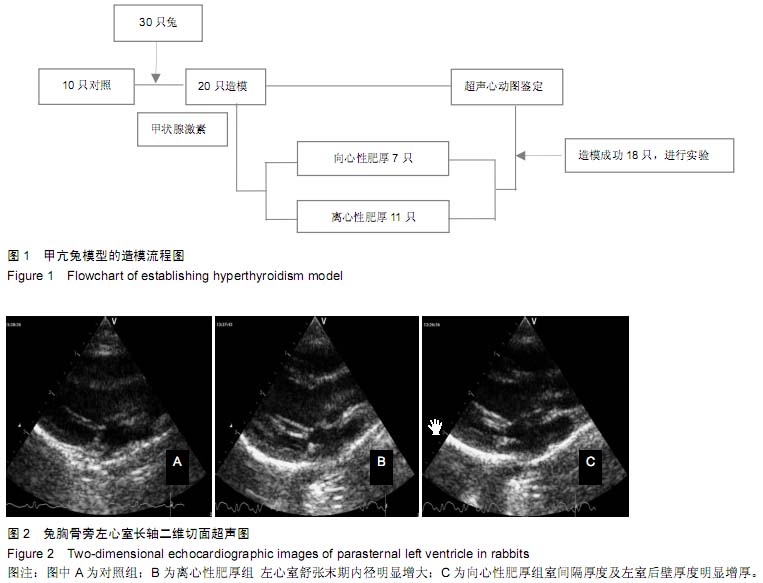
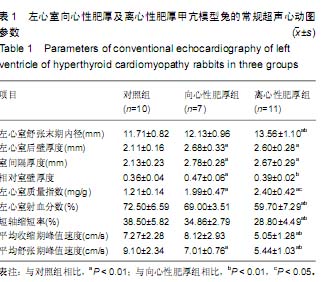
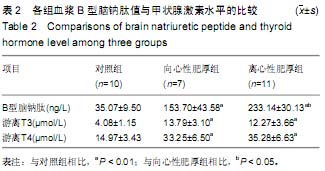
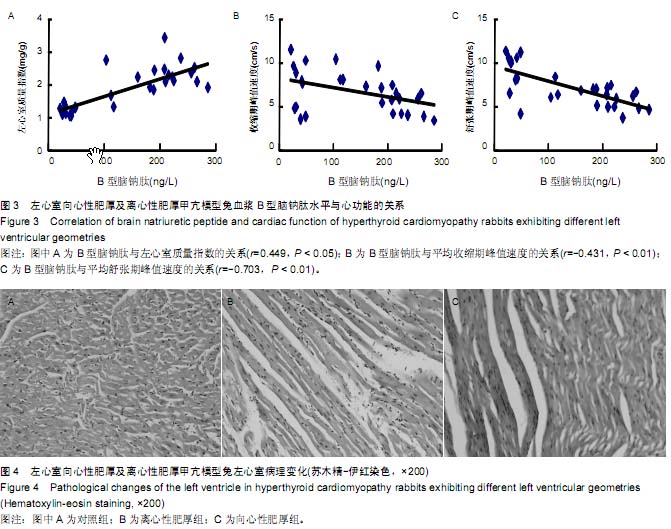
| [1] 赵永玲,李昭瑛.甲亢性心脏病发病机制的研究进展[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2009,7(3):343-344.
[2] 陆轶群,鲁燕,成兴波.甲亢性心脏病患者血浆B型脑钠肽水平的变化[J].苏州医学院学报(医学版),2005,25(4):630-632.
[3] 陈建军,阮玲英,董学君.BNP在甲亢性心脏病患者早期诊断及左心功能评估的价值[J].放射免疫学杂志,2013,26(4):456-459.
[4] Maack T. The broad homeostatic role of natriuretic peptides. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2006;50(2):198-207.
[5] Mair J. Biochemistry of B-type natriuretic peptide--where are we now? Clin Chem Lab Med. 2008;46(11):1507-1514.
[6] Ogawa Y, Nakao K, Mukoyama M, et al. Natriuretic peptides as cardiac hormones in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. The ventricle is a major site of synthesis and secretion of brain natriuretic peptide. Circ Res. 1991; 69(2):491-500.
[7] Pantos C, Xinaris C, Mourouzis I, et al. Thyroid hormone changes cardiomyocyte shape and geometry via ERK signaling pathway: potential therapeutic implications in reversing cardiac remodeling? Mol Cell Biochem. 2007; 297(1-2):65-72.
[8] 李华康,戴引,殷跃辉.Fas、FasL在兔甲亢性心脏病中的表达及其意义[J].重庆医科大学学报,2006,31(5):673-676.
[9] Ganau A, Devereux RB, Roman MJ, et al. Patterns of left ventricular hypertrophy and geometric remodeling in essential hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992;19(7):1550-1558.
[10] 王美兰.免疫比浊法与ELISA法在梅毒螺旋体抗体检测中的效果对比[J].医学检验与临床,2013,24(5):57-58.
[11] 李丽,刘一鸣,陈桐生,等.Graves病患者血清IL-17的表达[J].广东药学院学报,2014,30(3):363-365.
[12] 李晓娜,郑吉龙,单迪,等.兔不同死因死后脑组织CT影像学变化的时间规律性研究[J].解剖科学进展,2014,20(2):145-150.
[13] 卫海松,王亮亮,高海旺,等.急诊PCI治疗与急诊溶栓治疗对急性心肌梗死患者BNP及心功能的影响[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2011,19(11):1925.
[14] La Villa G, Padeletti L, Lazzeri C, et al. Plasma levels of natriuretic peptides during ventricular pacing in patients with a dual chamber pacemaker. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1994; 17(5 Pt 1):953-958.
[15] 徐倩,李盈,王惠玲.甲亢性心脏病患者血清B型脑钠肽水平与左心功能关系的研究[J].河北医学,2007,13(11):1280-1282.
[16] Lainchbury JG, Richards AM, Nicholls MG, et al. Brain natriuretic peptide and neutral endopeptidase inhibition in left ventricular impairment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84(2): 723-729.
[17] Schultz M, Faber J, Kistorp C, et al. N-terminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-pro-BNP) in different thyroid function states. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2004;60(1):54-59.
[18] Ozmen B, Ozmen D, Parildar Z, et al. Serum N-terminal-pro- B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-pro-BNP) levels in hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Endocr Res. 2007; 32(1-2):1-8.
[19] Arikan S, Tuzcu A, Gokalp D, et al. Hyperthyroidism may affect serum N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels independently of cardiac dysfunction. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007;67(2):202-207.
[20] Manuchehri AM, Jayagopal V, Kilpatrick ES, et al. The effect of thyroid dysfunction on N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide concentrations. Ann Clin Biochem. 2006;43(Pt 3): 184-188.
[21] Paku?a D, Marek B, Kajdaniuk D, et al. Plasma levels of NT-pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with overt and subclinical hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Endokrynol Pol. 2011;62(6):523-528.
[22] Magga J, Sipola P, Vuolteenaho O, et al. Significance of plasma levels of N-terminal Pro-B-type natriuretic peptide on left ventricular remodeling in non-obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy attributable to the Asp175Asn mutation in the alpha-tropomyosin gene. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101(8):1185- 1190.
[23] Schultz M, Kistorp C, Corell P, et al. N-terminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide during pharmacological heart rate reduction in hyperthyroidism. Horm Metab Res. 2009;41(4): 302-307.
[24] Prontera C, Emdin M, Zucchelli GC, et al. Analytical performance and diagnostic accuracy of a fully-automated electrochemiluminescent assay for the N-terminal fragment of the pro-peptide of brain natriuretic peptide in patients with cardiomyopathy: comparison with immunoradiometric assay methods for brain natriuretic peptide and atrial natriuretic peptide. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2004;42(1):37-44.
[25] Feringa HH, Bax JJ, Elhendy A, et al. Association of plasma N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide with postoperative cardiac events in patients undergoing surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysm or leg bypass. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98(1): 111-115. |