| [1]Shea TM, Doulgeris JJ, Gonzalez-Blohm SA, et al. Balancing rigidity and safety of pedicle screw fixation via a novel expansion mechanism in a severely osteoporotic model. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:318405.[2]Liu D, Zhang Y, Zhang B, et al. Comparison of expansive pedicle screw and polymethylmethacrylate-augmented pedicle screw in osteoporotic sheep lumbar vertebrae: biomechanical and interfacial evaluations. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74827.[3]Liu D, Zhang Y, Lei W, et al. Comparison of 2 kinds of pedicle screws in primary spinal instrumentation: biomechanical and interfacial evaluations in sheep vertebrae in vitro. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(2):E72-80.[4]Idowu OE, Adewole OA, Majekodunmi AA. Posterior spinal decompression, stabilization and arthrodesis in Nigerian adults: Profile and outcome. Niger Med J. 2012;53(1):42-46. [5]Tai CL, Tsai TT, Lai PL, et al. A Biomechanical Comparison of Expansive Pedicle Screws for Severe Osteoporosis: The Effects of Screw Design and Cement Augmentation. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0146294.[6]朱如森.不同强化椎弓根钉内固定方法在骨质疏松腰椎退行性疾患中的应用比较研究[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2013.[7]朱爱国,张烽,曹涌,等. 硫酸钙骨水泥增强椎弓根螺钉的生物力学分析[J]. 江苏医药,2015,41(12):1448-1449.[8]易早元. 经伤椎椎弓根植骨结合膨胀型椎弓根钉固定治疗老年性胸腰椎骨折[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2014,18(19):124-126.[9]杨彬奎. 骨水泥强化对老年性腰椎骨折患者腰椎椎弓根钉固定的影响[D].西安:第四军医大学,2008.[10]Singh K, Smucker JD, Gill S, et al. Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 as an adjunct in posterolateral lumbar spine fusion: a prospective CT-scan analysis at one and two years. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(6):416-423.[11]雷伟,吴子祥,李明全,等. 膨胀式脊柱椎弓根螺钉固钉的生物力学研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(11):669-672.[12]Reinhold M, Schwieger K, Goldhahn J, et al. Influence of screw positioning in a new anterior spine fixator on implant loosening in osteoporotic vertebrae. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(4):406-413.[13]Ramaswamy R, Evans S, Kosashvili Y. Holding power of variable pitch screws in osteoporotic, osteopenic and normal bone: are all screws created equal. Injury. 2010;41(2): 179-183.[14]Wu ZX, Gao MX, Sang HX, et al. Surgical treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar compressive fractures with open vertebral cement augmentation of expandable pedicle screw fixation: a biomechanical study and a 2-year follow-up of 20 patients. J Surg Res. 2012;173(1):91-98.[15]Wan SY, Lei W, Wu ZX, et al. Micro-CT evaluation and histological analysis of screw-bone interface of expansive pedicle screw in osteoporotic sheep. Chin J Traumatol. 2008; 11(2):72-77.[16]Cook SD, Salkeld SL, Whitecloud TS 3rd, et al. Biomechanical evaluation and preliminary clinical experience with an expansive pedicle screw design. J Spinal Disord. 2000;13(3):230-236.[17]Gao M, Li X, Zhen P, et al. Biomechanical study on effects of bone mineral density on fixation strength of expansive pedicle screw. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013; 27(8):969-973.[18]Gao M, Lei W, Wu Z, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of fixation strength of conventional and expansive pedicle screws with or without calcium based cement augmentation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(3):238-244.[19]桑宏勋,吴子祥,雷伟,等.新型可膨胀椎弓根螺钉在骨质疏松性腰椎融合与固定手术中的初步应用[J].中华骨科杂志, 2009,29(9): 822-826.[20]赵利涛,郭明柯,秦耀宗.微创经皮附加伤椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗30例胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效评价[J].实用临床医药杂志,2013, 17(17):29-31.[21]费宝国.椎弓根钉棒系统在胸腰椎骨折治疗中的疗效分析[J].实用临床医药杂志,2013,17(14):104-106.[22]窦以宝,罗学勤.经伤椎椎弓根植骨结合膨胀型椎弓根钉固定治疗老年性胸腰椎骨折[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(3):129-132.[23]Wan SY, Lei W, Wu ZX, et al. Micro-CT evaluation and histological analysis of screw-bone interface of expansile pedicle screw in osteoporotic sheep. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007;45(18):1271-1273.[24]Lei W, Wu Z. Biomechanical evaluation of an expansive pedicle screw in calf vertebrae. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(3): 321-326.[25]Lei W, Wu ZX. Biomechanical evaluation of an expansive pedicle screw in calf vertebrae. Chin J Traumatol. 2005;8(1): 39-45.[26]Nishikawa M, Ohata K, Baba M, et al. Chiari I malformation associated with ventral compression and instability: one-stage posterior decompression and fusion with a new instrumentation technique. Neurosurgery. 2004;54(6): 1430-1434.[27]Bostan B, Esenkaya I, Gunes T, et al. A biomechanical comparison of polymethylmethacrylate-reinforced and expansive pedicle screws in pedicle-screw revisions. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2009;43(3):272-276.[28]刘达,康夏,郑伟,等.骨质疏松绵羊腰椎膨胀式椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定稳定性的动态比较研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(8):747-751.[29]Zhang L, Sun Y, Jiang C, et al. Dorsal open reduction with pedicle screw rod internal fixation for lower cervical spine dislocation: A retrospective analysis of 12 cases. Neurochirurgie. 2016;62(5):245-250.[30]Liu D, Shi L, Lei W, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Expansive Pedicle Screw and Polymethylmethacrylate-augmented Pedicle Screw in Osteoporotic Synthetic Bone in Primary Implantation: An Experimental Study. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(7):E351-357.[31]Yeh KT, Lee RP, Chen IH, et al. Laminoplasty instead of laminectomy as a decompression method in posterior instrumented fusion for degenerative cervical kyphosis with stenosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:138. [32]Sun BF, Dong Y, Lü JY, et al. Expansive pedicle screws fixation combined with Wright artificial bone implantation for treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture of the elderly patients. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011;24(7):544-546.[33]Liu D, Wu ZX, Pan XM, et al. Biomechanical comparison of different techniques in primary spinal surgery in osteoporotic cadaveric lumbar vertebrae: expansive pedicle screw versus polymethylmethacrylate-augmented pedicle screw. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(9):1227-1232. [34]Gao M, Lei W, Wu Z, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of fixation strength of conventional and expansive pedicle screws with or without calcium based cement augmentation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(3):238-244.[35]Wan SY, Lei W, Wu ZX, et al. Micro-CT evaluation and histological analysis of screw-bone interface of expansive pedicle screw in osteoporotic sheep. Chin J Traumatol. 2008;11(2):72-77. |
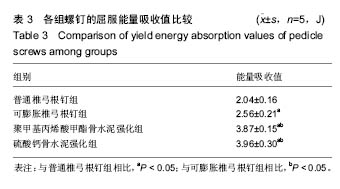
.jpg)
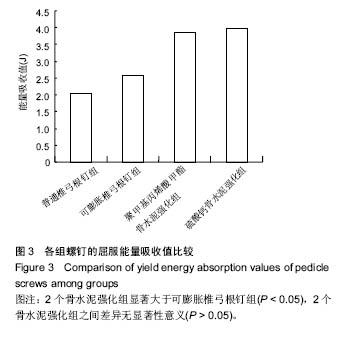
.jpg)