中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (9): 1414-1419.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.09.019
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
人羊膜间充质干细胞原位移植治疗大鼠脑梗死
王钰莹1,粟 旭2,刘 波3,刘 娟4,万 雪1
- 1遵义医学院附属医院,贵州省细胞工程重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563000;2遵义医学院药学院,贵州省遵义市 563000;3遵义医学院附属医院临床医学研究所,贵州省遵义市 563000;4遵义医学院教育部基础药理学重点实验室,贵州省遵义市 563000
Orthotopic transplantation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of cerebral infarction in rats
Wang Yu-ying1, Su Xu2, Liu Bo3, Liu Juan4, Wan Xue1
- 1Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Institute of Clinical Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 4Department of Pharmacology and Key Laboratory for Basic Pharmacology of Ministry of Education, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 人羊膜间充质干细胞:具有干细胞特性,表达胚胎干细胞和间充质干细胞的标志,在不同生长因子的调节下,可分化成3个胚层来源的不同组织细胞类型。人羊膜间充质干细胞具有向神经细胞分化的能力,其在特定条件下诱导后,能表达NSE、GFAP、NF、β-tubulin-Ⅲ、MAP-2及NeuN。 人羊膜间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死:已有研究发现,移植人羊膜间充质干细胞治疗肌萎缩性脊髓侧索硬化症小鼠,可延长其生存,改善其运动功能。Li等发现移植人羊膜间充质干细胞2周后,在缺血性区域可见存活的细胞,且移植8周后神经功能明显改善。Palmatir等发现人、猴和鼠的羊膜组织中存在可溶性的促进神经细胞生长的物质,能促进培养的脊髓后跟神经节细胞生长。
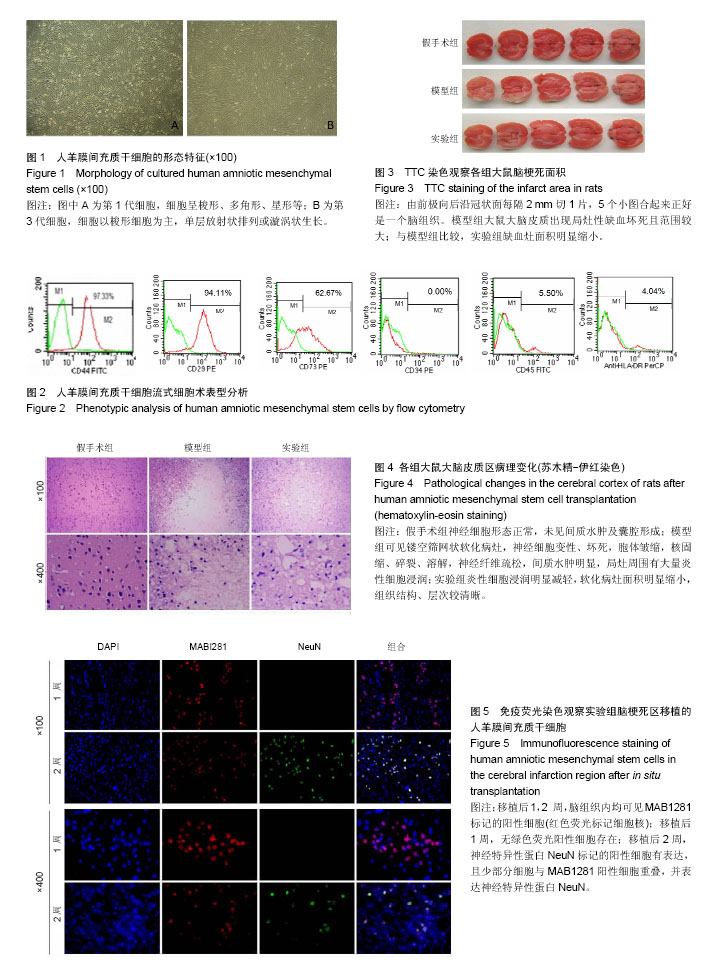
摘要 背景:前期实验研究发现,移植人羊膜间充质干细胞能有效改善脑梗死大鼠的神经损伤症状。 目的:观察移植人羊膜间充质干细胞在大鼠脑梗死区域的存活、定植和分化情况。 方法:将60只SD大鼠随机分为3组,实验组、模型组采用线栓法制作大脑中动脉闭塞模型,假手术组只结扎血管,不插入线栓;造模后1 d,实验组于受损纹状体和皮质两点原位植入10 μL第3代人羊膜间充质干细胞悬液(含细胞2×106/只),模型组与假手术组于相同部位注射等体积PBS。移植后1周连续监测体质量并进行神经缺损严重程度评分;移植后2周,TTC染色观察脑梗死面积,苏木精-伊红染色观察脑组织病理学变化,免疫荧光染色检测移植大鼠大脑神经细胞标志物神经元特异性核蛋白的表达。 结果与结论:①体质量与神经缺损严重程度评分:与假手术组比较,模型组、实验组体质量呈下降趋势,实验组降低少于模型组,但差异无显著性意义;模型组、实验组神经功能缺损评分随时间呈逐渐降低趋势,但实验组评分明显低于模型组;②脑梗死面积:模型组大脑皮质出现局灶性缺血坏死且范围较大,与模型组比较,实验组缺血灶面积明显缩小;③脑组织病理:实验组梗死病灶范围、神经细胞及炎细胞浸润均少于模型组;④免疫荧光染色:移植后1周,实验组脑组织可见较多的移植人羊膜间充质干细胞,2周后可见移植的人羊膜间充质干细胞向神经样细胞分化;⑤结果表明:人羊膜间充质干细胞移植可在大鼠脑梗死区域定植、存活,且在原位能分化为神经样细胞。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2399-9094(王钰莹)
中图分类号:
.jpg)