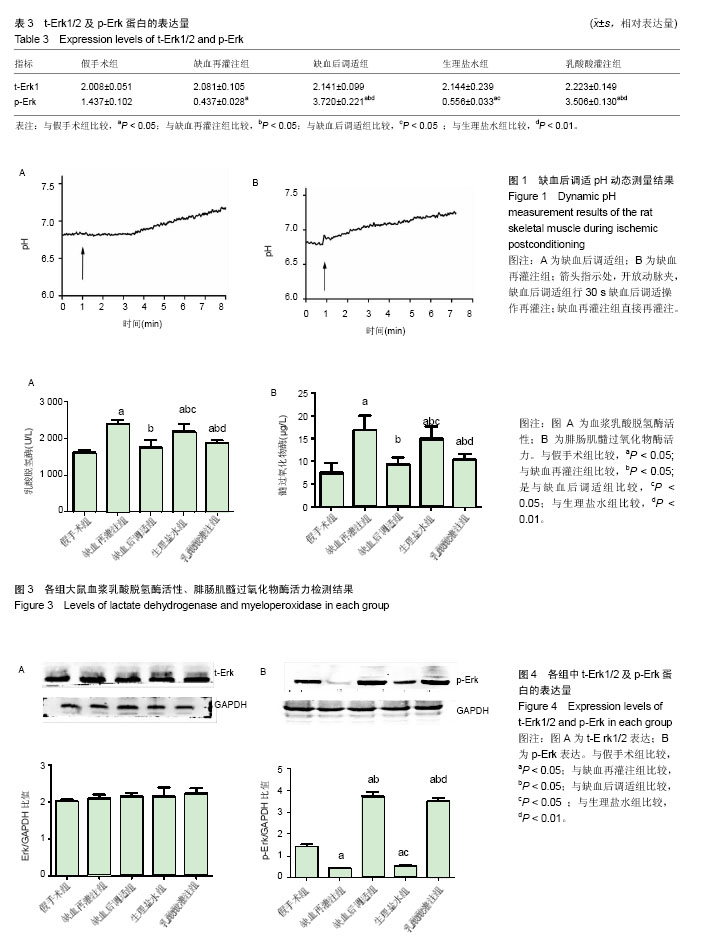
| [1] Jennings RB,Sommers HM,Smyth GA, et al. Myocardial necrosis induced by temporary occlusion of a coronary artery in the dog. Arch Pathol. 1960;70:68-78.[2] Orsini F,Chrysanthou E, Dudler T, et al. Mannan binding lectin-associated serine protease-2 (MASP-2) critically contributes to post-ischemic brain injury independent of MASP-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):213.[3] Ferchichi H, Bacha S, Kourda N, et al. Animal model of liver ischemia reperfusion: biochemical and histological evaluation.La Tunisie Me?dicale.2016;94(3):235.[4] Na KR,Choi H,Jeong JY, et al.Nafamostat Mesilate Attenuates Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Renal Injury. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(6):2192-2199.[5] Zu G,Yao J,Ji A,et al.Nurr1 promotes intestinal regeneration after ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting the expression of p21 (Waf1/Cip1). J Mol Med (Berl). 2017; 95(1):83-95.[6] Eckert P, Schnackerz K. Ischemic tolerance of human skeletal muscle. Ann Plast Surg. 1991;26(1):77-84.[7] Blaisdell FW.The pathophysiology of skeletal muscle ischemia and the reperfusion syndrome: a review. Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;10(6):620-630. [8] Appell HJ,Glöser S,Duarte JA,et al.Skeletal muscle damage during tourniquet-induced ischaemia. The initial step towards atrophy after orthopaedic surgery?. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1993;67(4):342-347.[9] Gillani S,Cao J,Suzuki T,et al.The effect of ischemia reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle. Injury.2012;43(6): 670-675.[10] Murry CE,Jennings RB,Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation.1986; 74(5):1124-1136.[11] Zaman J,Jeddi S,Daneshpour MS,et al.Ischemic postconditioning provides cardioprotective and antiapoptotic effects against ischemia-reperfusion injury through iNOS inhibition in hyperthyroid rats. Gene.2015; 570(2):185.[12] Cao QF,Qu MJ,Yang WQ,et al.Ischemia postconditioning preventing lung ischemia-reperfusion injury.Gene.2015; 554(1):120-124.[13] Hahn JY, Yu CW, Park HS, et al.Long-term effects of ischemic postconditioning on clinical outcomes: 1-year follow-up of the POST randomized trial. Am Heart J. 2015;169(5):639-646.[14] Duanmu WS,Cao L,Chen JY,et al.Ischemic postconditioning protects against ischemic brain injury by up-regulation of acid-sensing ion channel 2a. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(4): 641-645.[15] Zhao ZQ,Corvera JS,Halkos ME,et al. Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285(2):H579-88..[16] Park JW, Kang JW, Jeon WJ, et al. Postconditioning protects skeletal muscle from ischemia-reperfusion injury.Microsurgery.2010;30(3):223-229.[17] Cohen MV,Yang XM,Downey JM.The pH hypothesis of postconditioning: staccato reperfusion reintroduces oxygen and perpetuates myocardial acidosis. Circulation.2007; 115(14):1895.[18] 彭龙龙, 阳富春, 薄占东,等. 不同缺血后调适方案对大鼠模型肢体骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(5):739-744.[19] Jäger R, Roberts MD, Lowery RP, et al.Oral adenosine-5’-triphosphate (ATP) administration increases blood flow following exercise in animals and humans. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2014;11:28[20] Cohen MV,Yang XM,Downey JM.Acidosis, oxygen, and interference with mitochondrial permeability transition pore formation in the early minutes of reperfusion are critical to postconditioning's success. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008;103(5): 464-471.[21] Baines CP, Song CX, Zheng YT,et al.Protein Kinase Cε Interacts With and Inhibits the Permeability Transition Pore in Cardiac Mitochondria. Circ Res. 2003;92(8):873-880.[22] Juel C.Skeletal muscle Na+/H+ exchange in rats: pH dependency and the effect of training. Acta Physiol Scand. 1998;164(2):135-140.[23] Murphy RM,Dutka TL,Horvath D,et al.Ca2+-dependent proteolysis of junctophilin-1 and junctophilin-2 in skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 2013;591(3):719-729.[24] Lejay A,Meyer A,Schlagowski AI,et al.Mitochondria: mitochondrial participation in ischemia-reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;50:101-105.[25] Inserte J,Barba I,Hernando V,et al. Effect of acidic reperfusion on prolongation of intracellular acidosis and myocardial salvage. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;77(4):782-790. [26] Schulman D,Latchman DS,Yellon DM. Urocortin protects the heart from reperfusion injury via upregulation of p42/p44 MAPK signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;283(4):H1481-488.[27] Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Reperfusion injury salvage kinase signalling: taking a RISK for cardioprotection. Heart Failure Reviews.2007;12(3):217-234.[28] Yang XM, Proctor JB, Cui L,et al.Multiple, brief coronary occlusions during early reperfusion protect rabbit hearts by targeting cell signaling pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004; 44(5):1103-1110.[29] Hausenloy DJ,Yellon DM.New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: targeting the Reperfusion Injury Salvage Kinase (RISK)-pathway. Cardiovasc Res.2004;61(3):448-460.[30] Chiu WC,Chiou TJ,Chung MJ,et al.β2-Glycoprotein I Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Induced Angiogenesis by Suppressing the Phosphorylation of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2, Akt, and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase. PLoS One.2016 ;11(8):e0161950. [31] Wang L,Shan Y,Chen L,et al.Colchicine protects rat skeletal muscle from ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation. Iran J Basic Med Sci.2016; 19(6):670-675. |
.jpg)
.jpg)