中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4088-4104.doi: 10.12307/2026.706
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
紫堇灵治疗急性髓系白血病:潜在机制的网络药理学分析和实验验证
周 武1,2,张静馨2,刘远程2,胡承龙2,王斯奇2,许建霞2,黄 海1,2,韦四喜1,2
- 1贵州医科大学附属医院临床检验中心,贵州省贵阳市 550004;2贵州医科大学医学检验学院,贵州省贵阳市 550004
-
收稿日期:2025-06-27接受日期:2025-09-08出版日期:2026-06-08发布日期:2025-11-26 -
通讯作者:韦四喜,博士,主任技师,博士生导师,贵州医科大学医学检验学院,贵州省贵阳市 550004;贵州医科大学附属医院临床检验中心,贵州省贵阳市 550004 -
作者简介:周武,男,1996年生,贵州省铜仁市人,贵州医科大学临床检验诊断学在读硕士,主要从事血液肿瘤相关基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:贵州医科大学慢性疾病标志物研究重点实验室项目(校重点实验室[2024]fy004号),项目负责人:韦四喜
Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia with corynoline: network pharmacology analysis of potential mechanisms and experimental validation
Zhou Wu1, 2, Zhang Jingxin2, Liu Yuancheng2, Hu Chenglong2, Wang Siqi2, Xu Jianxia2, Huang Hai1, 2, Wei Sixi1, 2
- 1Clinical Laboratory Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2School of Medical Laboratory Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2025-06-27Accepted:2025-09-08Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-26 -
Contact:Wei Sixi, PhD., Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Clinical Laboratory Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; School of Medical Laboratory Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhou Wu, MS candidate, Clinical Laboratory Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; School of Medical Laboratory Science, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Key Laboratory Project for Chronic Disease Biomarkers Research at Guizhou Medical University, No. [2024] fy004 (to WSX)
摘要:
文题释义:
急性髓系白血病:一种起源于骨髓造血干细胞或祖细胞的恶性克隆性疾病,临床表现为骨髓及外周血中原始和幼稚髓系细胞异常增生,常伴随造血功能抑制和多器官浸润,具有高度的异质性和侵袭性。
网络药理学:一种基于系统生物学和多靶点策略的研究方法,主要通过构建“药物-靶点-疾病”网络,系统解析中药或天然产物的作用机制,揭示其“多成分–多靶点–多通路”的药效特征。
背景:研究提示紫堇灵具有抗食管鳞状细胞癌、三阴性乳腺癌等肿瘤药理活性;然而,在治疗急性髓系白血病中的药理作用及其分子机制尚未被系统研究。
目的:探讨紫堇灵对急性髓系白血病的治疗作用及潜在分子机制。
方法:体外培养人急性髓系白血病细胞株Kasumi-1与MOLM-13,分别加入不同浓度(4,6,8 μmol/L)紫堇灵处理,同时以二甲基亚砜作为对照,培养24,48,72 h,使用CCK-8法检测细胞活力,流式细胞术评估紫堇灵的药理活性。利用网络药理学预测紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病的靶点基因;通过GO与KEGG分析揭示其潜在机制;构建蛋白质相互作用网络并结合临床相关性分析筛选核心靶点;使用分子对接与分子动力学模拟评估其与核心靶点的结合能力;qRT-PCR与Western blot验证其分子机制。
结果与结论:①紫堇灵可抑制急性髓系白血病细胞增殖,诱导其凋亡,并引发G2/M期细胞周期阻滞。②网络药理学筛选出紫堇灵与急性髓系白血病相关的交集靶点基因102个。③GO和KEGG分析表明,紫堇灵通过调节蛋白磷酸化、诱导细胞凋亡及靶向磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路等机制治疗急性髓系白血病。④蛋白质相互作用网络与临床相关性分析筛选出视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14为核心靶点,分子对接与分子动力学模拟显示紫堇灵与这些核心靶点具有强相互作用。⑤qRT-PCR和Western blot结果显示,紫堇灵通过抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路激活及促进鼠双微体基因2蛋白降解激活p53转录功能来发挥抗急性髓系白血病作用。⑥此项研究揭示了紫堇灵在体外抗急性髓系白血病中的药理学作用及潜在机制,为天然化合物在急性髓系白血病中的应用提供更多理论依据。
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-6817-5371(周武)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
周 武, 张静馨, 刘远程, 胡承龙, 王斯奇, 许建霞, 黄 海, 韦四喜. 紫堇灵治疗急性髓系白血病:潜在机制的网络药理学分析和实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(16): 4088-4104.
Zhou Wu, Zhang Jingxin, Liu Yuancheng, Hu Chenglong, Wang Siqi, Xu Jianxia, Huang Hai, Wei Sixi. Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia with corynoline: network pharmacology analysis of potential mechanisms and experimental validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4088-4104.
