| [1] Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena-Cagnani CE, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126(3):466-476.
[2] Nathan RA. The burden of allergic rhinitis//Allergy and Asthma Proceedings. Ocean Side Publications Inc. 2007; 28(1):3-9.
[3] 钱迪,洪苏玲,杨玉成,等.我国西部部分地区变应性鼻炎流行病学抽样调查[J].第三军医大学学报,2008,30(6):539-542.
[4] Winther B, Innes DJ Jr, Mills SE, et al. Lymphocyte subsets in normal airway mucosa of the human nose. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1987;113(1):59-62.
[5] Sánchez-Velasco P, Mendizábal L, Antón EM, et al. Association of hypersensitivity to the nematode Anisakis simplex with HLA class II DRB1*1502-DQB1*0601 haplotype. Hum Immunol. 2000;61(3):314-319.
[6] Woszczek G, Kowalski ML, Borowiec M. Association of asthma and total IgE levels with human leucocyte antigen-DR in patients with grass allergy. Eur Respir J. 2002;20(1):79-85.
[7] Kim YK, Oh SY, Oh HB, et al. Positive association between HLA-DRB1*07 and specific IgE responses to purified major allergens of D. pteronyssinus (Der p 1 and Der p 2). Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002;88(2):170-174.
[8] 齐名,魏花,朱琴,等.二球悬铃木花粉变应原特应性体质与HLA- DRB1等位基因相关性分析[J].临床检验杂志, 2007,24(6): 401-403.
[9] 崔忠涛,张华.新疆部分地区汉族变应性鼻炎患者 HLA-DRB1 基因多态性分析[J].新疆医科大学学报,2010,33(3):253-254.
[10] 崔忠涛,张华,刘云连,等.新疆部分地区维, 汉族变应性鼻炎患者HLA-DQB1基因多态性分析[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2011,25(14):645-648.
[11] Munthe-Kaas MC, Carlsen KL, Carlsen KH, et al. HLA Dr-Dq haplotypes and the TNFA-308 polymorphism: associations with asthma and allergy. Allergy. 2007;62(9):991-998.
[12] Lincoln MR, Ramagopalan SV, Chao MJ, et al. Epistasis among HLA-DRB1, HLA-DQA1, and HLA-DQB1 loci determines multiple sclerosis susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(18):7542-7547.
[13] Brown JJ, Ollier WE, Arscott G, et al. Association of HLA-DRB1* and keloid disease in an Afro-Caribbean population. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(3):305-310.
[14] Berry MP, Graham CM, McNab FW, et al. An interferon-inducible neutrophil-driven blood transcriptional signature in human tuberculosis. Nature. 2010;466(7309):973-977.
[15] Lucey DR, Clerici M, Shearer GM. Type 1 and type 2 cytokine dysregulation in human infectious, neoplastic, and inflammatory diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996;9(4):532-562.
[16] 吴健.RCG与变应性哮喘TH1/TH2平衡[J].国外医学:呼吸系统分册,2001,21(3):151-153.
[17] Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, et al. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986; 136(7):2348-2357.
[18] Maggi E, Biswas P, Del Prete G, et al. Accumulation of Th-2-like helper T cells in the conjunctiva of patients with vernal conjunctivitis. J Immunol. 1991;146(4):1169-1174.
[19] Torres-Galván MJ, Quiralte J, Blanco C, et al. Linkage of house dust mite allergy with the HLA region. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1999;82(2):198-203.
[20] 杨晖,刘伟,贺芹.支气管哮喘患者Th亚群及血清中免疫球蛋白的变化[J].山东医药,2003,43(4):44-45.
