中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (31): 5057-5064.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.31.026
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
防旋髓内钉、动力髋螺钉及全髋关节置换修复老年股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析
乔永杰1,曹雪飞1,张吕丹2,王钦鹏3,甄 平4
- 兰州大学第二医院,1骨科,3神经内科,甘肃省兰州市 730000;解放军兰州军区兰州总医院,2呼吸科,4骨科,甘肃省兰州市 730050
A meta-analysis of proximal femoral nail anti-rotation, dynamic hip screw and total hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly
Qiao Yong-jie1, Cao Xue-fei1, Zhang Lv-dan2, Wang Qin-peng3, Zhen Ping4
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2Department of Pneumology, Lanzhou General Hospital, Lanzhou Military Area Command of Chinese PLA, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China; 3Department of Neurology, Second Hospital, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 4Department of Orthopedics, Lanzhou General Hospital, Lanzhou Military Area Command of Chinese PLA, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China)
摘要:
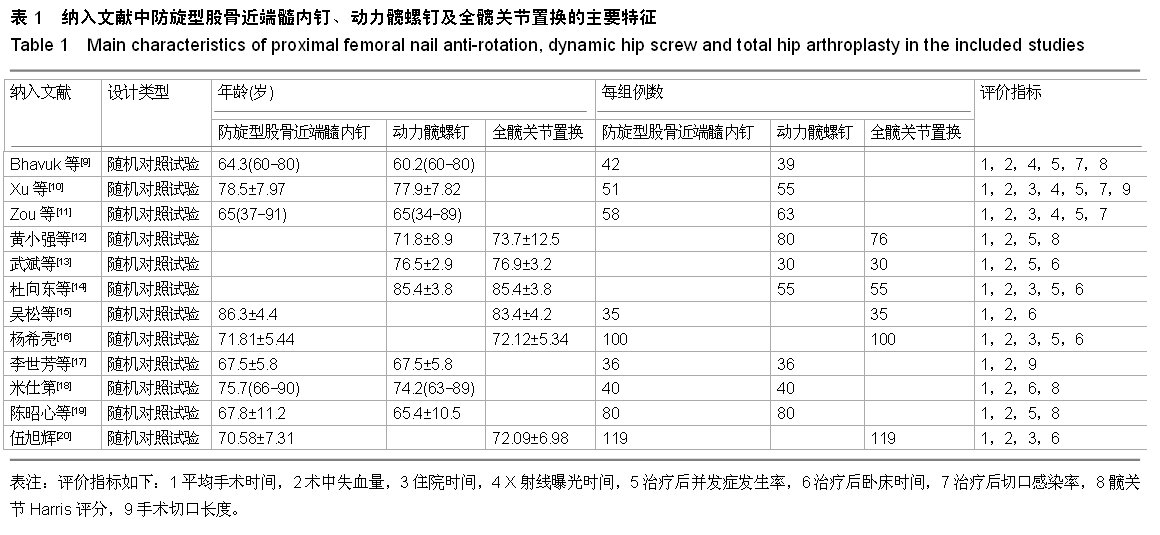
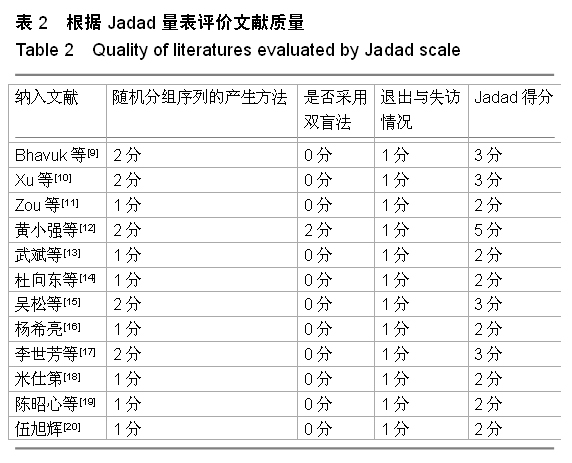
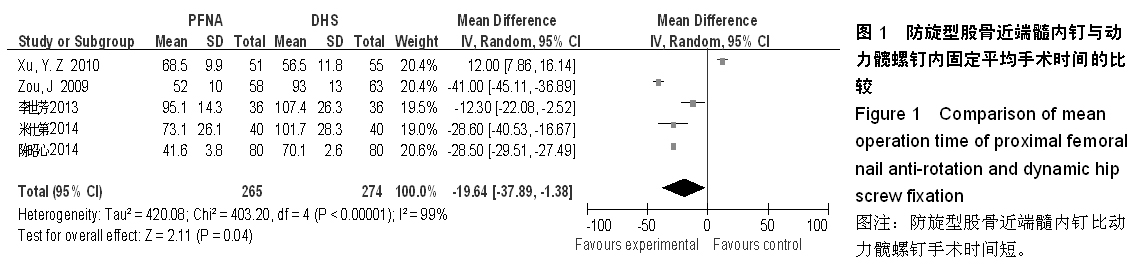
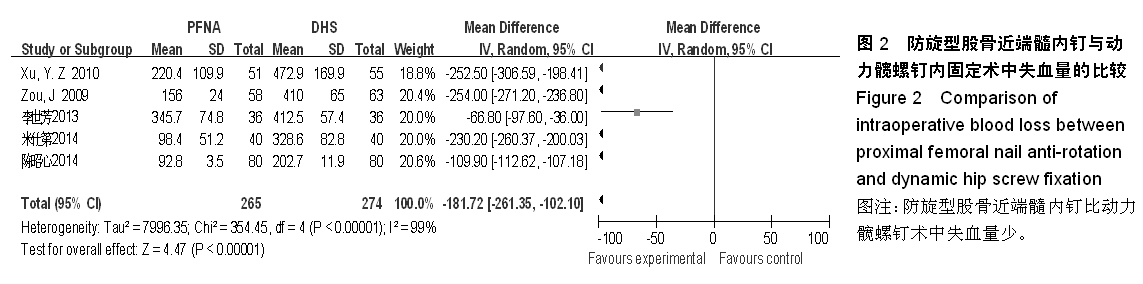
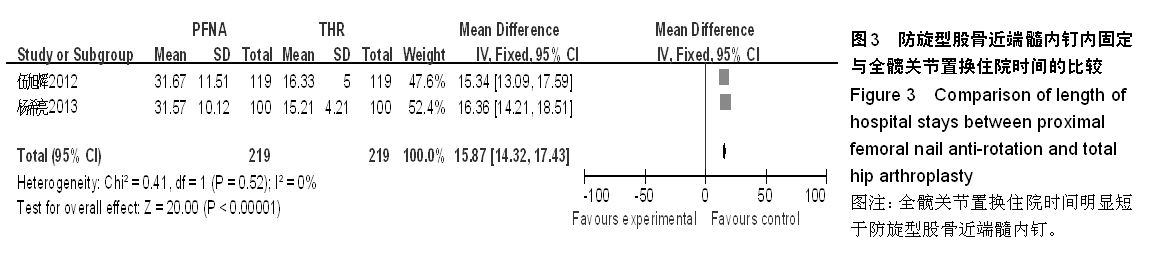
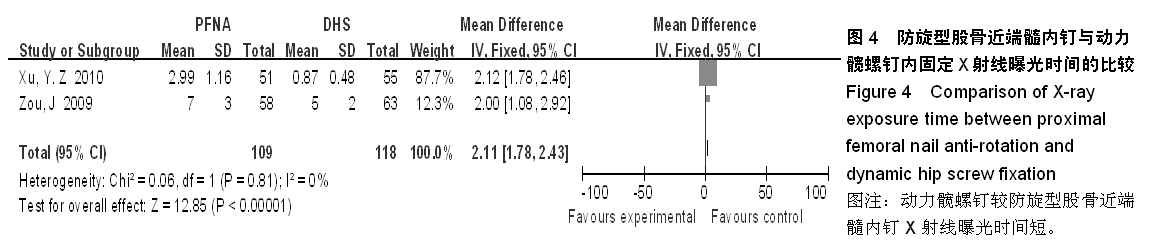
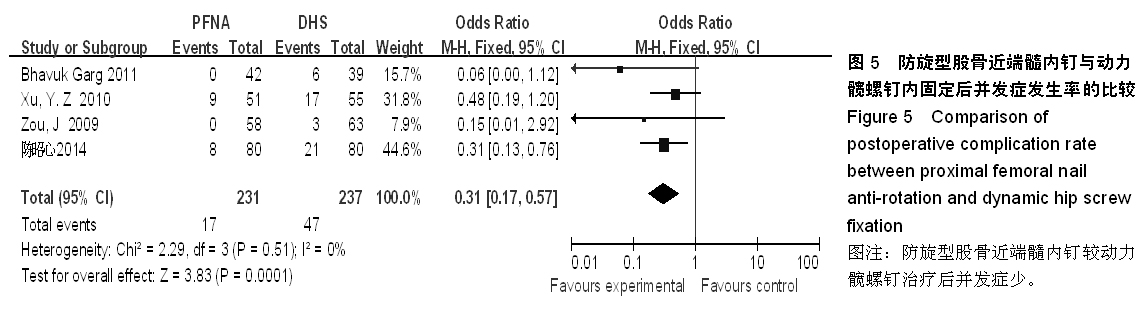
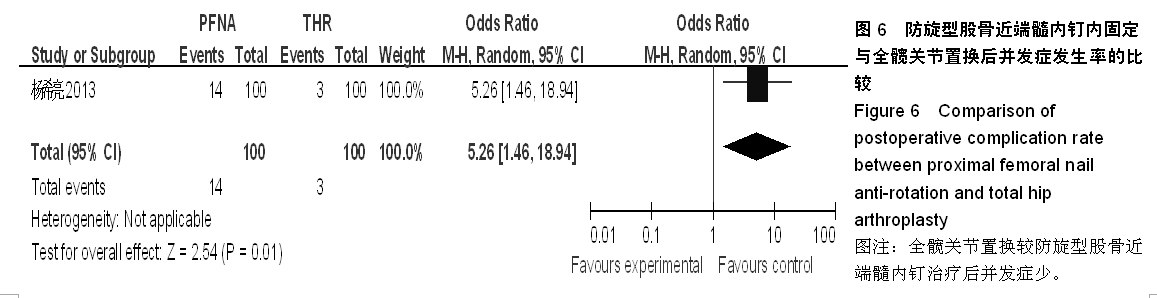
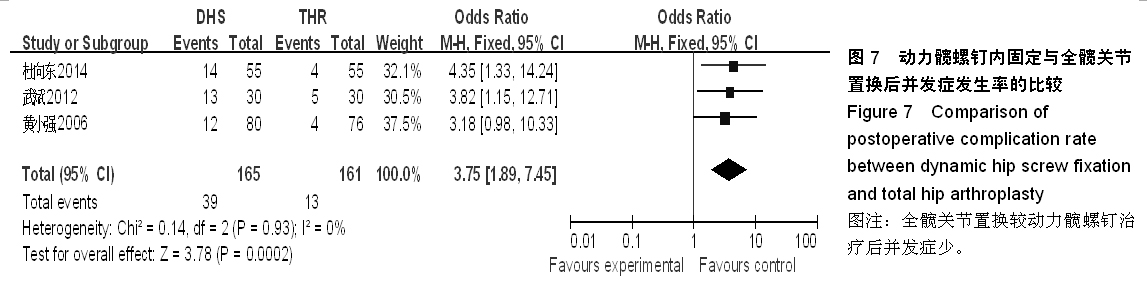
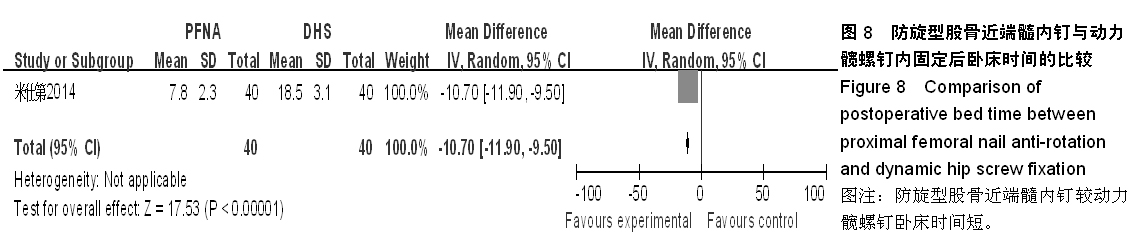
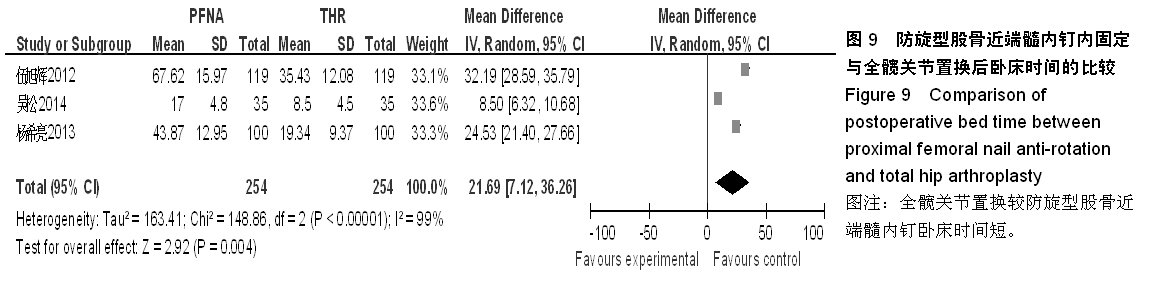
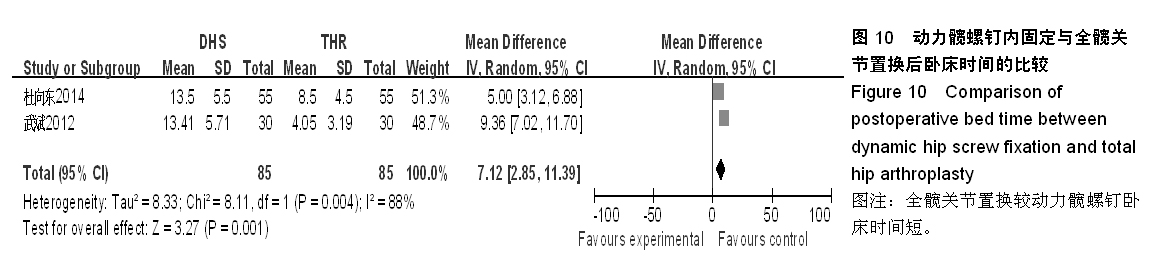
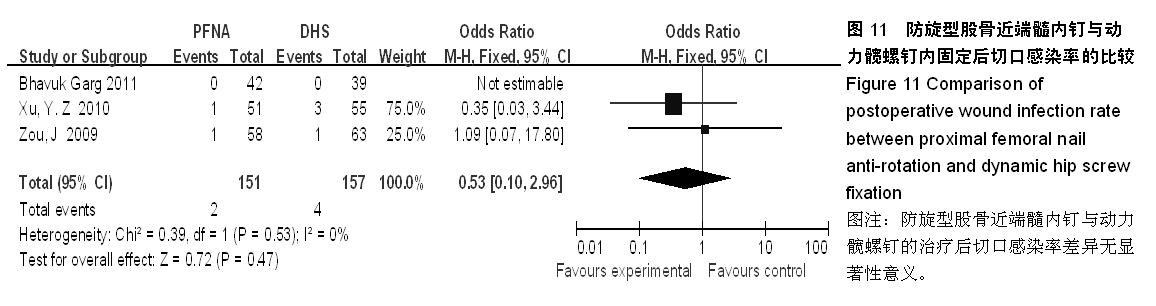