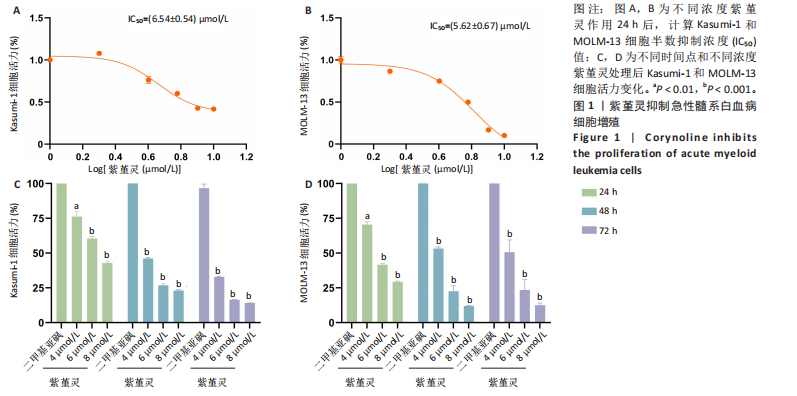
0.54) μmol/L和(5.62±0.67) μmol/L(图1A,B)。在此基础上,进一步采用低(4 μmol/L)、中(6 μmol/L)和高(8 μmol/L)浓度的紫堇灵处理细胞,分别于24,48 和72 h时点检测细胞活力。结果表明,随着紫堇灵浓度的升高,细胞活力在各时间点均呈现明显下降趋势(图1C,D)。以上结果提示,紫堇灵可在一定时间范围内以浓度依赖方式抑制Kasumi-1与MOLM-13细胞的增殖。
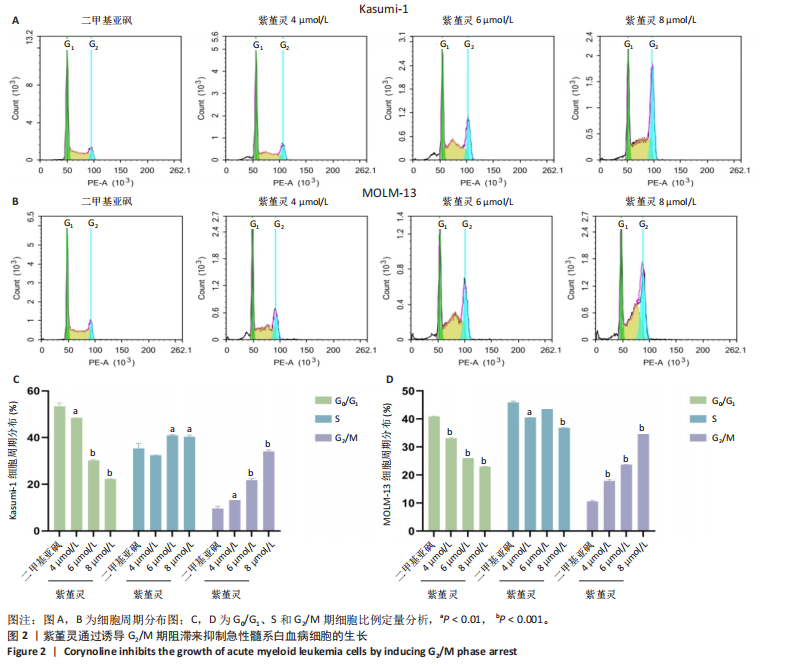
2.2 紫堇灵通过诱导G2/M期阻滞来抑制Kasumi-1与MOLM-13细胞生长 为进一步探讨紫堇灵抑制细胞增殖的机制,采用流式细胞术分析其对细胞周期分布的影响,见图2。结果显示,紫堇灵处理24 h后,Kasumi-1细胞G2/M期的细胞比例在4,6,8 μmol/L浓度下分别为(13.34±0.25)%,(21.78±0.64)%,(34.20±0.72)%,均高于对照组(9.67±0.91)%(图 2A,C)。在MOLM-13细胞中,G2/M期的细胞比例分别为(17.88±0.72)%,(23.69±0.28)%,(34.73±0.78)%,亦明显高于对照组(10.56±0.32)%(图 2B,D)。上述结果提示,紫堇灵通过诱导G2/M期阻滞从而抑制白血病细胞的生长。
2.3 紫堇灵诱导Kasumi-1与MOLM-13细胞凋亡 采用Annexin V-APC/7-AAD染色联合流式细胞术检测紫堇灵对细胞凋亡的影响,见图3。结果显示,在
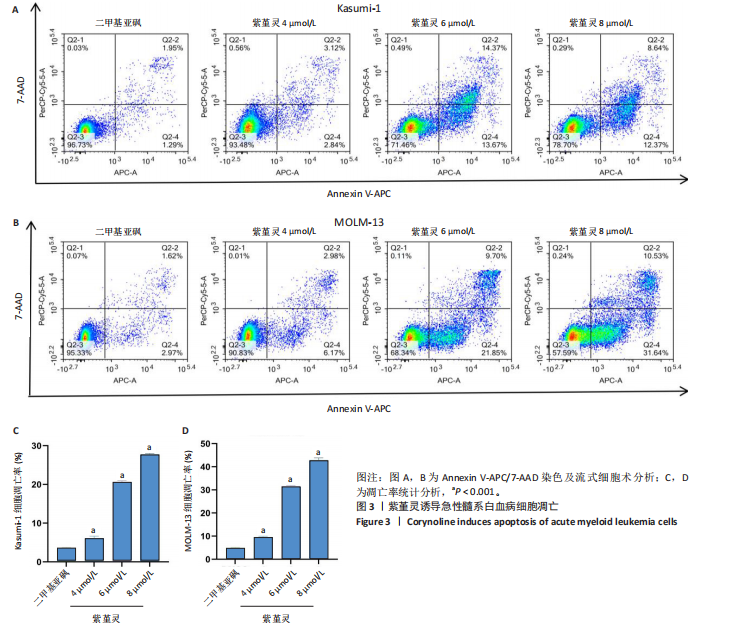
Kasumi-1细胞中,4,6,8 μmol/L紫堇灵处理24 h后,凋亡率分别为(5.93±0.71)%,(20.62±0.33)%,(27.75±0.24)%,明显高于对照组(3.47±0.21)%(图 3A,C);MOLM-13细胞的凋亡率分别为(9.55±0.37)%,(31.00±0.27)%,(42.88±0.86)%,也显著高于对照组(4.85±0.25)%(图 3B,D)。结果表明,紫堇灵可浓度依赖性诱导急性髓系白血病细胞凋亡,且MOLM-13对紫堇灵更敏感,因此被选为后续机制研究的模型细胞。
2.4 紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病的药物靶点预测 基于紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病的药理作用,研究通过网络药理学方法进一步探讨其可能作用机制。通过PubChem数据库获取紫堇灵的化学结构式(图4A),并利用PharmMapper、SwissTargetPrediction及TCMSP等数据库对其潜在药物靶点进行预测,共预测出292个靶点。同时,整合GeneCards、DrugBank和PharmGKB数据库检索预测出1 383个与急性髓系白血病相关的疾病基因。采用韦恩图分析方法对两者交集筛选,获得102个共同作用靶点(图4B)。为进一步揭示紫堇灵与急性髓系白血病之间的作用机制,使用Cytoscape 3.9.1 软件构建“药物-疾病-靶点”相互作用网络(图4C)。
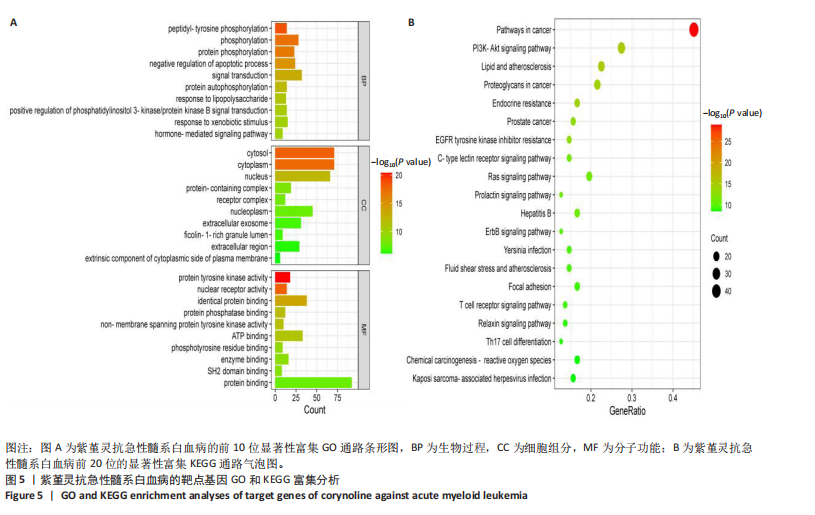
2.5 GO和KEGG富集分析 为明确紫堇灵调控急性髓系白血病的生物学过程及可能通路,将上述102个交集靶点导入DAVID数据库进行GO和KEGG富集分析。GO分析共识别出463条生物过程(BP)、54条细胞组分(CC)及116条分子功能(MF)富集项,选取P值前10的GO术语绘制条形图展示(图5A)。结果显示,生物过程(BP)主要富集于蛋白磷酸化、细胞凋亡的负调控及磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B信号通路等过程;细胞组分(CC)主要分布于细胞质、细胞核及蛋白质复合体;分子功能(MF)涉及蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性、核受体活性及蛋白结合等功能。KEGG富集结果显示共有144条信号通路显著富集,筛选前20位通路绘制气泡图(图5B)。其中磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B信号通路、癌症相关蛋白聚糖、脂质代谢与动脉粥样硬化等为主要通路。
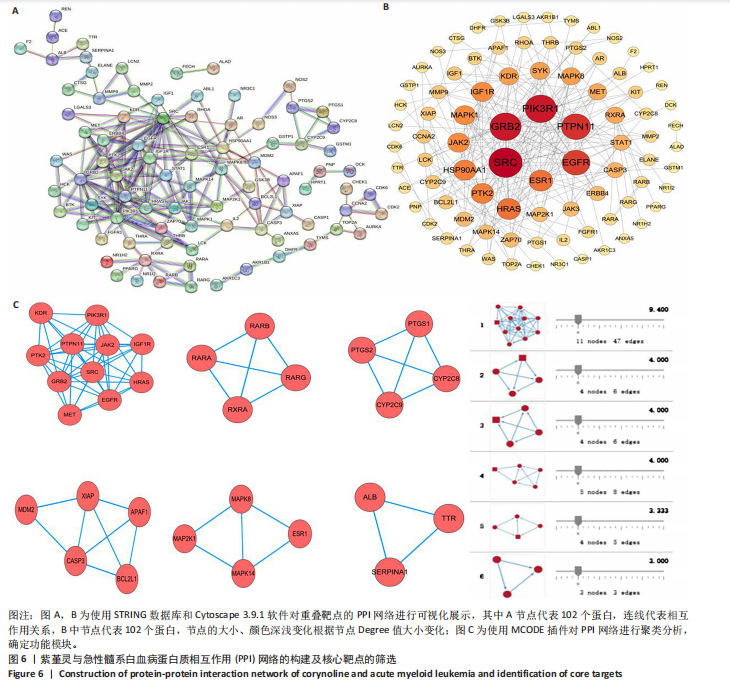
2.6 蛋白质相互作用网络的构建及核心靶点的筛选 利用STRING数据库,基于102个交叉靶点构建了蛋白质相互作用网络,并通过Cytoscape 3.9.1 软件进行可视化展示(图 6A,B)。该网络由86个节点和215条边组成。使用MCODE插件进行聚类分析,确定了6个紧密连接的子网络:聚类1(11个节点,47条边)、聚类2(4个节点,6条边)、聚类3(4个节点,6条边)、聚类4(5个节点,8条边)、聚类5(4个节点,5条边)以及聚类6(3个节点,3条边)。基于节点度(Degree)、介数中心性等拓扑参数,确定了5个核心靶点基因:蛋白酪氨酸激酶2(Protein tyrosine kinase 2,PTK2)、视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14(图6C),这些基因在网络中处于关键调控位置,可能参与紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病的主要生物过程。
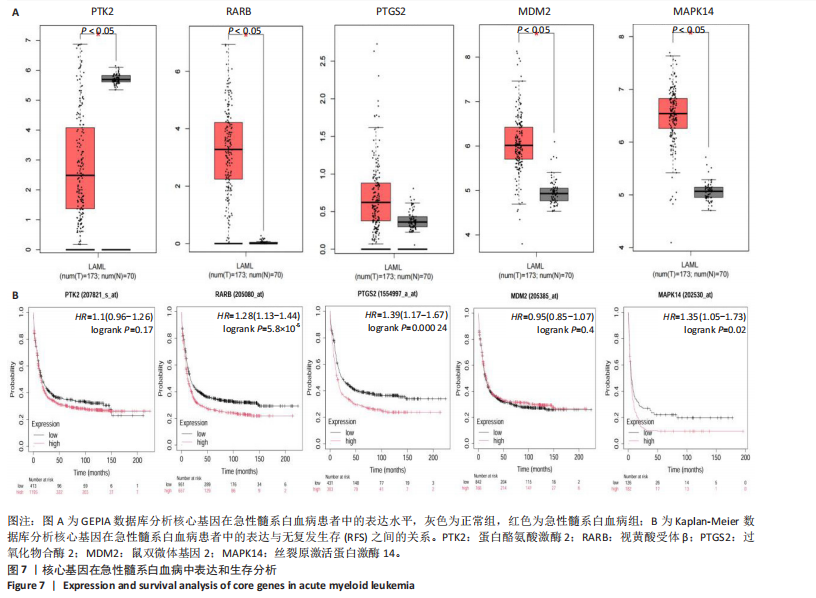
