Currently experiments addressing the osteotome technique are mainly focused on quantitative and qualitative detection of animal experiments, and histological and radiological examinations have been used to explore the morphological changes of surrounding bone tissues in term of bone density after bone condensing. Stenport et al [10] used an osteotome to seed the implants into a rabbit femur, and researchers found that the osseointegration of cancellous bone was accelerated using the osteotome technique and furthermore, a large-animal experiment was suggested. According to the findings from Al-Maseeh et al [11], dog’s humeral samples were taken to prepare implant sockets, and the healing manner was observed when there was a gap using the osteotomy technique. In their study, the bone drill method and osteotomy technique were both used to prepare implant sockets with a diameter of 8 mm, which 6 mm implants were inserted into. Therefore, there was a 1 mm gap between the implant and surrounding tissues. The socket produced using the osteotomy technique was prepared based on a 5 mm socket made by the bone drill. The socket prepared by the bone drill had no changes in the diameter immediately after implantation, but the diameter of socket prepared using the osteotomy technique was reduced by 17%, and the trabecular bone that was shifted showed a significant rebound. The results show a marked increase in bone density immediately and 2 weeks after implantation using the osteotomy technique as well as osseointegration rate at 2 and 4 weeks after implantation. However, these methods for evaluation of bone density in the implant sockets are not tools to accurately and quantitatively analyze the effect of osteotomy technique, and meanwhile, they also cannot judge whether the bone condensing can impact osseointegration time and efficiency. Overall, there is still a lack of systemic quantitative comparisons of differential socket preparation and osteotomy techniques in clinical experiments.
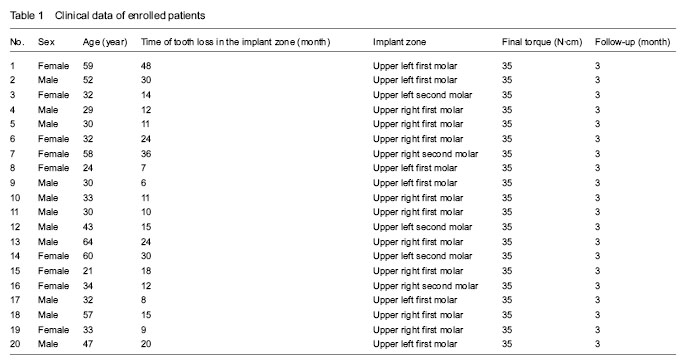
Can the osteotome technique improve implant success rate and accelerate osseointegration process?
Summers[9] first proposed in 1994 to increase the implant stability using the osteotome technique. Bone condensing is a method to prepare sockets using implant-matched osteotmes step-by-step instead of traditional bone drills, which can laterally compress the cancellous bone effectively, and meanwhile raise the bone density around the implant socket to minimize the bone loss caused by drilling. Al-Maseeh et al [11] found that using the osteotome technique, the implant was more tightly bonded with the surrounding bone because of bone bounce, which accelerates osseointegration process. However, the experimental design of bone condensing was to insert an implant with a smaller diameter than that of the socket, and the diameter of the socket could restore to 83% of original size immediately after implantation, which was still larger than the diameter of implant, indicating there was no pressure on the bone tissue after implantation. Additionally, the bone condensing was done based on a socket with a diameter that was 3 mm less than the final diameter prepared by the bone drill. In clinic, implants with a diameter no less than the socket diameter are preferred, based on which, the bone condensing can inevitably lead to changes in the three-dimensional structure of the bone. The changes in bone structure may directly affect the blood circulation around the implant, thus influencing the blood supply of bone and bone healing process.
Previous literature suggests that the success rate of maxillary dental implantation is slightly lower than that of the mandible, especially near the maxillary tuberosity area, which is mainly because the sclerotin of maxilla is looser than that of the mandible. In addition, due to changes in estrogen levels, osteoporosis induced by increased calcium loss is also very common in the middle-aged women after menopause[12].
Based on clinical experience, the osteotome technique has achieved good clinical effects in the maxilla. As a result of loose and fine fibers of the trabecular bone (osteoid IV), there is relatively little influence on the blood circulation under the bone condensing as well as a lower probability of adverse reactions. Currently, there is still a lack of proven and reliable experimental evidence for whether the bone condensing can improve the success rate of dental implantation and accelerate osseointegration process. For osteoid I and II with higher bone mineral density, the bone condensing cannot be used to squeeze the bone wall effectively, or even result in osteonecrosis because of excessive implant-bone interface stress. At present, choosing the appropriate implant is a necessary mean to improve the early stability and success rate of implants in patients with osteoporosis scheduled for osteotome treatment[13].
Resonance frequency analysis of the osteotome technique effects on implant stability during osseointegration
In the past, X-ray, CT and bone densitometry were used to predict the primary stability of implants based on the bone substance in the implant region, and to develop an implanting plan before surgery. During the socket preparation, the appropriate implants were chosen based on sclerotin classification in order to obtain a higher stability. The most commonly used method for bone type classification is Lekholm and Zarb classification. This method refers to a relatively rough classification of clinical bone types, which cannot objectively predict the exact stability of implants immediately after implantation as well as variation trends of the implant stability in the late stage, and thus there is a certain restriction in the clinical application.
Resonance frequency analysis is a new kind of implant stability measurement tool developed in recent years, and its value is determined by the hardness of the bone around the implant and distance from bone sensing cantilever to the first-contacted bone. This tool is more objective to measure the clinical implant stability, which is non-invasive, convenient and accurate for long-term monitoring of implant stability[14]. The value of resonant frequency is generally converted into implant stability coefficient that can be used to analyze the expression value of implant stability. Resonance frequency analysis using OSSTELL device can be used to monitor the osseointegration during the healing process of implant and assist clinicians to determine when the upper structure can be loaded. The implant stability can be divided into primary implant stability (immediately after implantation) and biostability (after bone healing). Poor primary stability can lead to the formation of fibrous connective tissue between the bone and implant; inversely, too much emphasis on the primary stability may lead to excessive pressure on the bone, damaging the local micro-circulation and bone metabolism as well as impacting the biostability formation[15-20].
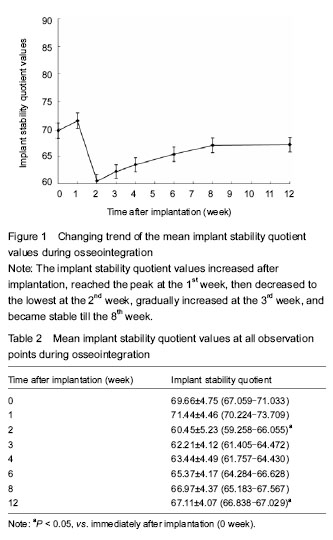
In this study, the resonant frequency analyzer was used to monitor the implant stability quotient for 12 consecutive weeks following bone condensing, and the results showed significant differences existed in the implant stability quotient during the measurement period. The implant stability quotient reflected the rigid relationship between implant and bone. At dental implantation, the value of implant stability quotient was 69.66±4.75. Bone condensing caused the formation of a high-density peri-implant area, indicating the osteotome technique is effective to improve the primary implant stability. After implantation, the implant stability quotient had an increase trend within the 1st week, which may be interpreted as an increase in bone mineral density around the implant due to bone condensing, and afterwards, the socket had the ability to restore the original volume due to bone viscoelasticity. An increase in the rigidity between implant and surrounding bone tissue led to the rise of the implant stability quotient. At 2 weeks after implantation, the implant stability quotient reached the lowest point, indicating the bone resorption process, and then, it began to rise gradually at 3 weeks. This may be a process of mature lamellar bone instead of woven bone, and the rigidity between the implant and surrounding bone tissue became larger followed by an increase in the implant stability quotient[21-28]. At 8-12 weeks after implantation, the implant stability quotient (biostability) was at a plateau stage. Histological observation showed that the implant interface and surrounding bone tissue were completely replaced by mature lamellar bone tissues. At the same time, the rigidity between the implant and surrounding bone had no changes. Therefore, the implant stability quotient kept smooth at this stage[29-32].
Findings from the present study have demonstrated that the osteotome technique can bring out a higher implant stability quotient in the preosseous tissue of maxillary posterior teeth. The resonant frequency analysis can preliminarily reflect the changes in the implant stability quotient due to bone condensing quantitatively, and it is confirmed that it takes a relative prolonged time for biostability that can plateau. Generally, a relative prolonged time for implant restoration is recommended for IV osteoid area to ensure the implantation success. In this study, we only preliminarily investigated the changing trend of implant stability quotients due to osteotome technique, and bigger sample size and better stability data are needed for further understanding.