| [1] Khoueir P, Kim KA, Wang MY. Classification of posterior dynamic stabilization devices. Neurosurgical Focus. 2007;22(1):E3.[2] Prud'homme M, Barrios C, Rouch P, et al. Clinical Outcomes and Complications After Pedicle-anchored Dynamic or Hybrid Lumbar Spine Stabilization: A Systematic Literature Review. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(8):E439-448. [3] Kaner T, Ozer AF. Dynamic stabilization for challenging lumbar degenerative diseases of the spine: a review of the literature. Adv Orthop.2013;2013:753470.[4] Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN. Pedicle screw-based posterior dynamic stabilization: literature review. Adv Orthop. 2012;2012:424268.[5] 彭超,何智勇,母建松,等.Dynesys 动态稳定系统置入内固定与后路腰椎间融合修复腰椎退行性病的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(44):7117-7121.[6] 杨波,万盛钰,曾勉东,等.Dynesys系统治疗腰椎退行性疾病对邻近节段的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(17): 3057-3064.[7] 丁立祥,陈迎春,张亘瑗,等.后路动态稳定系统内固定治疗腰椎间盘突出症的稳定性评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(22):4123-4129.[8] Wang JC,Arnold PM,Hermsmeyer JT, et al.Do lumbar motion preserving devices reduce the risk of adjacent segment pathology compared with fusion surgery:a systematic review. Spine. 2012;37(22):S133-143.[9] 闫家智,吴志宏,汪学松,等.腰椎三维有限元模型建立和应力分析[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(17):l162-1165.[10] Rahm MD, Hall BB. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar fusion with instrumentation: a retrospective study. Spinal Disord.1996;9(5):392-400.[11] Shim CS, Park SW, Lee SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(22 Suppl): E820-827.[12] Lee JC, Choi SW. Adjacent Segment Pathology after Lumbar Spinal Fusion. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(5): 807-817.[13] Hilibrand AS, Robbins M. Adjacent segment degeneration and adjacent segment disease: the consequences of spinal fusion? Spine J. 2004;4(6 Suppl):190S-194S.[14] Yang BH, Li HP, Zhang T, et al. The incidence of adjacent segment degeneration after cervical disc arthroplasty(CDA): a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35032. [15] Botelho RV, Moraes OJ, Fernandes GA, et al. A systematic review of randomized trials on the effect of cervical disc arthroplasty on reducing adjacent-level degeneration. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28(6):E5. [16] Skeppholm M, Lindgren L, Henriques T, et al. The Discover artificial disc replacement versus fusion in cervical radiculopathy--a randomized controlled outcome trial with 2-year follow-up. Spine J. 2015;15(6):1284-1294.[17] Hilibrand AS, Robbins M. Adjacent segment degeneration and adjacent segment disease: the consequences of spinal fusion? Spine J. 2004;4(6 Suppl):190S-194S.[18] Li ZH, Li FN, Yu SZ, et al. Two year follow-up results of the Isobar TTL semi-rigid rod system for the treatment of lumbar degenerative disease. J Clin Neurosci. 2013; 20:394-399. [19] Ren C, Song Y, Liu L, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration and disease after lumbar fusion compared with motion-preserving procedures: a meta-analysis, Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2014;24 (Suppl 1):S245-S253.[20] 周盛源,陈雄生,贾连顺,等.棘突间动态稳定装置Coflex预防腰椎融合术后相邻节段退变的短期随访疗效观察[J].中华外科杂志,2012,9:772-775.[21] Cabello J, Cavanilles-Walker JM, Iborra M, et al. The protective role of dynamic stabilization on the adjacent disc to a rigid instrumented level. An in vitro biomechanieal analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133:443-448.[22] Putzier M, Hoff E, Tohtz S, et al.Dynamic stabilization adjacent to single-level fusion:part II.No clinical benefit for asymptomatic,initially degenerated adjacent segments after 6 years follow-up.Eur Spine J.2010; 19(12):2181-2189.[23] Krag MH, Seroussi RE, Wilder DG, et al. Internal displacement distribution from in vitro loading of human thoracic and lumbar spinal motion segments: experimental results and theoretical predictions. Spine.1987;12(2):1001-1007.[24] Tang S, Meng X. Does disc space height of fused segment affect adjacent degeneration in ALIF? A finite element study. Turk Neurosurg.2011;21(3):296-303.[25] 朱立新,王健,曹延林,等.基于CT数据构建人体腰骶椎的有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,6(30): 5511-5515.[26] Schmidt H, Galbusera F, Rohlmann A, et al. What have we learned from finite element model studies of lumbar intervertebral discs in the past four decades? J Biomech. 2013;46(14):2342-2355. [27] Carpenter RD. Finite element analysis of the hip and spine based on quantitative computed tomography. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2013;11(2):156-162.[28] 刘建航,靳安民,段扬,等.半坚强内固定系统与USS坚强内固定系统的三维有限元分析比较[J].第二军医大学学报, 2013, 34(4):416-420.[29] Galbusera F, Bellini CM, Anasetti F, et al. Rigid and flexible spinal stabilization devices: a biomechanical comparison. Med Eng Phys.2011;33:490-496.[30] Barrey C, Perrin G, Champain S. Pedicle-Screw-Based Dynamic Systems and Degenerative Lumbar Diseases: Biomechanical and Clinical Experiences of Dynamic Fusion with Isobar TTL. ISRN Orthop. 2013;2013: 183702.[31] 李建江,楚戈,杨涛,等.经皮椎间孔镜下TESSYS技术修复腰椎固定融合后邻近节段退行性变[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(26):4186-4190. |
.jpg)
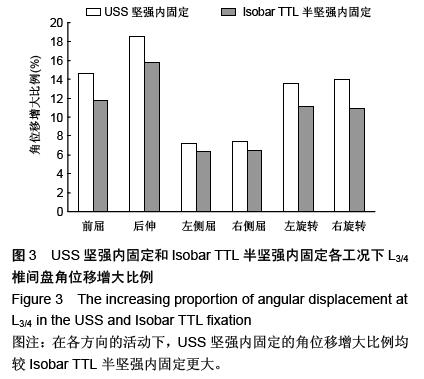
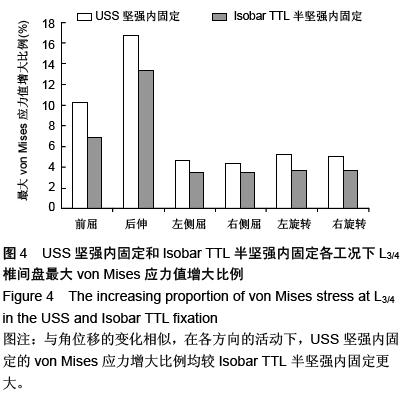
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)