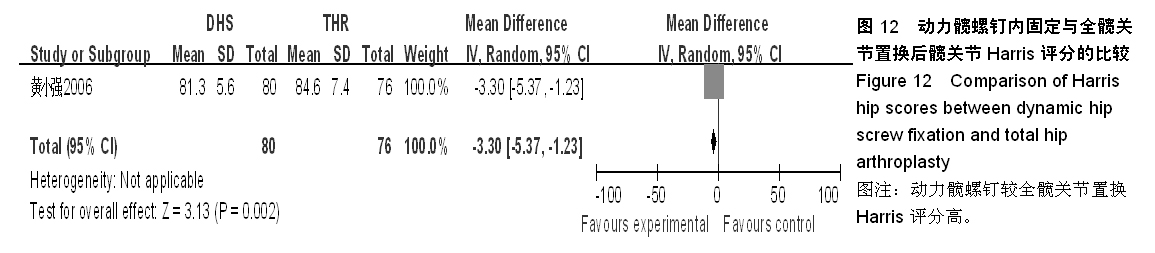
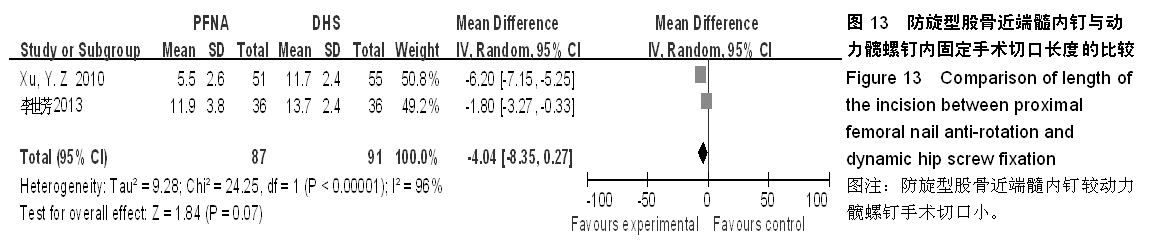
背景:股骨转子间骨折在治疗上选择何种方案仍存在较大争议。对于几种主流方法修复转子间骨折的疗效,已有大量的临床试验论著发表,但这些结果的评价缺乏独立性,可能存在变量及观察研究中无法测量的偏倚,因此使得相关研究进展受到了限制。 目的:通过Meta分析比较防旋型股骨近端髓内钉、动力髋螺钉与人工全髋关节置换对老年股骨转子间骨折的修复效果。 方法:计算机检索Cochrane图书馆、PubMed数据库、Web of Science数据库及中国生物医学文献数据库(CBM),收集防旋型股骨近端髓内钉、动力髋螺钉与全髋关节置换修复老年股骨转子间骨折的随机对照试验,采用循证医学Meta分析方法对患者X射线曝光时间、治疗后并发症发生率、治疗后卧床时间、治疗后切口感染率、髋关节Harris评分、平均手术时间、术中出血、住院时间及手术切口长度进行综合评价。严格评价纳入标准及方法学质量并提取相关资料。统计学软件采用Cochrane协作网提供的RevMan 5.0。 结果与结论:共纳入12个随机对照试验,共包含1 454例患者。防旋型股骨近端髓内钉和动力髋螺钉内固定两种方法在平均手术时间、术中失血量、X射线曝光时间、治疗后并发症发生率、治疗后卧床时间上差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。防旋型股骨近端髓内钉固定和全髋关节置换两种方法在住院时间、治疗后并发症发生率、治疗后卧床时间上差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。动力髋螺钉内固定和全髋关节置换两种方法在治疗后并发症发生率、治疗后卧床时间、髋关节Harris评分上差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。提示在手术时间、术中出血量、住院时间、治疗后并发症、治疗后卧床时间上防旋型股骨近端髓内钉明显优于动力髋螺钉和全髋关节置换,具有明显优势;在X射线曝光时间上,动力髋螺钉要优于防旋型股骨近端髓内钉;但在住院时间、治疗后并发症、治疗后卧床时间方面,全髋关节置换要优于动力髋螺钉和防旋型股骨近端髓内钉。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: