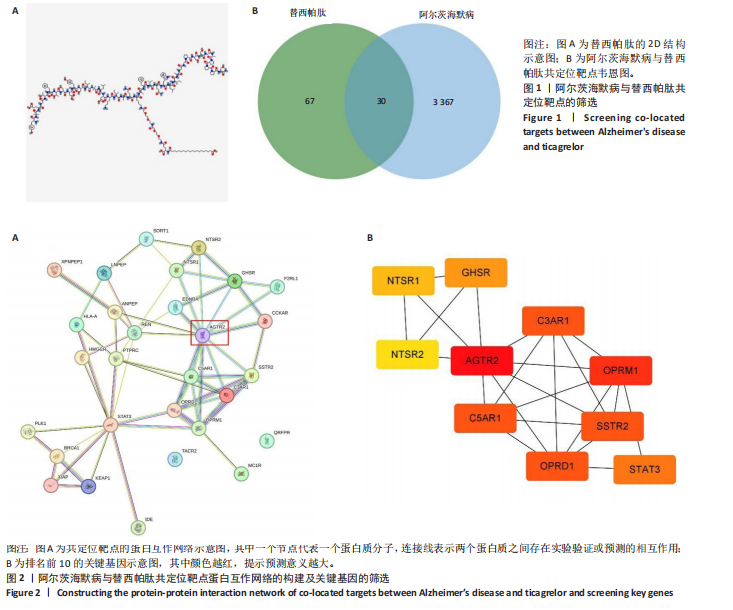
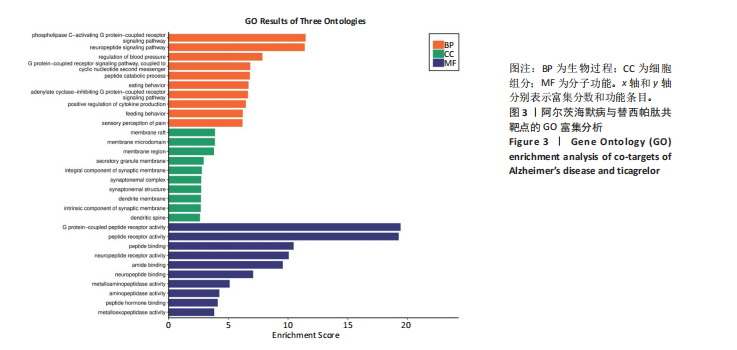
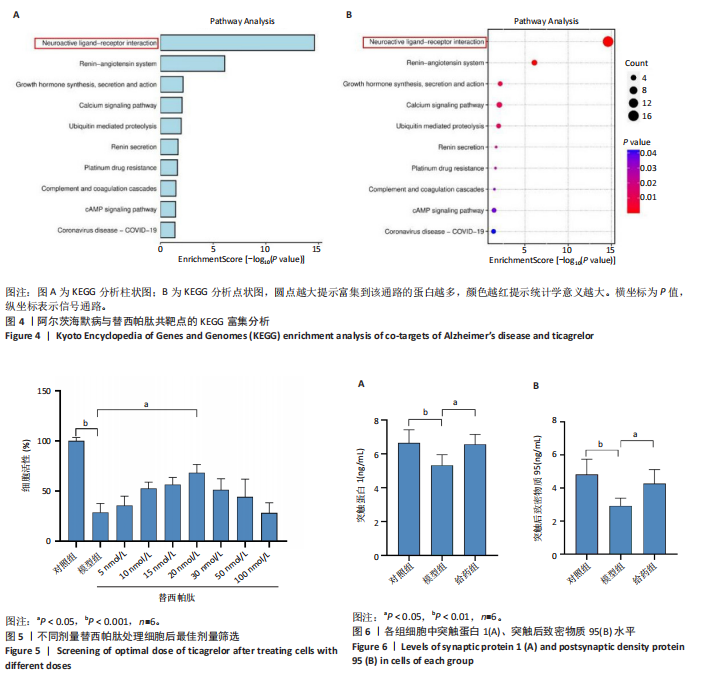
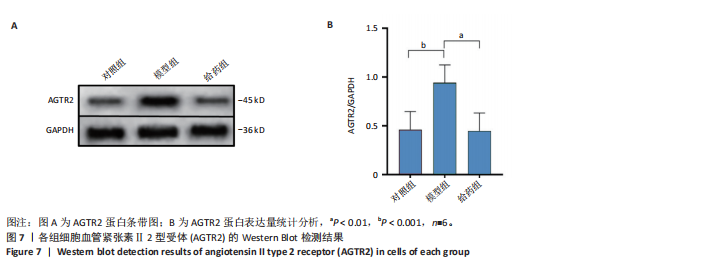
[1] SCHELTENS P, DE STROOPER B, KIVIPELTO M, et al.Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2021;397(10284):1577-1590.
