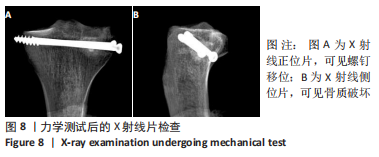
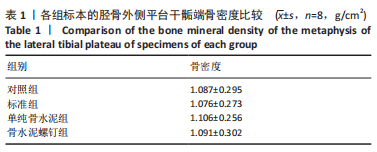
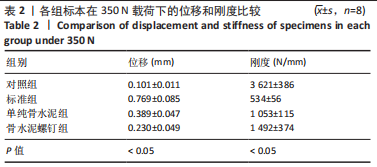
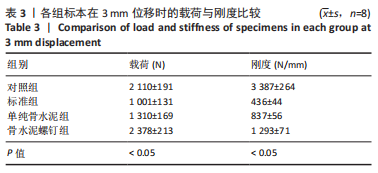
[1] RUTH JT. Fractures of the tibial plateau. Am J Knee Surg. 2001;14(2):125-128.
[2] WEIGEL DP, MARSH JL. High-energy fractures of the tibial plateau Knee function after longer follow-up. Boneurg Am. 2002;84:1541-1551.
[3] 程永刚,蔡执中,黄伟,等. 胫骨平台骨折术后关节面塌陷的相关因素分析[J]. 浙江创伤外科,2020,25(1):14-16.
[4] SIMPSON D, KEATING JF. Outcome of tibial plateau fractures managed with calcium phosphate cement. Injury. 2004;35(9):913-918.
[5] YOUNGER EM, CHAPMAN MW. Morbidity at bone graft donor sites. J Orthop Trauma. 1989;3(3):192-195.
[6] PELTIER LF. The use of plaster of Paris to fill large defects in bone: a preliminary report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;382:3-5.
[7] TURNER TM, URBAN RM, GITELIS S, et al. Resorption evaluation of a large bolus of calcium sulfate in a canine medullary defect. Orthopedics. 2003; 26(5 Suppl):s577-s579.
[8] WATSON JT. The use of an injectable bone graft substitute in tibial metaphyseal fractures. Orthopedics. 2004;27(1 Suppl):s103-s107.
[9] 王栋,潘子翔,姜文学.胫骨平台球囊成形术的临床研究进展[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2020,26(8):716-720.
[10] LIEBERMAN IH, DUDENEY S, REINHARDT MK, et al. Initial outcome and efficacy of“kyphoplasty”in the treatment of painfulosteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine. 2001;26:1631-1638.
[11] 陈金民,陈穗生,丁晶,等.球囊扩张可注射硫酸钙骨水泥填充治疗胫骨平台塌陷骨折的可行性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(18):2795-2799.
[12] 张勇,杨林.关节镜辅助下经前外侧入路内固定治疗胫骨平台后外侧塌陷骨折[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(2):189-191.
[13] KFURI M, SCHATZKER J. Revisiting the Schatzker classification of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2018;49(12):2252-2263.
[14] MILLAR SC, ARNOLD JB, THEWLIS D, et al. A systematic literature review of tibial plateau fractures: What classifications are used and how reliable and useful are they? Injury. 2018;49(3):473-490.
[15] 单贤贞,周友龙,王银海,等.关节镜辅助下球囊成形术在胫骨平台骨折患者中的应用效果及对肢体功能的影响研究[J]. 中国内镜杂志,2018, 24(5):58-62.
[16] BERIS AE, SOUCACOS PN, GLISSON RR, et al. Load tolerance of tibial plateau depressions reinforced with a cluster of K-wires. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 1996;55:12-15.
[17] BROWN TD, ANDERSON DD, NEPOLA JV, et al. Contact stress aberrations following imprecise reduction of simple tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Res. 1988;6(6):851-862.
[18] BENNETT WF, BROWNER B. Tibial plateau fractures: a study of associated soft tissue injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 1994;8(3):183-188.
[19] LLINAS A, MCKELLOP HA, MARSHALL GJ, et al. Healing and remodeling of articular incongruities in a rabbit fracture model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75(10):1508-1523.
[20] LEFKOE TP, TRAFTON PG, EHRLICH MG, et al. An experimental model of femoral condylar defect leading to osteoarthrosis. J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7(5):458-467.
[21] HONKONEN SE. Indications for surgical treatment of tibial condyle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;302:199-205.
[22] LACHIEWICZ PF, FUNCIK T. Factors influencing the results of open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 259:210-215.
[23] YEO QY, KEE KE. Use of a biphasic cement bone substitute in the management of metaphyseal fractures. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(4):789-791.
[24] LIANG J, ZHANG Q, LIU P, et al. Arthroscopic-assisted inflatable bone tamp reduction for treatment of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2018; 49(11):2061-2067.
[25] WANG JQ, JIANG BJ, GUO WJ, et al. Arthroscopic-assisted balloon tibioplasty versus open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) for treatment of Schatzker II-IV tibial plateau fractures: study protocol of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2018;8(8):e21667.
[26] VENDEUVRE T, GRUNBERG M, GERMANEAU A, et al. Contribution of minimally invasive bone augmentation to primary stabilization of the osteosynthesis of Schatzker type II tibial plateau fractures: Balloon vs bone tamp. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2018;59:27-33.
[27] KRAUSE M, HUBERT J, DEYMANN S, et al. Bone microarchitecture of the tibial plateau in skeletal health and osteoporosis. Knee. 2018;25(4):559-567.
[28] HE QF, SUN H, SHU LY, et al. Tibial plateau fractures in elderly people: an institutional retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):276.
|