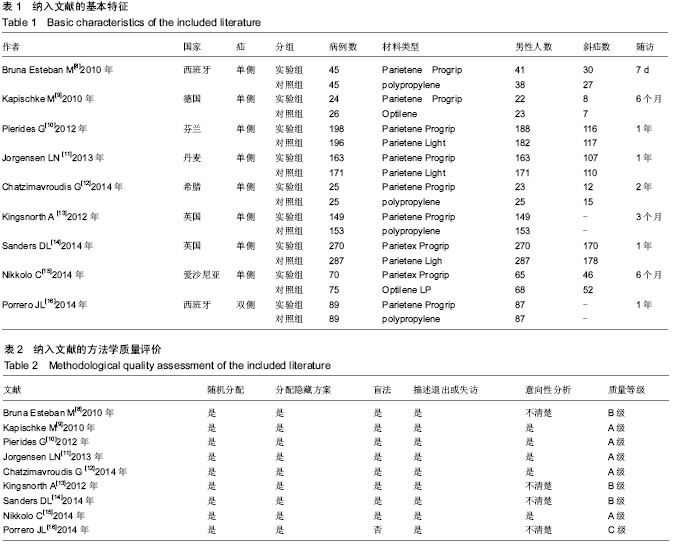
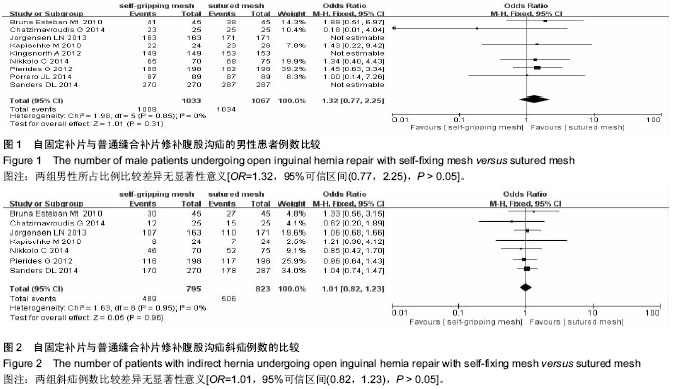
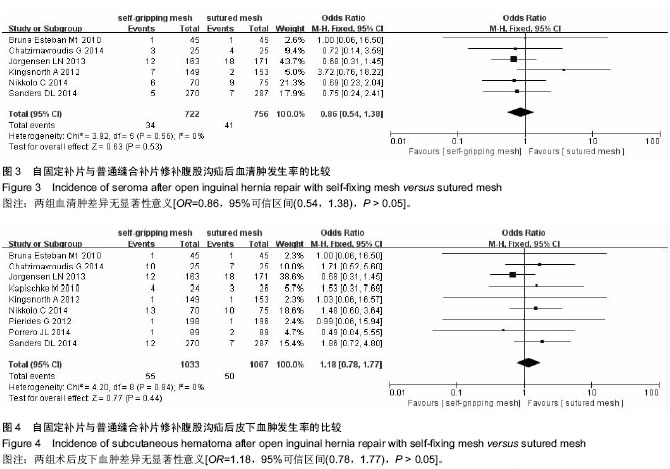
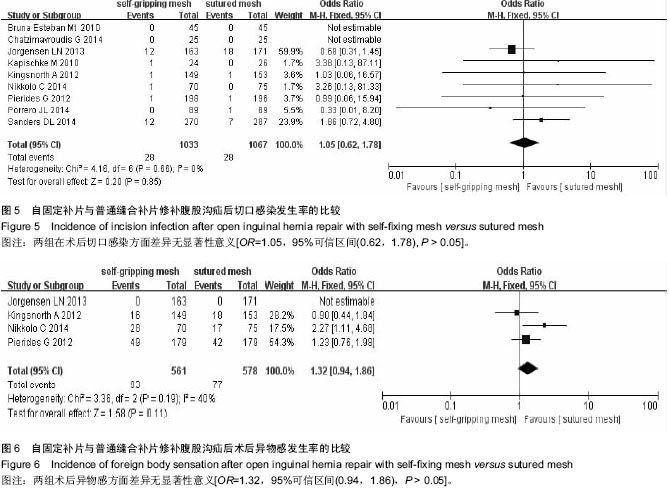
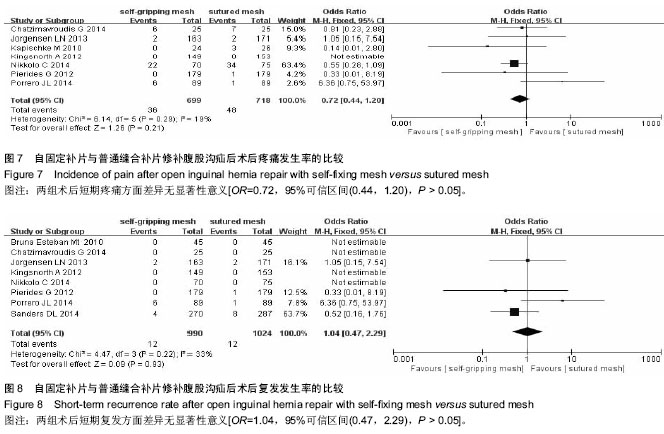
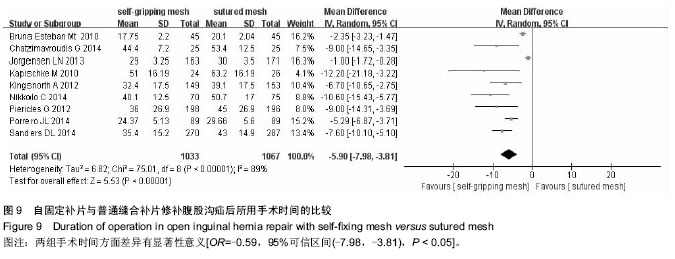
| [1] Lichtenstein IL,Shulman AG,Amid PK,et al.The tension-free hernioplasty.Am J Surg.1989;157(2):188-193.
