中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (34): 5512-5512.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.34.019
• 细胞外基质材料 extracellular matrix materials • 上一篇 下一篇
动物源Ⅰ型胶原蛋白可引起BALB/c小鼠细胞免疫反应和组织免疫毒性
雷 静1,2,李奕恒3,刘旭昭2,3,汤顺清1,2
- 1暨南大学生物医学工程研究所,广东省广州市 510632; 2广东省医用胶原工程技术研究开发中心,广东省广州市 510663; 3广州创尔生物技术股份有限公司,广东省广州市 510663
Cellular immune response and immune toxicity to BALB/c mice for animal-based collagen
Lei Jing1, 2, Li Yi-heng3, Liu Xu-zhao2, 3, Tang Shun-qing1, 2
- 1Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Medical Collagen Engineering Technology Research and Development Center, Guangzhou 510663, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangzhou Trauer Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510663, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
背景:天然纯胶原被认为具有较低的免疫原性和较好的生物相容性。
目的:体外评估动物源Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的免疫原性。
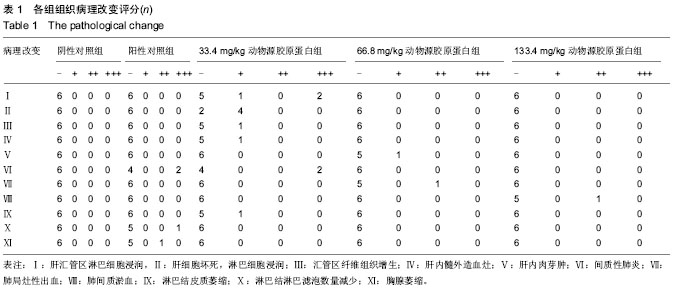
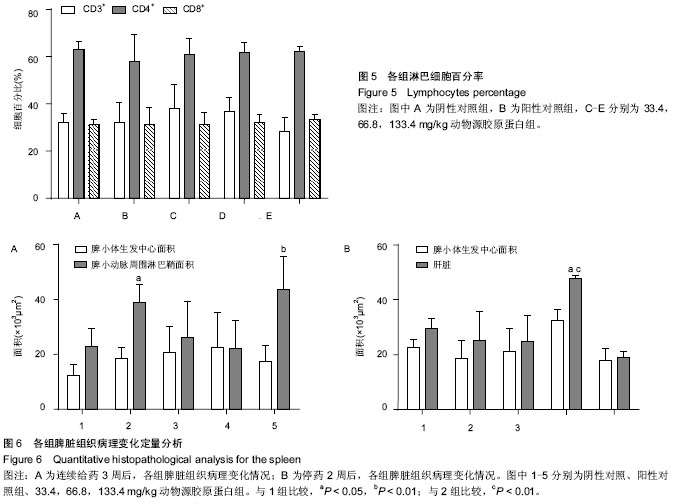
方法:将牛跟腱经免疫原性清除后,提取制成Ⅰ型胶原蛋白,HPLC测定胶原蛋白纯度,荧光染色定量胶原蛋白中残留DNA。将50只BALB/c小鼠随机均分为5组,分别皮下注射生理盐水(阴性对照)、小牛来源Ⅰ型胶原蛋白标准品(阳性对照)、33.4,66.8,133.4 mg/kg的动物源Ⅰ型胶原蛋白,1次/d,连续注射12 d后,检测注射胶原蛋白后小鼠淋巴细胞的增殖、细胞分型及NK细胞杀伤功能;连续注射3周后,取脾脏、肝脏及肺组织进行病理组织学检查。
结果与结论:相比Ⅰ型胶原蛋白标准品,纯化后的牛源性Ⅰ型胶原蛋白纯度可达到99%以上,而残留DNA低于1 mg/L,远远低于目前常规脱细胞基质中DNA的残留水平50-100 µg/g(干质量)。注射12 d后,各组均未发生淋巴细胞增殖、NK细胞杀伤功能及淋巴细胞亚群的比例的变化。注射3周后,66.8,133.4 mg/kg动物源胶原蛋白组小鼠脾小动脉周围淋巴鞘面积明显增厚变大,有可能引发偶发性的肝损伤和肺损伤,而脾小体生发中心面积未发生明显变化。表明连续皮下注射动物源胶原蛋白可引发BALB/c小鼠发生较低水平的脾淋巴细胞免疫应答,可能引起偶发性肝、肺损伤。
中图分类号: