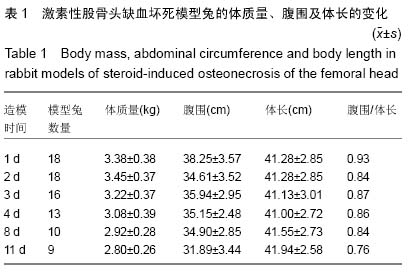
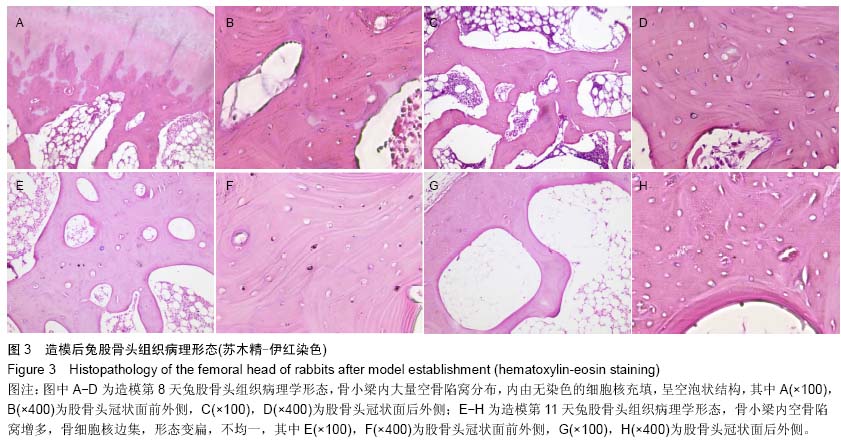
| [1] Qi X, Zeng Y. Biomarkers and pharmaceutical strategies in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A literature review. J Int Med Res. 2015;43(1):3-8.
[2] Powell C, Chang C, Gershwin ME. Current concepts on the pathogenesis and natural history of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011;41(1): 102-113.
[3] 王?懋,张长青.股骨头坏死实验动物模型:分类与实验应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(36):5879-5884.
[4] 费腾,阎作勤.激素性股骨头坏死发病机制的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2011,5(4):504-508.
[5] 冯金柱,王瑞,赵建宁.建立股骨头坏死动物模型的最新信息[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(44):8279-8282.
[6] Fan M, Peng J, Qin L, et al. Experimental animal models of osteonecrosis. Rheumatol Int. 2011;31(8):983-994.
[7] 李瑞琦,张国平,李宜炯,等.提高激素性股骨头坏死模型成活率的方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(50):8729-8734.
[8] Qin L, Zhang G, Sheng H, et al. Multiple bioimaging modalities in evaluation of an experimental osteonecrosis model induced by a combination of lipopolysaccharide and methylprednisolone. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008;22(3):258-264.
[9] Miyanishi K, Yamamoto T, Irisa T, et al. A high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as a potential risk factor for corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001;40(2): 196-201.
[10] 张成龙,尹华,章建华.股骨头坏死动物模型研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2013,23(3):58-62.
[11] Kim HK. Pathophysiology and new strategies for the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(7):659-669.
[12] Motomura G, Yamamoto T, Irisa T, et al. Dose effects of corticosteroids on the development of osteonecrosis in rabbits. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(12):2395-2399.
[13] 刘伟,赵劲民,苏伟,等.低剂量激素诱导股骨头缺血性坏死模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(43):8050- 8054.
[14] 赵广辉.联合用药对激素性股骨头坏死干预作用的实验研究[D].郑州:郑州大学, 2009.
[15] Tian L, Dang XQ, Wang CS, et al. Effects of sodium ferulate on preventing steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis in rabbits. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013;14(5):426-437.
[16] 王伟,刘利英,王坤正,等.激素性股骨头坏死模型的建立及其发病机理的探讨[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2007,28(5): 544-547.
[17] Saito S, Ohzono K, Ono K. Early arteriopathy and postulated pathogenesis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. The intracapital arterioles. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;(277): 98-110.
[18] Wu X, Yang S, Wang H, et al. G-CSF/SCF exert beneficial effects via anti-apoptosis in rabbits with steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2013;94(1):247-254.
[19] Fan L, Li J, Yu Z, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor prevents steroid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rabbits by promoting angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(9): e107774.
[20] Noa M, Más R, Valle M, et al. Effect of D-003, a Mixture of High Molecular Weight Aliphatic Acids, on Glucocorticoid- and Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-Induced Osteonecrosis. Iran J Pharm Res. 2012;11(4):1201-1208.
[21] 杨建平,王黎明,徐燕,等.单次低剂量脂多糖联合甲基强的松龙诱导股骨头坏死的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008, 22(3): 271-275.
[22] 苏强,孙天胜,王秋良,等.不同剂量内毒素联合激素建立兔股骨头缺血性坏死模型的影像学评估[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(11):2108-2111.
[23] 李超,尚希福,李旭,等.提高激素性股骨头坏死兔模型动物存活率的实验研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2014,49(12):1726-1729.
[24] 陈冠儒,王萧枫,王利明,等.兔激素性股骨头坏死造模中的致死因素与干预分析[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2012,22(5):342-344.
[25] 李瑞琦,张国平,李宜炯,等.激素性股骨头坏死模型:不同构建技术分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(37):6676-6681. |