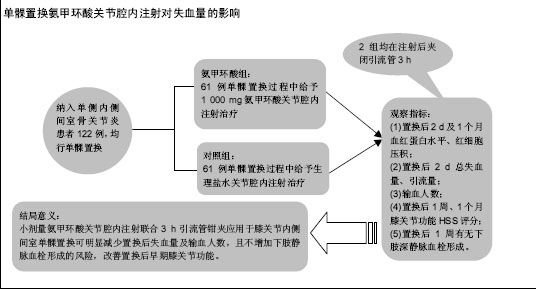
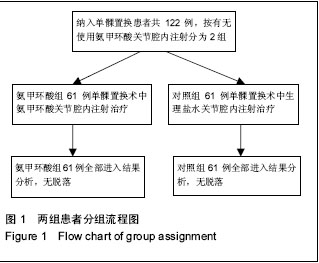
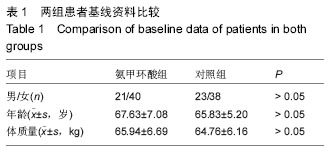
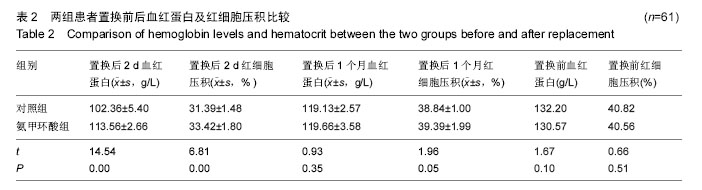
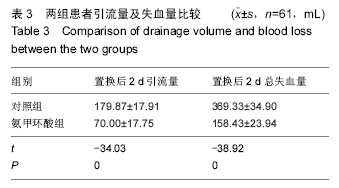
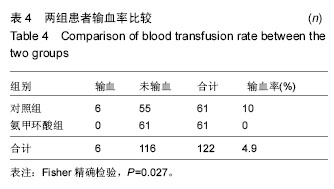
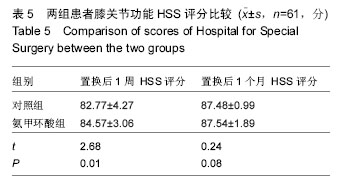
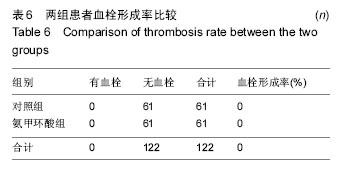
| [1] Kristensen PW, Holm HA, Varnum C.Up to 10-year follow-up of the Oxford medial partial knee arthroplasty--695 cases from a singleinstitution.J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(9 Supp1):195-198.[2] 周友龙,陈奇,康一凡,等. 小切口单髁置换术治疗膝关节内侧间室骨性关节炎的早期疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,28(8):716-718.[3] Katsumata S,Nagashima M,Kato K. Changes in coagulation-fibrinolysis markerandneutrophil elastase following the use of tourniquet duringtotal knee arthroplastyand the influence ofneutrophil elastaseonthromboembolism.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49(4):510-516.[4] 尹俊萍,苗海敏,乔国勇,等.膝关节置换中应用骨水泥和止血带对凝血功能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(44):8186-8190.[5] Vamvakas EC,Blajchman MA.Transfusion-related mortality: the ongoingrisksofallo geneicbloodtransfusion and theavailablestrategies for theirprevention.Blood.2009;113(15):3406-3417.[6] 尹建石,刘欣伟,赵东风,等.术中关节腔内注射氨甲环酸对TKA失血量的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015, 30(2): 205-206.[7] 郑萍,翁绳健,吴立忠,等.关节腔内注射氨甲环酸对单侧人工全膝关节置换术后引流量的影响[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(4):357-359.[8] Ishida K,Tsumura N,Kitagawa A,et al. Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop.2011;35(11):1639-1645.[9] 马金辉,孙伟,高福强,等.关节腔注射氨甲环酸单侧全膝关节置换者的失血量及肢体周径变化:随机对照[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,81(35):5577-5582.[10] 柴星宇,苏长征,庞涛, 等.全膝关节置换后静脉与局部应用氨甲环酸对失血量的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(35):5604-5609.[11] 侯振扬,苏长征,庞涛,等.初次单侧骨水泥型全膝关节置换:氨甲环酸使用方式对失血量的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(9):1329-1334.[12] Jain RK,Neville LT,Ezzet KA,et al. Two Year Follow-up of the Preservation Unicompartmental Knee Implant. HSS J. 2011;7(2):125-129.[13] Gross JB. Estimating allowable blood loss:corrected for dilution. Anesthesiolog.1983;58(3):277-280.[14] Nadler SB,Hidalgo JH,Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51(2): 224-232.[15] Sehat KR,Evans RL,Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(4):561-565.[16] MacGillivray RG, Tarabichi SB, Hawari MF, et al. TranexamicAcid to Reduce Blood Loss After Bilateral Total KneeArthroplasty : A Prospective, Randomized Double Blind Study.J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(1):24-28.[17] 吕厚山.现代人工关节外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2006:69-78.[18] Tan J, Chen H, Liu Q, et al. A meta-analysis of the effectivenessand safety of using tranexamic acid in primary unilateral totalknee arthroplasty. J Surg Res.2013;184(2): 880-887.[19] Petaja J, Myllynen P, Myllyla G, et al. Fibrinolysis afterapplication of a pneumatic tourniquet. Acta Chir Scand. 1987;153(11-12):647-651.[20] Klenerman L, Chakrabarti R, Mackie I, et al. Changes inhaemostatic system after application of a tourniquet. Lancet.1977;1(8019):970-972.[21] Reikeras O,Clementsen T. Time course of thrombosis and fibrinolysis in total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet application. Local versus systemicactivations. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2009; 28(4):425-428.[22] McCormack PL. Tranexamic acid:a review of its use in the treatment of hyperfibrinolysis. Drugs. 2012;72(5): 585-617.[23] 刘江俊,刘忠强,田少奇,等.氨甲环酸对减少单侧全膝关节置换术后出血的疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2014, 22(23): 2144-2148.[24] McCormack PL. Tranexamic acid: a review of its use in thetreatment of hyperfibrinolysis. Drugs. 2012;72(5): 585-617.[25] 闵鹏,彭银虓,胡江海,等.氨甲环酸对单侧全膝关节置换失血量的影响及安全性评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(17):2655-2660.[26] 王荣,田少奇,哈承志,等.氨甲环酸减少双侧全膝关节置换失血量的有效性及安全性评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(22):3451-3456.[27] 曹万军,朱绍灵,刘显东,等.氨甲环酸用于全膝关节置换降低失血量的有效性及安全性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(31):4944-4948.[28] Wong J,Abrishami A,El Beheiry H,et al. Topical application of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(15): 2503-2513.[29] Akizuki S,Yasukawa Y,Takizawa T. A new method of hemostasis for cementless total knee arthroplasty. Bull Hosp Jt Dis.1997;56(4):222-224.[30] Maniar RN, Kumar G, Singhi T, et al. Most effective regimen oftranexamic acid in knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomizedcontrolled study in 240 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(9): 2605-2612.[31] Tanaka N, Sakahashi H, Sato E, et al. Timing of theadministration of tranexamic acid for maximum reduction inblood loss in arthroplasty of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2001;83(5):702-705.[32] Kiely N,Hockings M,Gambhir A. Does temporary clamping of drains following knee arthroplasty reduce bloodloss? A randomisedcontrolled trial. Knee. 2001; 8:325-327.[33] Larsson J,Lewis DH,Liljedahl SO,et al. Early biochemical and hemodynamic changes after operationin a bloodless field.Eur Surg Res.1977;9(5): 311-20.[34] Wong J,Abrishami A,El Beheiry H,et al. Topical application of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(15): 2503-2513.[35] 计忠伟,包倪荣,赵建宁,等.关节腔注射氨甲环酸对全膝关节置换术后疗效影响的Meta分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,3(02):164-168.[36] 胡洪新,林海滨. 氨甲环酸在髋膝关节置换术中应用的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(4): 532-535.[37] Akizuki S,Yasukawa Y,Takizawa T.A new method of hemostasis for cementless total knee arthroplasty. 1997;56(4):222-224.[38] 李飞雄,王智勇,张志强.全膝关节置换中应用氨甲环酸有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(9):1463-1469.[39] 武婷,文其祥. 氨甲环酸与抑肽酶对血液保护功能的对比研究[J].中国体外循环杂志,2005,3(1):10-13.[40] Poeran J, Rasul R, Suzuki S, et al. Tranexamic acid use andpostoperative outcomes in patients undergoing total hip or kneearthroplasty in the United States: retrospective analysis ofeffectiveness and safety. BMJ. 2014;349:g4829.[41] Dahuja A, Dahuja G, Jaswal V, et al. A Prospective Study on Role of Tranexamic Acid in Reducing Postoperative Blood Loss in Total Knee Arthroplasty and Its Effect on Coagulation Profile. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(4):733-735.[42] Yang ZG,Chen WP,Wu LD.Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid inreducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2012;94(13):1153-1159.[43] Cid J,Lozano M. Tranexamic acid reduces allogeneic red cel transfusions in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty:results of a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Transfusion.2005;45:1302-1307.[44] 李阳,张卫国,李洪敬.全膝关节置换关节内应用氨甲环酸的临床对比研究[J].医学与哲学(B),2013,34(9):27-30. |
.jpg)