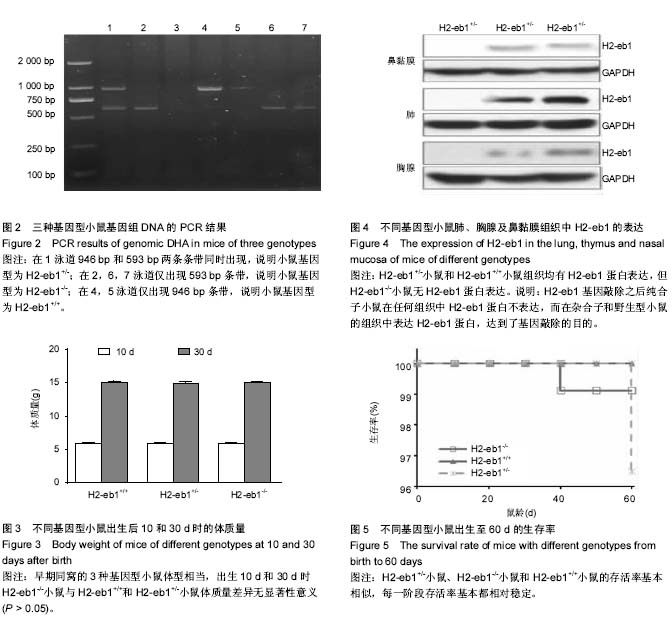
[21] 韩灵,孙悦奇,付清玲,等.呼吸道变应性炎性反应小鼠模型的建立[J]. 2013,48(3):224-228.
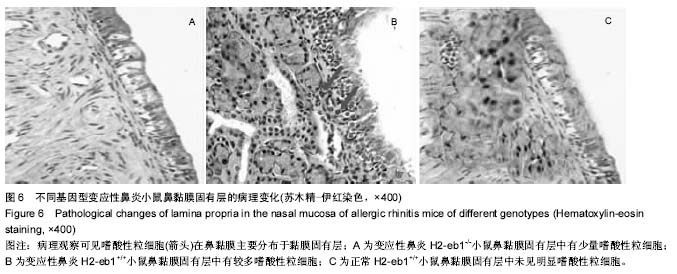
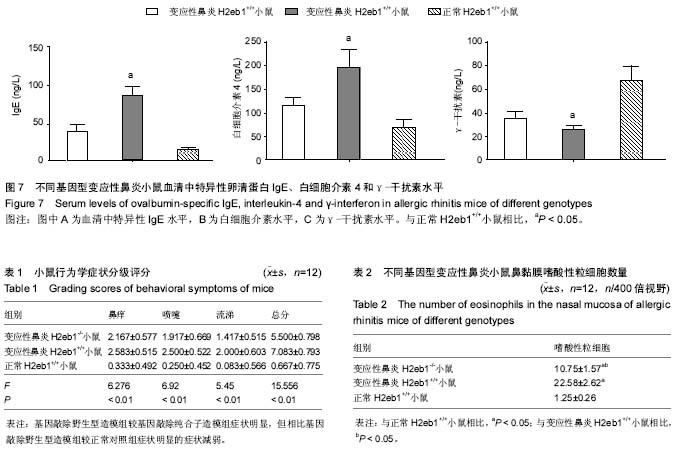
[22] 冯会杰,杨扬,周焕,等.变应性鼻炎鼻黏膜组织重塑的研究[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2012,26(5):205-208.
[23] Stern ME, Siemasko K, Gao J, et al. Role of interferon-gamma in a mouse model of allergic conjunctivitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46(9):3239-3246.
[24] Chae SC, Park YR, Li CS, et al. Analysis of the variations in IL-28RA gene and their association with allergic rhinitis. Exp Mol Med. 2006;38(3):302-309.
[25] Lee SM, Gao B, Dahl M, et al. Decreased FoxP3 gene expression in the nasal secretions from patients with allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140(2):197-201.
[26] Sogut A, Yilmaz O, Kirmaz C, et al. Regulatory-T, T-helper 1, and T-helper 2 cell differentiation in nasal mucosa of allergic rhinitis with olive pollen sensitivity. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012;157(4):349-353. |