| [1] Loeser RF. Aging and osteoarthritis: the role of chondrocyte senescenceand aging changes in the cartilage matrix. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2009;17:971-979.[2] Hosseinzadeh A, Kamrava SK, Joghataei MT, et al. Apoptosis signaling pathways in osteoarthritis and possible protective role of melatonin. J Pineal Res.2016;61(4):411-425.[3] Schroder M, Kaufman RJ. ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Mutation Res 2005;569:29-63.[4] Dandekar A, Mendez R, Zhang K. Cross talk between ER stress, oxidative stress, and inflammation in health and disease. Methods Mol Biol.2015;1292:205-214.[5] Wickner W, Schekman R. Protein translocation across biological membranes. Science.2005; 310:1452-1456.[6] Patterson SE, Dealy CN. Mechanisms and models of endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrodysplasia. Dev Dyn.2014;243(7):875-893.[7] Yamabe S, Hirose J, Uehara Y, et al. Intracellular accumulation of advanced glycation end products induces apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrocytes. FEBS J. 2013;280(7):1617-1629.[8] Adams CS, Horton WE. Chondrocyte apoptosis increases with age in the articular cartilage of adult animals. Anat Rec.1998;250:418-425.[9] Lee K, Tirasophon W, Shen X, et al. IRE1- mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2Pmediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes Dev.2002;16:452-466.[10] Scheper W, Nijholt DA, Hoozemans JJ. The unfolded protein response and proteostasis in Alzheimer disease: Preferential activation of autophagy by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Autophagy. 2011;7(8):910-911. [11] Nugent AE,Speicher DM,Gradisar I,et al. Advanced osteoarthritis in humans is associated with altered collagen VI expression and upregulation of ER-stress markers Grp78 and bag-1. J Histochem Cytochem. 2009;57:923-931.[12] Takada K, Hirose J, Senba K,et al. Enhanced apoptotic and reduced protective response in chondrocytes following endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritic cartilage. Int J Exp Pathol. 2011; 92:232-242.[13] Guo FJ, Xiong Z, Lu X, et al. ATF6 upregulates XBP1S and inhibits ER stress-mediated apoptosis in osteoarthritis cartilage. Cell Signal.2014;26: 332-342.[14] Oikawa D, Kimata Y, Kohno K. Self-association and BiP dissociation are not sufficient for activation of the ER stress sensor Ire1. J Cell Sci.2007;120:1681-1688;[15] Shin YJ, Han SH, Kim DS, et al. Autophagy induction and CHOP under-expression promotes survival of fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients under endoplasmic reticulum stress. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(1):R19.[16] Ceylan-Isik AF, Sreejayan N, Ren J. Endoplasmic reticulum chaperon tauroursodeoxycholic acid alleviates obesity-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction.J Mol Cell Cardiol.2011;50(1):107-116.[17] Woo SJ, Kim JH, Yu HG. Ursodeoxycholic acid and tauroursodeoxycholic acid suppress choroidal neovascularization in a laser-treated rat model. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2010;26(3):223-229.[18] Rivard AL, Steer CJ, Kren BT, Administration of tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) reduces apoptosis following myocardial infarction in rat. Am J Chin Med. 2007, 35(2):279-295.[19] Malo A, Krüger B, Seyhun E. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress, trypsin activation, and acinar cell apoptosis while increasing secretion in rat pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;299(4):877-886.[20] Liu C, Cao Y, Yang X, et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress in the chondrocytes of patients with osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Med.2015;36(4): 1081-1087. |
.jpg)
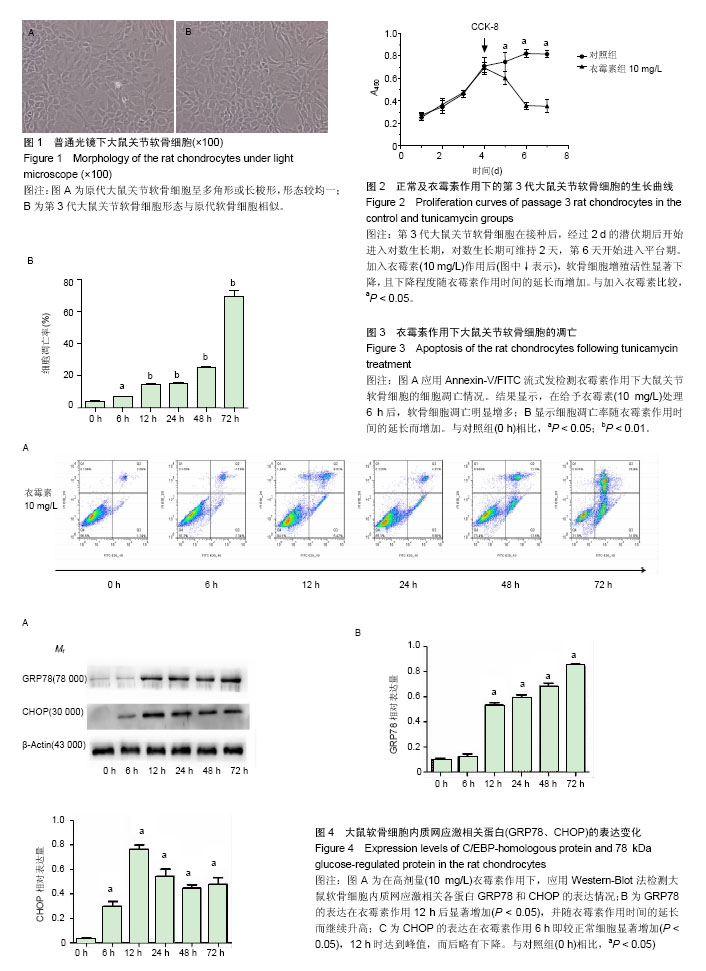
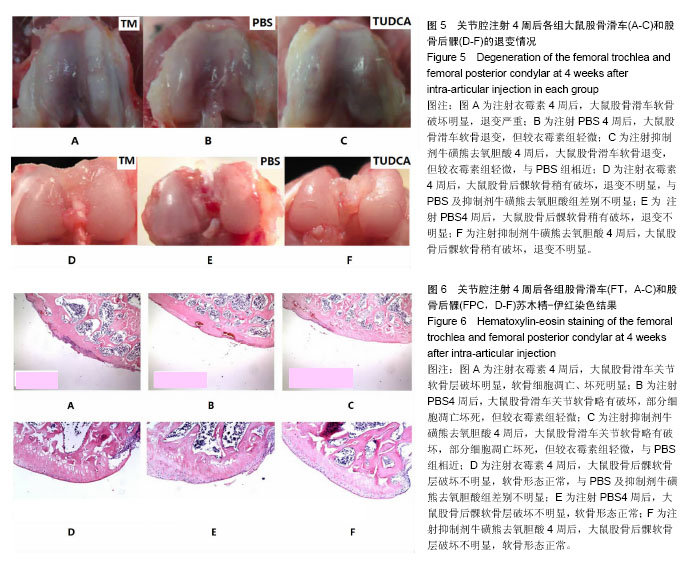
.jpg)