| [1] 朱雄增,张杰.肺腺癌IASLC/ATS/ERS国际多学科分类解读[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2012,28(3):241-244.[2] Warth A,Muley T,Meister M,et al.The novel histologic International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer / American Thoracic Society / European Respiratory Society classification system of lung adenocarcinoma is a stage-independent predictor of survival.J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30(13): 1438-1446.[3] 刘标,周晓军.非小细胞肺癌个体化治疗的靶向分子检测[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2012,28(8):831-837.[4] Russell P A,Wainer Z,Wright G M,et al. Does lung adenocarci noma subtype predict patient survival? A clinicopathologic study based on the new International association for the study of lung cancer/American thoracic society/European respiratory society international multidisciplinary lung adenocarcinoma classification.J Thoracic Oncol. 2011;6( 9) : 1496-1504.[5] Warth A,Stenzinger A,von Brünneck A C,et al. Interobserver variability in the application of the novel IASLC/ATS/ERS classifi-cation for pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Eur Respir J. 2012;40(5):1221-1227.[6] 章必成,杨波,刘健,等. 肺腺癌瘤周微淋巴管密度的检测及其预后意义[J].临床肿瘤学杂志,2010,15(11): 978-981.[7] 张力. 脑转移瘤的诊断和治疗[C].中华医学会第五届全国胸部肿瘤及内窥镜学术会议论文汇编,2011.[8] Motoi N,Szoke J,Riely GJ,et al. Lung adenocarcinoma: modification of the 2004 WHO mixed subtype to include the major histologic subtype suggests correlations between papillary and micropapillary adenocarcinoma subtypes,EGFR mutations and gene expression analysis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32(6): 810-827.[9] 刘丽,姜建威.肺腺癌新增分类及研究新进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2014,8(6):1128-1133.[10] Mc Carroll JA,Gan PP,Liu M,et al. β-Ⅲ-tubulin is a multi functional protein involved in drug sensitivity and tumorigenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70(12): 4995-5003.[11] 石祥宇,庞青松,赵纲,等. 伴微乳头结构肺腺癌的研究进展[J]. 中国肺癌杂志,2015,18(11):701-705.[12] Hung JJ,Yeh YC,Jeng WJ,et al. Predictive value of the international association for the study of lung cancer/American Thoracic Society/ European Respiratory Society classification of lung adenocarcinoma in tumor recurrence and patient survival. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(22): 2357-2364.[13] 刘雨桃,石远凯,胡兴胜,等.吉非替尼治疗EGFR基因突变状态不明的青年晚期肺腺癌疗效分析[J].中国肺癌杂志,2014,17(5): 401-405.[14] 丁粉干,刘标,张新华,等.不同肺腺癌分级评分系统在I期肺腺癌预后评估中的意义[J].中华病理学杂志,2012,41(3):145-150.[15] Shi Y,Au JS,Thongprasert S,et al. A prospective,molecular epide miologystudy of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non -small - celllung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology(PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9(2):154 -162.[16] 冯瑞娥.最新国际肺腺癌多学科分类中的病理分类及其临床意义[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2012,35(2):95-96.[17] 金鑫,赵绍宏,高洁,等.纯磨玻璃密度肺腺癌病理分类及影像表现特点分析[J].中华放射学杂志,2014,48(4):283-287.[18] Backos DS,Franklin CC,Reigan P. The role of glutathione in brain tumor drug resistance. Bio Chem Pharmacol. 2012; 83(8): 1005-1012.[19] 周晓军,刘摇标.解读2011年IASLC/ATS/ERS肺腺癌国际多学科分类[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2011,27(8):801-805.[20] 刘颖汇,朱彦君,郭延林,等.肺腺癌中C/EBPα、MVD表达的临床意义及相关性分析[J].临床肺科杂志,2013,18(11):2057-2059.[21] Fujikawa Y,Urano Y,Komatsu T,et al. Design and synthesis of highly sensitive fluorogenic substrates for glutathione S-transferase and application for activity imaging in living cells. Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(44): 14533-14543.[22] 王凯,李晓军,陈芳芳,等. ID3 蛋白在肺腺癌中的表达及临床病理学意义[J].临床检验杂志,2011,29(2): 118-120.[23] Citti A,Boldrini R,lnserra A,et al. Expression of multidrug resistance-associated proteins in paediatric soft tissue sarcomas before and after chemotherapy.Oncol. 2012;41(1): 117-124.[24] Cao Y,Zhang L,Kamimura Y,et al. B7-H1 over-expression regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and accelerates carcinogenesis in skin. Cancer Res.2011;71(4): 1235-1243.[25] 史妍婷,井欢,王莹,等.补中益气汤含药血清逆转A549/DDP的顺铂耐药及对mTOR表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2013, 19(9):215-219.[26] 季旭明,欧阳兵,吴智春,等.温下方含药血清诱导A549/DDP细胞凋亡及对Bcl-2,Bax,p53蛋白表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(12):123-126.[27] Ye MX,Zhao YL, Li Y, et al. Curcumin reverses cis-platin resistance and promotes human lung adenocarcinoma A549 / DDP cell apoptosis through HIF-1α and caspase-3 mechanisms. Phytomedicine. 2012;19( /9): 779-787.[28] 张莹,贾英杰,李小江,等.消岩汤对耐顺铂人肺腺癌A549/DDP细胞多药耐药基因调控作用的研究[J].药物评价研究,2014,37(6): 507-510.[29] 张继新,崔力方,周全,等.肺腺癌转移至胸膜孤立性纤维性肿瘤临床病理观察[J].诊断病理学杂志,2014,21(3):145-148.[30] 马云帆,范梦颖,陈克能.肺鳞癌与肺腺癌的免疫组化指标的诊断及预后意义[J].中国肺癌杂志,2014,17(6):506-510.[31] 俎云芬,王熙才,刘馨,等.甲状腺转录因子在宣威肺腺癌中的表达及临床意义[J].中国肺癌杂志,2013,16(3):131-137.[32] 王艳芬,刘标,徐艳,等.窖蛋白-1表达与肺腺癌临床病理特征和预后的关系[J].中华病理学杂志,2014,43(4):251-255.[33] 张莹,贾英杰,李小江,等.注射用黄芪多糖对耐顺铂人肺腺癌细胞A549/DDP耐药逆转作用研究[J].药物评价研究,2012,35(6): 417-419.[34] Kim TJ,Goo JM,Lee KW,et al. Clinical,pathological and thin-section CT features of persistent multiple ground glass opacity nodules: comparison with solitary ground-glass opacity nodule. Lung Cancer. 2009;64(2):171-178.[35] Eisenberg RL,Bankier AA,Boiselle PM. Compliance with Fleischner Society guidelines for management of small lung nodules: a survey of 834 radiologists. Radiology. 2010;255(1): 218-224.[36] Yoshizawa A,Motoi N,Riely GJ,et al. Impact of proposed IASLC/ATS/ERS classification of lung adenocarcinoma: prognostic subgroups and implications for further revision of staging based on analysis of 514 stage I cases. Mod Pathol. 2011;24 (5):653-664.[37] Sawada E,Nambu A,Motosugi U,et al. Localized mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma of the lung: thin-section computed tomography and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography findings. Jpn J Radiol. 2010;28(4): 251-258.[38] 唐晓勇,唐迎雪.浙贝母碱对肺癌A549/DDP细胞多药耐药的逆转作用观察及机制探讨[J].山东医药,2012,52(18):4-6.[39] 李泽慧,安超,胡凯文,等.浙贝母总生物碱对人肺腺癌A549/顺铂细胞耐药性的逆转作用[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2013, 27(3):315-320.[40] Kim TJ,Park CM,Goo JM,et al. Is there a role for FDG PET in the management of lung cancer manifesting predominantly as ground-glass opacity? AJR Am J Roentgenol.2012;198(1): 83-88.[41] Selle F, Gligorov J, Soares DG, et al. [High-dose chemotherapy as a strategy to overcome drug resistance in solid tumors].Bull Cancer. 2016;103(10):861-868. [42] Buryk MA, Picarsic JL, Creary SE, et al. Identification of Unique, Heterozygous Germline Mutation, STK11 (p.F354L), in a Child with an Encapsulated Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma within Six Months of Completing Treatment for Neuroblastoma. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2015;18(4): 318-323. [43] Terunuma H. Autologous Immune Enhancement Therapy for Cancer - Our experience since 2004. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2012;8(3):205-206.[44] Taniguchi A, Takigawa N, Hotta K, et al. [A relapse of small-cell lung cancer ten years after concomitant chemoradiotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy with autologous peripheral blood stem cell transfusion]. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2011;49(9):697-701. [45] Terashita S, Hirano K, Hirai T, et al.[Successful treatment of small cell lung cancer with secondary immune thrombocytopenic purpura]. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2009;47(11):1036-1040. [46] Hah JO. Intensive chemotherapy with autologous PBSCT for advanced adrenocortical carcinoma in a child. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008;30(4):332-334. [47] Stemmer SM, Hardan I, Brenner HJ, et al. High-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplant in women with de novo chemosensitive metastatic breast cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2004;27(3):250-255.[48] Hotta K, Ueoka H, Kiura K, et al. Successful treatment of limited disease-small cell lung cancer with multimodality treatment consisting of concurrent chemoradiotherapy, high-dose chemotherapy with autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation and surgical resection. Intern Med. 2003;42(12):1223-1227.[49] Ziske C, Gorschlüter M, Mey U, et al. Sequential high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell support in patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2002;22(6B):3723-3726. |
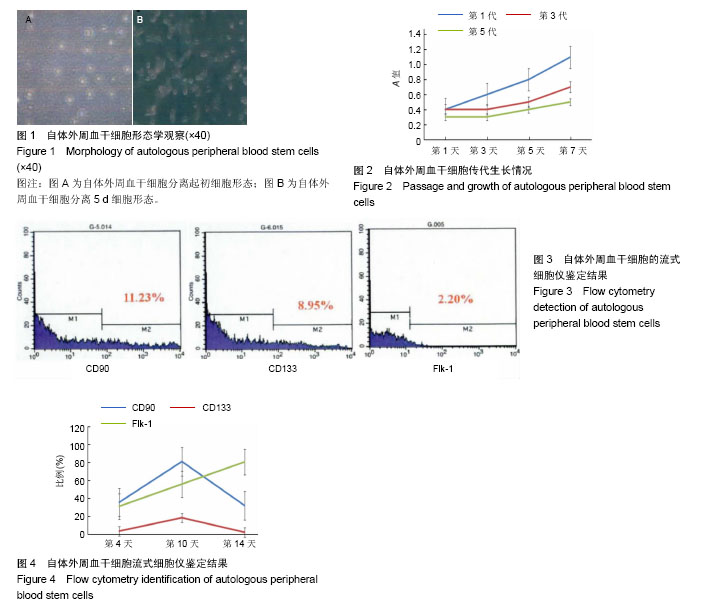
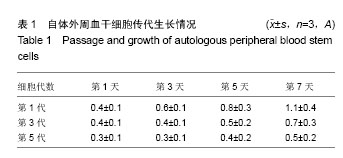
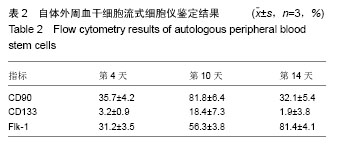
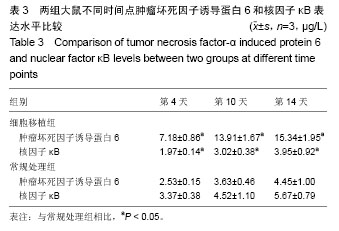
.jpg)
.jpg)