中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (27): 4339-4344.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.27.014
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
早期稳定型动脉粥样硬化斑块模型兔损伤区拉曼光谱特征及旋转手法的影响
谌祖江1,黄学成1,向孝兵2,陈 超1,李义凯1
- 1南方医科大学中医药学院,广东省广州市 510515;
2广州市正骨医院运动医学科,广东省广州市 510045
早期稳定型动脉粥样硬化斑块模型兔损伤区拉曼光谱特征及旋转手法的影响
Chen Zu-jiang1, Huang Xue-cheng1, Xiang Xiao-bing2, Chen Chao1, Li Yi-kai1
- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China;
2Guangzhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guangzhou 510045, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
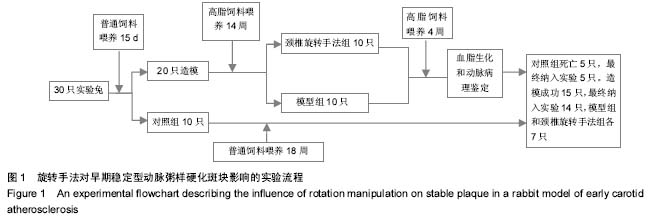
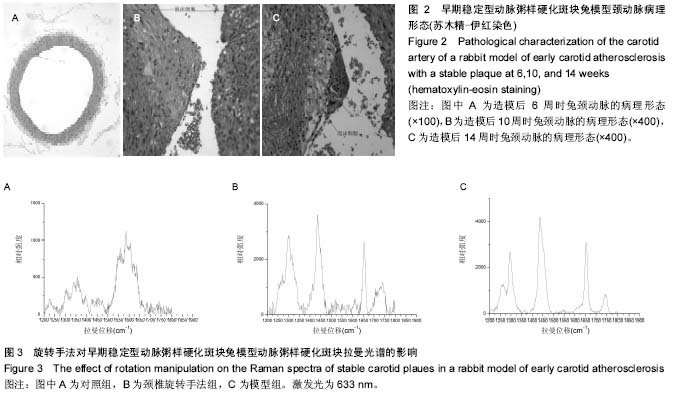
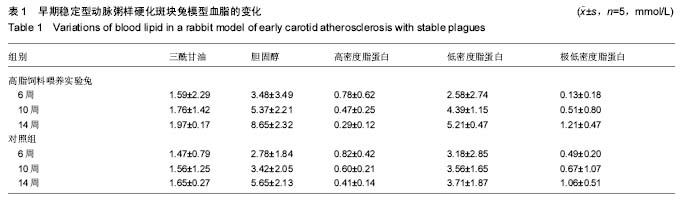
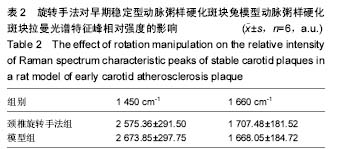
背景:研究普遍认可颈椎旋转手法可增加颈动脉粥样硬化不稳定型斑块脱落的风险,然而该手法对颈动脉粥样硬化早期稳定型斑块的影响研究甚少。 目的:探索颈椎旋转手法对动脉粥样硬化斑块模型兔脂质含量的影响。 方法:将30只雄性新西兰兔经普通饲料喂养15 d后,随机选取10只作为对照组,继续以普通饲料喂养至18周。剩余20只改用含2%胆固醇、10%猪油和88%普通颗粒饲料的高脂饲料喂养至18周,建立早期稳定型动脉粥样硬化斑块动物模型。高脂饲料喂养14周时,将高脂饲料喂养实验兔随机分为颈椎旋转手法组和模型组,各10只。颈椎旋转手法组兔施行颈椎旋转手法,左右各旋转1次(手法以兔子颈椎旋转至极限即止),1次/3 d,共5次。 结果与结论:对照组兔拉曼光谱图上未见明显的1 450 cm-1及1 660 cm-1脂质特征峰,颈椎旋转手法组和模型组兔动脉粥样硬化斑块均有明显的1 450 cm-1及1 660 cm-1脂质特征峰,但颈椎旋转手法组和模型组特征峰的相对强度差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。说明在颈动脉粥样硬化病变早期,短期内施用颈椎旋转手法并不会增加模型兔颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的脂质含量。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
中图分类号: