• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
减少人工膝关节置换失血:两种方法的比较
卢耀甲,熊传芝,李小磊,胡翰生,陈 岗,王 强,卢志华
- 江苏省苏北人民医院关节外科,扬州大学临床医学院,江苏省扬州市 225001
Comparison of two methods for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty
Lu Yao-jia, Xiong Chuan-zhi, Li Xiao-lei, Hu Han-sheng, Chen Gang, Wang Qiang, Lu Zhi-hua
- Joint Surgery Department, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, Clinical Medical School of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225001, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
人工膝关节置换:是指采用金属、高分子聚乙烯等材料,根据人体膝关节的形态、构造及功能制成人工膝关节假体,通过外科手术植入人体内,代替患病的膝关节,从而缓解膝关节疼痛,恢复膝关节功能的一种技术。
止血带原理:止血带止血是用于四肢大出血急救时简单、有效的止血方法,它通过压迫血管阻断血行来达到止血目的。但如使用不当或使用时间过长,止血带可造成远端肢体缺血、坏死,造成残废,为此,只有在出血猛烈,用其它方法不能止血时才能应用止血带。 止血带以橡皮条或橡皮管为好,不宜用布带、电线等无弹性的带子。绑扎位置应在伤口的上方(近心端),并尽量靠近伤口,以上臂的上1/3和大腿上中部为好,小腿和前臂不能上止血带,因该处有两根骨头,血管正好走在两骨之间,上止血带起不到压迫血管的作用。上臂的中1/3部位亦不能上止血带,因它可能引起神经损伤而致手臂瘫痪。
摘要
背景:减少手术失血在一定程度上可以预防人工膝关节置换的并发症,可以减轻术后患肢肿胀和不适,有利于患者术后康复。
目的:探讨减少人工膝关节置换失血的方法。
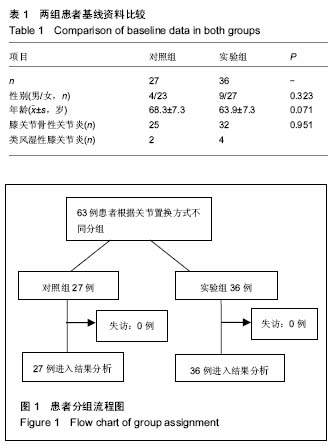
方法:将单侧初次人工膝关节置换的患者分为2组。对照组(27例)采用传统的手术方法,全程使用止血带,并留置引流管;实验组(36例)对手术方法进行改良,只有在安装假体时使用止血带,对软组织出血予以充分止血,缝合关节囊后在关节腔内注射止血药液,置换后不留置引流管。比较2组患者的术前、置换后血红蛋白、置换后血红蛋白的下降值、膝关节疼痛评分、关节活动度、输血率、伤口愈合情况等临床结果。
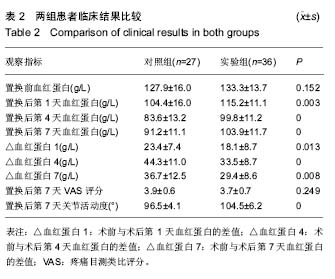
结果与结论:①两组患者关节置换前血红蛋白差异无显著性意义,置换后第1,4,7天对照组血红蛋白均显著低于实验组,而且对照组血红蛋白跟置换前相比的下降值均显著高于实验组;②两组的膝关节疼痛评分差异无显著性意义;③置换后第7天实验组膝关节活动度显著大于对照组。④对照组置换后输血率为18.5%,1例患者伤口愈合不良;实验组置换后没有患者需要输血,所有患者伤口均正常愈合。⑤两组患者均未出现置换后感染、血肿形成等并发症。⑥结果说明,通过改良手术方法,可以减少人工膝关节置换术的失血量,避免膝关节置换后输血,有助于置换后康复。
ORCID: 0000-0002-2670-8299(卢耀甲)
中图分类号:

.jpg)