[2] GRIFFITHS J, GRANT SGN. Synapse pathology in Alzheimer’s disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023;139:13-23.
[3] KAMATHAM PT, SHUKLA R, KHATRI DK, et al. Pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease: Breaking the memory barrier. Ageing Res Rev. 2024;101:102481.
[4] LIU E, ZHANG Y, WANG JZ. Updates in Alzheimer’s disease: from basic research to diagnosis and therapies. Transl Neurodegener. 2024;13(1): 45.
[5] RAJENDRAN K, KRISHNAN UM. Mechanistic insights and emerging therapeutic stratagems for Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2024; 97:102309.
[6] HUANG N, HUANG W, WANG M, et al. Biomaterials in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Anti-Neuroinflammatory Perspective. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025;14(19):e2500498.
[7] TZIORAS M, MCGEACHAN RI, DURRANT CS, et al. Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023;19(1):19-38.
[8] ZHANG X, LIU F, GU Z. Tissue Engineering in Neuroscience: Applications and Perspectives. BME Front. 2023;4:0007.
[9] YAN Y, LI X, GAO Y, et al. 3D bioprinting of human neural tissues with functional connectivity. Cell Stem Cell. 2024;31(2):260-74.e7.
[10] YAO X, XUE T, CHEN B, et al. Advances in biomaterial-based tissue engineering for peripheral nerve injury repair. Bioact Mater. 2025;46: 150-172.
[11] LIAO W, SHI Y, LI Z, et al. Advances in 3D printing combined with tissue engineering for nerve regeneration and repair. J Nanobiotechnol. 2025; 23(1):5.
[12] ZHANG B, HU Y, DU H, et al. Tissue engineering strategies for spiral ganglion neuron protection and regeneration. J Nanobiotechnol. 2024; 22(1):458.
[13] ZIVARI-GHADER T, VALIOGLU F, EFTEKHARI A, et al. Recent progresses in natural based therapeutic materials for Alzheimer’s disease. Heliyon. 2024;10(4):e2635.
[14] WU P, XU C, ZOU X, et al. Capacitive-Coupling-Responsive Hydrogel Scaffolds Offering Wireless In Situ Electrical Stimulation Promotes Nerve Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2024;36(14):e2310483.
[15] NOWELL J, BLUNT E, EDISON P. Incretin and insulin signaling as novel therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease . Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28(1):217-229.
[16] GUO X, LEI M, ZHAO J, et al. Tirzepatide ameliorates spatial learning and memory impairment through modulation of aberrant insulin resistance and inflammation response in diabetic rats. Front Pharmacol. 2023; 14:1146960.
[17] PIRTTILÄ T, KIM KS, MEHTA PD, et al. Soluble amyloid beta-protein in the cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia and controls. J Neurol Sci. 1994;127(1):90-95.
[18] JANELIDZE S, MATTSSON N, PALMQVIST S, et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat Med. 2020;26(3):379-386.
[19] WEI Y, XIA X, WANG X, et al. Enhanced BBB penetration and microglia-targeting nanomodulator for the two-pronged modulation of chronically activated microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025;15(2):1098-1111.
[20] WANG ZJ, LI XR, CHAI SF, et al. Semaglutide ameliorates cognition and glucose metabolism dysfunction in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via the GLP-1R/SIRT1/GLUT4 pathway. Neuropharmacology. 2023;240:109716.
[21] DU P, ZHANG X, LIAN X, et al. O-GlcNAcylation and Its Roles in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;97(3):1051-1568.
[22] HÖLSCHER C. Glucagon-like peptide-1 class drugs show clear protective effects in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease clinical trials: A revolution in the making? . Neuropharmacology. 2024;253:109952.
[23] HONG CT, CHEN JH, HU CJ. Role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. J Biomed Sci. 2024;31(1):102.
[24] 柴世凡, 李欣儒, 叶育采, 等. 索马鲁肽治疗阿尔茨海默病的潜在靶点:沉默信息调节因子1 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(20):3235-3239.
[25] MÜLLER TD, ADRIAENSSENS A, AHRÉN B, et al. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Mol Metab. 2025;95:102118.
[26] ZHOU ZD, YI L, POPŁAWSKA-DOMASZEWICZ K, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in neurodegenerative diseases: Promises and challenges. Pharmacol Res. 2025;216:107770.
[27] DIZ-CHAVES Y, MAASTOR Z, SPUCH C, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor activation: anti-inflammatory effects in the brain. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1671-1677.
[28] KARIMI MA, GHOLAMI CHAHKAND MS, DADKHAH PA, et al. Comparative effectiveness of semaglutide versus liraglutide, dulaglutide or tirzepatide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2025;16:1438318.
[29] KARAGIANNIS T, MALANDRIS K, AVGERINOS I, et al. Subcutaneously administered tirzepatide vs semaglutide for adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Diabetologia. 2024;67(7):1206-1222.
[30] HEISE T, MARI A, DEVRIES JH, et al. Effects of subcutaneous tirzepatide versus placebo or semaglutide on pancreatic islet function and insulin sensitivity in adults with type 2 diabetes: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-arm, phase 1 clinical trial. Lancet Diabetes. Endocrinol 2022;10(6):418-429.
[31] MELSON E, ASHRAF U, PAPAMARGARITIS D, et al. What is the pipeline for future medications for obesity? . Int J Obes. 2025;49(3):433-451.
[32] MASKERY M, GOULDING EM, GENGLER S, et al. The Dual GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonist DA4-JC Shows Superior Protective Properties Compared to the GLP-1 Analogue Liraglutide in the APP/PS1 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2020;35:1533317520953041.
[33] SALLES GN, CALIÓ ML, HÖLSCHER C, et al. Neuroprotective and restorative properties of the GLP-1/GIP dual agonist DA-JC1 compared with a GLP-1 single agonist in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology. 2020;162:107813.
[34] ZHANG Z, SHI M, LI Z, et al. A Dual GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonist Is More Effective than Liraglutide in the A53T Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2023;2023:7427136.
[35] YANG J, GU Y, CHEN H, et al. Tirzepatide’s innovative applications in the management of type 2 diabetes and its future prospects in cardiovascular health. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1453825.
[36] CIARDULLO S, MORIERI ML, DANIELE G, et al. GLP1-GIP receptor co-agonists: a promising evolution in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2024;61(8):941-950.
[37] PARVANOVA A, ABBATE M, RESEGHETTI E, et al. Mechanisms and treatment of obesity-related hypertension-Part 2: Treatments. Clin Kidney J. 2025;18(3):sfaf035.
[38] FONTANELLA RA, GHOSH P, PESAPANE A, et al. Tirzepatide prevents neurodegeneration through multiple molecular pathways .J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):114.
[39] ALSHEHRI GH, AL-KURAISHY HM, WAHEED HJ, et al. Tirzepatide: a novel therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease. Metab Brain Dis. 2025; 40(5):221.
[40] YANG S, ZHAO X, ZHANG Y, et al. Tirzepatide shows neuroprotective effects via regulating brain glucose metabolism in APP/PS1 mice. Peptides. 2024;179:171271.
[41] FATIMA N, PATEL SN, HUSSAIN T. Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor: A Target for Protection Against Hypertension, Metabolic Dysfunction, and Organ Remodeling. Hypertension. 2021;77(6):1845-1856.
[42] PORRELLO ER, DELBRIDGE LM, THOMAS WG. The angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor: an enigmatic seven transmembrane receptor. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009;14(3):958-972.
[43] SHEN L, CHEN DY, LOU QQ, et al. Angiotensin Type 2 Receptor Pharmacological Agonist Relieves Neurocognitive Deficits via Reducing Neuroinflammation and Microglial Engulfment of Dendritic Spines. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2023;18(1-2):41-57.
[44] SMITH HC, YU Z, IYER L, et al. Sex-Dependent Effects of Angiotensin Type 2 Receptor-Expressing Medial Prefrontal Cortex Interneurons in Fear Extinction Learning. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2024;4(5):100340.
[45] TAYLER HM, MACLACHLAN R, GÜZEL Ö, et al. Altered Gene Expression Within the Renin-Angiotensin System in Normal Aging and Dementia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024;79(1):glad241.
[46] THATHIAH A, DE STROOPER B. G protein-coupled receptors, cholinergic dysfunction, and Abeta toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Signal. 2009;2(93):re8.
[47] MONTEIRO AR, BARBOSA DJ, REMIÃO F, et al. Alzheimer’s disease: Insights and new prospects in disease pathophysiology, biomarkers and disease-modifying drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;211:115522.
[48] 李欣儒, 柴世凡, 李蔚然, 等 阿尔茨海默病发病机制相关基因生物信息学分析及实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(35):5653-5658.
[49] KRISHNAMURTHY HK, JAYARAMAN V, KRISHNA K, et al. An overview of the genes and biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2025;104:102599.
[50] ZHANG Y, CHEN H, LI R, et al. Amyloid β-based therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: challenges, successes and future. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):248.
[51] ZHENG Q, WANG X. Alzheimer’s disease: insights into pathology, molecular mechanisms, and therapy. Protein Cell. 2025;16(2):83-120.
[52] AHN EH, PARK JB. Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer’s Disease Induced by Amyloid-β and Tau Phosphorylation Along with RhoA Activity: Perspective of RhoA/Rho-Associated Protein Kinase Inhibitors for Neuronal Therapy. Cells. 2025;14(2):89.
[53] JIA B, XU Y, ZHU X. Cognitive resilience in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanism and potential clinical intervention. Ageing Res Rev. 2025;106:102711.
[54] LAZAROV O, GUPTA M, KUMAR P, et al. Memory circuits in dementia: The engram, hippocampal neurogenesis and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2024;236:102601.
[55] LEE C, KAANG BK. Clustering of synaptic engram: Functional and structural basis of memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem.2024; 216: 107993.
[56] TADDEI RN, KED. Synapse vulnerability and resilience underlying Alzheimer’s disease. EBioMedicine. 2025;112:105557.
[57] BÄHLER M, GREENGARD P. Synapsin I bundles F-actin in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Nature. 1987;326(6114):704-707.
[58] GYLYS KH, FEIN JA, YANG F, et al. Synaptic changes in Alzheimer’s disease: increased amyloid-beta and gliosis in surviving terminals is accompanied by decreased PSD-95 fluorescence. Am J Pathol. 2004;165(5):1809-1817.
[59] SUN J, XU J, LING Y, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviated Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):189.
[60] AJWAD N, MUSTAPHA M, IDRIS Z, et al. The Recent Applications of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Hydrogels in Neurological Disorders. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2025. doi: 10.1089/ten.teb.2024.0353.
[61] JIN J, ZHANG H, LU Q, et al. Nanocarrier-mediated siRNA delivery: a new approach for the treatment of traumatic brain injury-related Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(9):2538-5555.
[62] IYASWAMY A, THAKUR A, GUAN XJ, et al. Fe65-engineered neuronal exosomes encapsulating corynoxine-B ameliorate cognition and pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023; 8(1):404.
|