[2] Paajanen H.A single-surgeon randomized trial comparing three composite meshes on chronic pain after Lichtenstein hernia repair in local anesthesia. Hernia.2007;11(4):335.
[3] Ferzli GS,Edwards ED,Khoury GE.Chronic pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy. J Am Coll Surg.2007;205(2):333.
[4] Eklund A,Montgomery A,Bergkvist L,et al.Chronic pain 5 years after randomized comparison of laparoscopic and Lichtenstein inguinal hernia repair(Br J Surg 2010; 97: 600-608).Br J Surg. 2010;97(9):600-608.
[5] Chastan P.Tension free open inguinal hernia repair using an innovative self gripping semi-resorbable mesh.J Minim Access Surg.2006;2(3):139-143.
[6] Anadol AZ,Akin M,Kurukahvecioglu O,et al.A prospective comparative study of the efficacy of conventional Lichtenstein versus self adhesive mesh repair for inguinal hernia.Surg Today.2011;41(11):1498-1503.
[7] Quyn AJ,Weatherhead KM,Daniel T.Chronic pain after open inguinal hernia surgery: suture fixation versus self-adhesive mesh repair.Langenbecks Arch Surg.2012;397(8):1215-1218.
[8] Bruna Esteban M,Cantos Pallarés M,Artigues Sánchez De Rojas E.Use of adhesive mesh in hernioplasty compared to the conventional technique. Results of a randomized prospective study.Cir Esp.2010;88(4):253-258.
[9] Kapischke M,Schulze H,Caliebe A.Self-fixating mesh for the Lichtenstein procedure a prestudy.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2010;395(4):317-322.
[10] Pierides G,Scheinin T,Remes V,et al.Randomized comparison of self-fixating and sutured mesh in open inguinal hernia repair. Br Surg.2012;99 (5):630-636.
[11] Jorgensen LN,Sommer T,Assaadzadeh S,et al.Randomized clinical trial of self-gripping mesh versus sutured mesh for Lichtenstein hernia repair.Br J Surg.2013;100(4):474-481.
[12] Chatzimavroudis G,Papaziogas B,Koutelidakis I,et al. Lichtenstein technique for inguinal hernia repair using polypropylene mesh fixed with sutures vs. self-fixating polypropylene mesh: a prospective randomized comparative study .Hernia,2014;18(2):193-198.
[13] Kingsnorth A,Gingell-Littlejohn M,Nienhuijs S,et al. Randomized controlled multicenter international clinical trial of self-gripping Parietex TM ProGrip TM polyester mesh versus lightweight polypropylene mesh in open inguinal hernia repair: interim results at 3 months.Hernia.2012;16(3): 287-294.
[14] Sanders DL,Nienhuijs S,Ziprin P,et al.Randomized clinical trial comparing self-gripping mesh with suture fixation of lightweight polypropylene mesh in open inguinal hernia repair.Br J Surg.2014;101(11):1373-1382.
[15] Nikkolo C,Vaasna T,Murruste M,et al.Single-center, single-blinded, radomized study of self-gripping versus sutured mesh in open inguinal hernia repair.J Surg Res, 2015;194(1):77-82.
[16] Porrero JL,Castillo MJ,Pérez-Zapata A,et al.Randomised clinical trial: conventional Lichtenstein vs. hernioplasty with self-adhesive mesh in bilateral inguinal hernia surgery. Hernia. 2014.[Epub ahead of print]
[17] KIinge U,KIosterhaIfen B,Conze J,et al.Modified mesh for hernia repair that is adapted to the physiology of the abdominal wall.Eur J Surg.1998;164:951-960.
[18] 王家胜,胡铁弋,陈勇,等.应用轻型与重型网片开放式修补腹股沟疝的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(47):8294-8300.
[19] Fang Z,Zhou J,Ren F,et al.Self-gripping mesh versus sutured mesh in open inguinal hernia repair: system review and meta-analysis.Am J Surg.2014;207(5):773-781.
[20] Zhang C,Li F,Zhang H.Self-gripping versus sutured mesh for inguinal hernia repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis of current literature.J Surg Res.2013;185(2):653-660.
[21] Gao M,Han J,Tian J,et al.VYPRO II mesh for inguinal hernia repair: a meta -analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Surg.2010;251(5):838-842.
[22] 朱海峰,王福荣,董文亮,等.自固定补片与普通平片在无张力疝修补术中的临床研究[J].中华疝和腹壁外科杂志(电子版),2014, 8(4):339-341.
[23] Sajid MS,Farag S,Singh KK,et al.Systematic review and meta-analysis of published randomized controlled trials comparing the role of self-gripping mesh against suture mesh fixation in patients undergoing open inguinal hernia repair. Updates Surg.2014;66(3):189-196.
[24] Bresnahan E,Bates A,Wu A,et al.The use of self-gripping (Progrip™) mesh during laparoscopic total extraperitoneal (TEP) inguinal hernia repair: a prospective feasibility and long-term outcomes study.Surg Endosc.2014.[Epub ahead of print]
[25] Birk D,Hess S,Garcia-Pardo C,et al.Low recurrence rate and low chronic pain associated with inguinal hernia repair by laparoscopic placement of Parietex ProGrip™ mesh: clinical outcomes of 220 hernias with mean follow-up at 23 months. Hernia.2013;7(3):313-320.
|