| [1]DeBakey ME. Development of mechanical heart devices. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79(6):S2228-2231.[2]Lietz K, Long JW, Kfoury AG, et al. Outcomes of left ventricular assist device implantation as destination therapy in the post-REMATCH era: implications for patient selection. Circulation. 2007;116(5):497-505.[3]Rose EA, Gelijns AC, Moskowitz AJ, et al. Long-term use of a left ventricular assist device for end-stage heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(20):1435-1443.[4]Thunberg CA, Gaitan BD, Arabia FA, et al. Ventricular Assist Devices Today and Tomorrow. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2010;24(4):656-680.[5]Pagani FD, Miller LW, Russell SD, et al. Extended mechanical circulatory support with a continuous-flow rotary left ventricular assist device. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(4): 312-321.[6]Wiliams DF. On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2008;29(20):2941-2953.[7]Ito Y, Hasuda H, Sakuragi M, et al. Surface modification of plastic, glass and titanium by photoimmobilization of polyethylene glycol for antibiofouling. Acta Biomater. 2007; 3(6):1024-1032.[8]Krishnan LK, Varghese N, Muraleedharan CV, et al. Quantitation of platelet adhesion to Ti and DLC-coated Ti in vitro using (125)I-labeled platelets. Biomol Eng. 2002;19(2-6): 251-253.[9]Treves C, Martinesi M, Stio M, et al. In vitro biocompatibility evaluation of surface-modified titanium alloys. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92(4):1623-1634.[10]Kuo WH, Wang MJ Chien HW, et al. Surface modification with poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate-co-acrylic acid) to reduce fibrinogen adsorption, platelet adhesion, and plasma coagulation. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12(12):4348-4356.[11]Choi J, Konno T, Matsuno R, et al. Surface immobilization of biocompatible phospholipid polymer multilayered hydrogel on titanium alloy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2008;67(2): 216-223.[12]Ye SH, Johnson CA, Woolley JR, et al. Surface modification of a titanium alloy with a phospholipid polymer prepared by a plasma-induced grafting technique to improve surface thromboresistance. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2009; 74(1):96-102.[13]Ye SH, Johnson CA Jr, Woolley JR, et al. Simple surface modification of a titanium alloy with silanated zwitterionic phosphorylcholine or sulfobetaine modifiers to reduce thrombogenicity. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010;79(2): 357-364.[14]Choi J, Konno T, Takai M, et al. Controlled drug release from multilayered phospholipid polymer hydrogel on titanium alloy surface. Biomaterials. 2009;30(28):5201-5208.[15]Yang Z, Wang J, Luo R, et al. The covalent immobilization of heparin to pulsed-plasma polymeric allylamine films on 316L stainless steel and the resulting effects on hemocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2010;31(8):2072-2083.[16]Li G, Yang P, Liao Y, et al. Tailoring of the titanium surface by immobilization of heparin/fibronectin complexes for improving blood compatibility and endothelialization: an in vitro study. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12(4):1155-1168.[17]Subramanian A, Lin HY. Crosslinked chitosan: its physical properties and the effects of matrix stiffness on chondrocyte cell morphology and proliferation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;75(3):742-753.[18]Meng S, Liu Z, Shen L, et al. The effect of a layer-by-layer chitosan–heparin coating on the endothelialization and coagulation properties of a coronary stent system. Biomaterials. 2009;30(12):2276-2283.[19]Sheng YH, Kong XQ, Li SJ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(22): 4308-4312.盛燕辉,孔祥清,李世杰,等.壳聚糖/肝素和壳聚糖/重组水蛭素共价包被镍钛合金片的体外生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(22):4308-4312.[20]Li G, Yang P, Qin W, et al. The effect of coimmobilizing heparin and fibronectin on titanium on hemocompatibility and endothelialization. Biomaterials. 2011;32(21):4691-4703.[21]Li G, Zhang F, Liao Y, et al. Coimmobilization of heparin/fibronectin mixture on titanium surfaces and their blood compatibility. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010; 81(1):255-262.[22]Smith PK, Mallia AK, Hermanson GT. Colorimetric method for the assay of heparin content in immobilized heparin preparations. Anal Biochem.1980;109(2):466-473.[23]Gaunt A. Anaesthesia for cardiothoracic transplantation and ventricular assist devices. Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine. 2006;7(9):317-320.[24]Sin DC, Kei HL, Miao X. Surface coatings for ventricular assist devices. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2009;6(1):51-60.[25]Eisenstein E L, Anstrom K J, Kong D F, et al. Clopidogrel use and long-term clinical outcomes after drug-eluting stent implantation. JAMA. 2007;297(2):159-168.[26]Liu M, Xing L, Dai ZF, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(48):9478-9480.刘萌,邢雷,戴志飞,等.新型肝素铁抗凝血涂层修饰血管内支架[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(48):9478-9480.[27]Luo P, Yang J, Liu WY. Zhongguo Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng Xuebao. 2010;29(004):614-618.罗鹏,杨剑,刘维永.体外循环管道表面改性的回顾与进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2010,29(004):614-618. [28]Zeng WJ, Zhi QY. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(42):7903-7906.曾伟杰,支峭原.药物缓释涂层支架的材料学特点及其生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(42):7903-7906. [29]Chen J, Chen C, Chen Z, et al. Collagen/heparin coating on titanium surface improves the biocompatibility of titanium applied as a blood-contacting biomaterial. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(2):341-349.[30]Chuang TW, Masters KS. Regulation of polyurethane hemocompatibility and endothelialization by tethered hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides. Biomaterials. 2009;30(29): 5341-5351. |
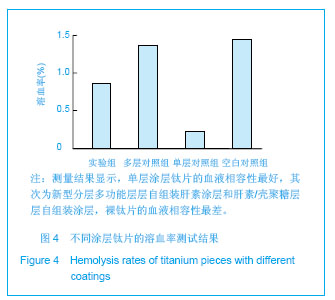
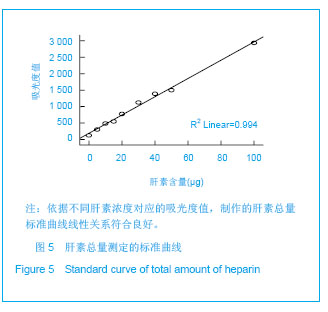
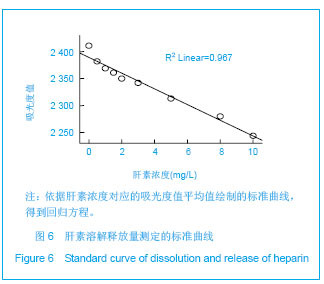
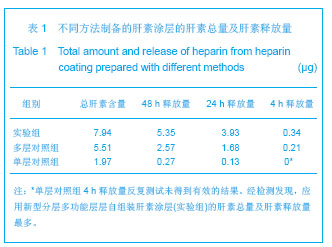
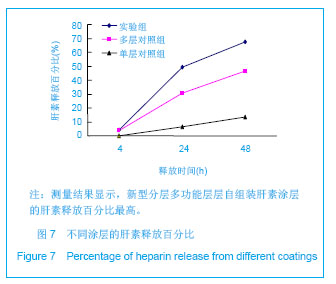
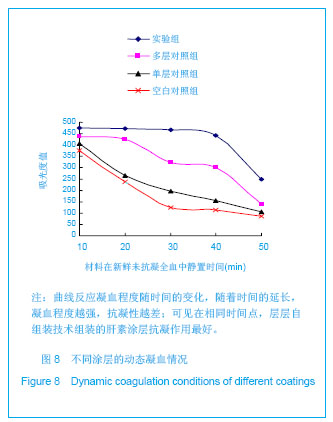
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)