2.7 核心基因在急性髓系白血病中表达和生存分析 为探究核心靶点的临床意义,利用GEPIA2数据库分析蛋白酪氨酸激酶2、视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14的表达水平进行分析。结果显示,与正常对照组相比,急性髓系白血病样本中视黄酸受体β、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14的表达显著上调(图7A),提示这些基因可能作为紫堇灵治疗急性髓系白血病的潜在靶点。通过Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库进行的生存分析表明,视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14的高表达水平与急性髓系白血病患者较差的总体生存率显著相关(图7B)。这些发现表明,紫堇灵可能通过调控疾病进展中的关键基因发挥其抗急性髓系白血病作用,从而突显这些分子作为治疗干预靶点的重要价值。综合研究结果提示,视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14可能是介导紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病活性的关键分子靶标。
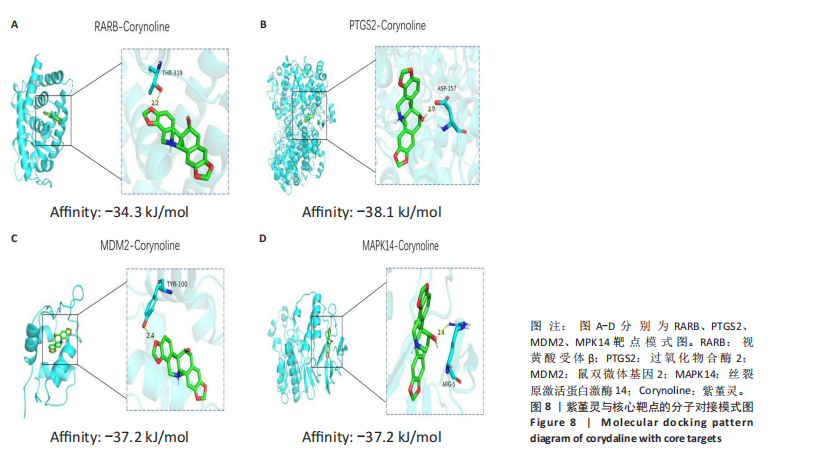
2.8 分子对接分析 为了验证网络药理学预测的潜在治疗效果,采用分子对接的方法来评估小分子药物与核心靶点的结合亲和力。结果显示对视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14靶点与紫堇灵相应的结合能分别为-34.3,-38.1,-37.2和-37.2 kJ/mol,见图8。结合能< -20.9 kJ/mol表明结合活性良好,结合能< -29.3 kJ/mol表明结合活性强[35]。紫堇灵与视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14蛋白结合能均< -29.3 kJ/mol,表明结合活性强。分子对接结果提示视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14蛋白与紫堇灵相互作用是发挥的治疗急性髓系白血病的潜在作用机制。
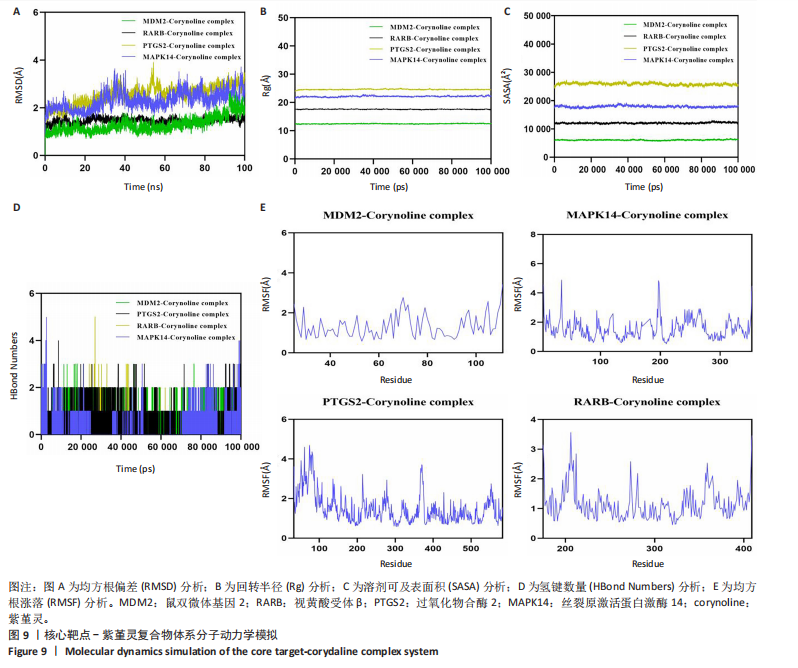
2.9 分子动力学模拟 为评估紫堇灵与靶蛋白复合物的稳定性,研究进行了100 ns的分子动力学模拟。均方根偏差(root mean square deviation,RMSD)轨迹分析表明,鼠双微体基因2-紫堇灵和视黄酸受体β-紫堇灵复合物在大约10 ns后达到稳定状态,平均均方根偏差值分别为-1.6 ?和-1.5 ?。相比之下,过氧化物合酶2-紫堇灵和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14-紫堇灵复合物在约98 ns后达到稳定状态,其均方根偏差值分别为3.1 ?和2.7 ?(图9A),显示出良好的整体稳定性。为进一步表征复合物的构象动态变化,研究开展了回转半径(Rg)和溶剂可及表面积(SASA)分析(图9B,C)。结果表明,在模拟过程中,所有复合物未发生显著的结构收缩或扩张,提示其整体构象稳定。氢键分析显示,各复合物在大部分模拟时间内均维持约2个氢键(图9D),表明分子间相互作用稳定。此外,均方根涨落(root mean square fluctuation,RMSF)分析显示,大多数残基的均方根涨落值低于3 ?(图9E),提示复合物具有较低的构象柔性和较强的结构稳定性。综合上述分子动力学模拟结果,紫堇灵与鼠双微体基因2、视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14靶蛋白形成的复合物均表现出良好的稳定性,进一步从分子层面支持了其潜在的抗急性髓系白血病活性。
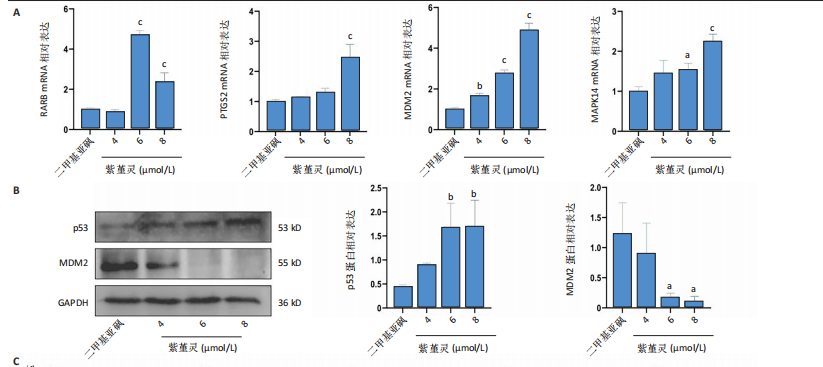
2.10 紫堇灵通过调控鼠双微体基因2-p53轴及抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路发挥抗急性髓系白血病作用 为探讨紫堇灵的分子机制,首先通

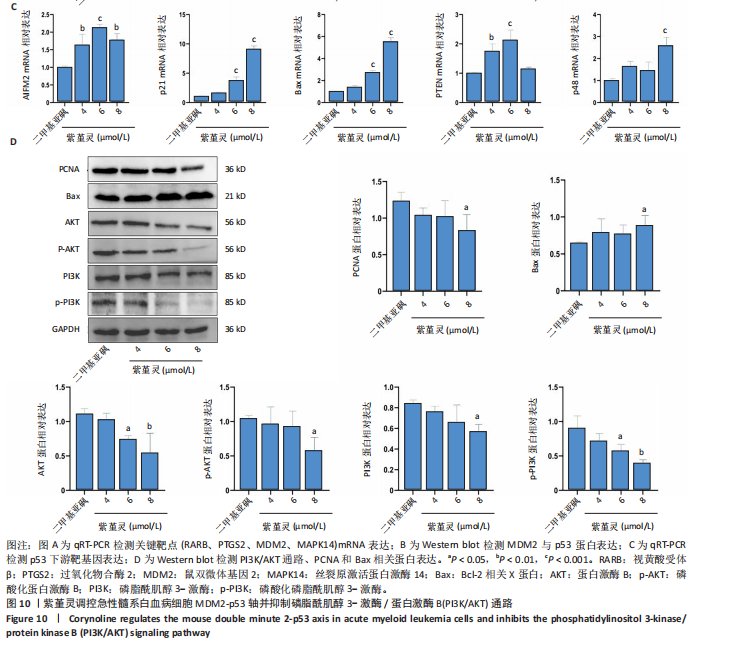
过 qRT-PCR 检测其处理 MOLM-13细胞24 h后核心靶点表达情况。结果显示,视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2与丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14 mRNA水平均显著上调,其中鼠双微体基因2 表达呈现浓度依赖性上调趋势(图10A)。然而,Western blot 检测显示随着药物浓度升高,鼠双微体基因2蛋白水平反而呈下降趋势,同时p53蛋白表达上调(图10B),提示紫堇灵可能通过促进鼠双微体基因2降解而间接稳定并激活p53。鼠双微体基因2作为p53的主要负调控因子,可通过促进其泛素化及后续的蛋白酶体降解发挥作用[36];p53作为一个转录因子,p53的再激活可通过调控下游基因的转录参与细胞DNA 修复、周期调节、凋亡和衰老等生物学过程[37]。进一步分析p53下游靶基因表达,qRT-PCR 结果显示 AIFM2、p21、Bax、p48等基因均被上调,其中p21和Bax呈显著浓度依赖性上调(图10C),提示紫堇灵可通过激活 p53/p21/Bax 信号轴诱导细胞凋亡与周期阻滞。
结合此前 KEGG 富集分析,提示紫堇灵可能调控磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路。Western blot结果进一步证实其可浓度依赖性抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、蛋白激酶B及其磷酸化形式(磷酸化磷脂酰
肌醇3-激酶、磷酸化蛋白激酶B)的表达,同时伴随增殖细胞核抗原下调与Bax上调(图 10D),支持其对细胞增殖与凋亡的双重调控作用。综上,紫堇灵可能通过如下两种机制发挥其抗急性髓系白血病效应:①促进鼠双微体基因2蛋白降解,激活p53通路,进而调控细胞周期与凋亡;②抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路,降低细胞增殖能力并增强凋亡响应。
| [1] BHANSALI RS, PRATZ KW, LAI C. Recent advances in targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2023;16(1):29. [2] DÖHNER K, THIEDE C, JAHN N, et al. Impact of NPM1/FLT3-ITD genotypes defined by the 2017 European LeukemiaNet in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2020;135(5):371-380. [3] ZHANG N, WU J, WANG Q, et al. Global burden of hematologic malignancies and evolution patterns over the past 30 years. Blood Cancer J. 2023;13(1):82. [4] LIU H. Emerging agents and regimens for AML. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):49. [5] KOGAN SC. Curing APL: differentiation or destruction?. Cancer Cell. 2009;15(1):7-8. [6] LUO H, VONG CT, CHEN H, et al. Naturally occurring anti-cancer compounds: shining from Chinese herbal medicine. Chin Med. 2019; 14:48. [7] ZHAO W, ZHENG X D, TANG P Y, et al. Advances of antitumor drug discovery in traditional Chinese medicine and natural active products by using multi-active components combination. Med Res Rev. 2023; 43(5):1778-1808. [8] NAEEM A, HU P, YANG M, et al. Natural Products as Anticancer Agents: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Molecules. 2022;27(23):8367. [9] YANG C, ZHANG C, WANG Z, et al. Corynoline Isolated from Corydalis bungeana Turcz. Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Effects via Modulation of Nfr2 and MAPKs. Molecules. 2016;21(8):975. [10] KIM DK. Inhibitory effect of corynoline isolated from the aerial parts of Corydalis incisa on the acetylcholinesterase. Arch Pharm Res. 2002; 25(6):817-819. [11] FANG ZZ, ZHANG YY, GE GB, et al. Identification of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms involved in the metabolism of corynoline, and assessment of its herb-drug interactions. Phytother Res. 2011;25(2): 256-263. [12] LIU B, SU K, WANG J, et al. Corynoline Exhibits Anti-inflammatory Effects in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Stimulated Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells through Activating Nrf2. Inflammation. 2018; 41(5):1640-1647. [13] SHI Y, YUAN Q, CHEN Y, et al. Corynoline inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth via targeting Pim-3. Phytomedicine. 2024;123:155235. [14] LI SL, KONG XY, FANG Y. [(+)-corynoline Regulates the Proliferation,Stemness and Apoptosis of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells]. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022;44(2):244-252. [15] YI C, LI X, CHEN S, et al. Natural product corynoline suppresses melanoma cell growth through inducing oxidative stress. Phytother Res. 2020;34(10):2766-2777. [16] LI S, ZHANG B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application. Chin J Nat Med. 2013;11(2): 110-120. [17] LI X, LIU Z, LIAO J, et al. Network pharmacology approaches for research of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Chin J Nat Med. 2023;21(5):323-332. [18] FANG T, LIU L, LIU W. Exploring the mechanism of fraxetin against acute myeloid leukemia through cell experiments and network pharmacology.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024;24(1):226. [19] JIAO Y, SHI C, SUN Y. Unraveling the Role of Scutellaria baicalensis for the Treatment of Breast Cancer Using Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4):3594. [20] KIM S, CHEN J, CHENG T, et al. PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1): D1388-D1395. [21] WANG X, SHEN Y, WANG S, et al. PharmMapper 2017 update: a web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(W1):W356-W360. [22] DAINA A, MICHIELIN O, ZOETE V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W357-W364. [23] RU J, LI P, WANG JA, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13. [24] UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025;53(D1):D609-D617. [25] HAMOSH A, SCOTT AF, AMBERGER JS, et al. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(Database issue): D514-D517. [26] KNOX C, WILSON M, KLINGER CM, et al. DrugBank 6.0: the DrugBank Knowledgebase for 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52(D1): D1265-D1275. [27] SAFRAN M, CHALIFA-CASPI V, SHMUELI O, et al. Human Gene-Centric Databases at the Weizmann Institute of Science: GeneCards, UDB, CroW 21 and HORDE. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(1):142-146. [28] SHERMAN BT, HAO M, QIU J, et al. DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(W1):W216-W221. [29] TANG Z, KANG B, LI C, et al. GEPIA2: an enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W556-W560. [30] GYŐRFFY B.Integrated analysis of public datasets for the discovery and validation of survival-associated genes in solid tumors. Innovation (Camb). 2024;5(3):100625. [31] MORRIS GM, HUEY R, LINDSTROM W, et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility.J Comput Chem. 2009;30(16):2785-2791. [32] BERMAN H M, WESTBROOK J, FENG Z, et al. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):235-242. [33] JO S, KIM T, IYER VG, et al. CHARMM-GUI: a web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J Comput Chem. 2008;29(11):1859-1865. [34] MARK P, NILSSON L. Structure and dynamics of liquid water with different long-range interaction truncation and temperature control methods in molecular dynamics simulations.J Comput Chem. 2002; 23(13):1211-1219. [35] JIA G, JIANG X, LI Z, et al. Decoding the Mechanism of Shen Qi Sha Bai Decoction in Treating Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021:9:796757. [36] SHANGARY S, WANG S. Targeting the MDM2-p53 interaction for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(17):5318-5324. [37] MARVALIM C, DATTA A, LEE SC. Role of p53 in breast cancer progression: An insight into p53 targeted therapy. Theranostics. 2023;13(4):1421-1442. [38] CASSIER P A, CASTETS M, BELHABRI A, et al. Targeting apoptosis in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 2017;117(8):1089-1098. [39] YANG X, WANG J. Precision therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):3. [40] BULLINGER L, DöHNER K, DöHNER H. Genomics of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Diagnosis and Pathways. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(9):934-946. [41] GRIMWADE D, IVEY A, HUNTLY BJ. Molecular landscape of acute myeloid leukemia in younger adults and its clinical relevance.Blood. 2016;127(1):29-41. [42] GAO X, ZUO X, MIN T, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine for acute myelocytic leukemia therapy: exploiting epigenetic targets. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1388903. [43] MILLER WH JR, SCHIPPER HM, LEE JS, et al. Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res. 2002;62(14):3893-3903. [44] SHEN ZX, SHI ZZ, FANG J, et al. All-trans retinoic acid/As2O3 combination yields a high quality remission and survival in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(15):5328-5335. [45] ESTEY E, GARCIA-MANERO G, FERRAJOLI A, et al. Use of all-trans retinoic acid plus arsenic trioxide as an alternative to chemotherapy in untreated acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 2006;107(9):3469-3473. [46] LALLEMAND-BREITENBACH V, DE THÉ H. Retinoic acid plus arsenic trioxide, the ultimate panacea for acute promyelocytic leukemia?. Blood. 2013;122(12):2008-2010. [47] BURNETT AK, RUSSELL NH, HILLS RK, et al. Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid treatment for acute promyelocytic leukaemia in all risk groups (AML17): results of a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(13):1295-1305. [48] HUANG Z, YANG Y, FAN X, et al. Network pharmacology-based investigation and experimental validation of the mechanism of scutellarin in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:952677. [49] WANG X, WANG Y, CHEN J, et al. On the mechanism of wogonin against acute monocytic leukemia using network pharmacology and experimental validation. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):10114. [50] ZHAO L, ZHANG H, LI N, et al. Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;309:116306. [51] JIANG M, LI J, WU J, et al. Case report: A rare case of TBL1XR1-RARB positive acute promyelocytic leukemia in child and review of the literature.Front Oncol. 2022;12:1028089. [52] FANG D D, TANG Q, KONG Y, et al. MDM2 inhibitor APG-115 exerts potent antitumor activity and synergizes with standard-of-care agents in preclinical acute myeloid leukemia models. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):90. [53] KONOPLEVA M Y, RöLLIG C, CAVENAGH J, et al. Idasanutlin plus cytarabine in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia: results of the MIRROS trial. Blood Adv. 2022;6(14):4147-4156. [54] MATOU-NASRI S, NAJDI M, ALSAUD NA, et al. Blockade of p38 MAPK overcomes AML stem cell line KG1a resistance to 5-Fluorouridine and the impact on miRNA profiling. PLoS One. 2022;17(5):e0267855. [55] YUAN TL, CANTLEY LC. PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene. 2008;27(41):5497-510. [56] BERTACCHINI J, HEIDARI N, MEDIANI L, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72(12): 2337-2347. [57] LI J, QU P, ZHOU XZ, et al. Pimozide inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells by alleviating the Warburg effect through the P53 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;150:113063. [58] HE J, ZHU G, GAO L, et al. Fra-1 is upregulated in gastric cancer tissues and affects the PI3K/Akt and p53 signaling pathway in gastric cancer.Int J Oncol. 2015;47(5):1725-1734. [59] JAMAL SME, ALAMODI A, WAHL RU, et al. Melanoma stem cell maintenance and chemo-resistance are mediated by CD133 signal to PI3K-dependent pathways. Oncogene. 2020;39(32):5468-5478. [60] YAO Y, ZHANG Q, LI Z, et al. MDM2: current research status and prospects of tumor treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2024;24(1):170. [61] BRUMMER T, ZEISER R. The role of the MDM2/p53 axis in antitumor immune responses. Blood. 2024;143(26):2701-2709. [62] KOJIMA K, KONOPLEVA M, SAMUDIO I J, et al. MDM2 antagonists induce p53-dependent apoptosis in AML: implications for leukemia therapy. Blood.2005;106(9):3150-3159. [63] SHANGARY S, WANG S. Small-molecule inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction to reactivate p53 function: a novel approach for cancer therapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2009;49:223-241. [64] HU J, CAO J, TOPATANA W, et al. Targeting mutant p53 for cancer therapy: direct and indirect strategies. J Hematol Oncol. 2021; 14(1):157. [65] LIU F, LI X, YAN H, et al. Downregulation of CPT2 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis through p53 pathway in colorectal cancer.Cell Signal. 2022;92:110267. [66] FREEDMAN DA, WU L, LEVINE AJ. Functions of the MDM2 oncoprotein. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999;55(1):96-107. |
| [1] | 周思瑞, 徐玉坤, 赵可伟. 白芷细胞外囊泡对抗黑色素的思路和方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1747-1754. |
| [2] | 陈钰璘, 何莹莹, 胡 凯, 陈枝凡, 聂 莎, 蒙衍慧, 李闰珍, 张小朵, 李宇稀, 唐耀平. 瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡防治动脉粥样硬化的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [3] | 彭志伟, 陈 雷, 佟 磊. 木犀草素促进糖尿病小鼠创面愈合的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [4] | 郭 英, 田 峰, 王春芳. 类风湿关节炎潜在药物靶点:来自欧洲数据库的大样本分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [5] | 王正业, 刘万林, 赵振群. miRNA在激素诱导股骨头坏死机制中的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [6] | 陈伊娴, 陈 晨, 卢立恒, 汤锦鹏, 于晓巍. 雷公藤甲素治疗骨关节炎的网络药理学分析与实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [7] | 王正业, 刘万林, 赵振群. 血管内皮生长因子A 靶向调控血管化治疗激素性股骨头坏死的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 671-679. |
| [8] | 赵 宇, 薛 云, 黄家俊, 吴迪友, 杨 彬, 黄俊卿. 菟丝子总黄酮抑制激素性股骨头坏死的成骨细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4289-4298. |
| [9] | 吴 雪, 张林翱, 罗世芳, 刘非凡, 万 艳, 白元美, 曹菊林, 解宇环, 郭沛鑫. 丹灯通脑软胶囊抗缺血性脑卒中:指纹图谱与网络药理学分析药效及作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4517-4528. |
| [10] | 武祎琳, 田红英, 孙佳乐, 焦佳佳, 赵梓涵, 邵金环, 赵凯悦, 周 敏, 李 倩, 李泽鑫, 岳昌武. 复方甜地丁对乳腺增生小鼠模型的干预作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4377-4389. |
| [11] | 姜欢欢, 穆 胜, 马文欣, 刘 畅, 刘自钰, 蒲 静, 朱向东, 惠 宏, 马会明. 韭菜子有效成分多靶点干预少弱精子症模型大鼠的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 3044-3057. |
| [12] | 程 乐, 朱才丰, 周冰原, 高大红, 崔晓雅, 李 静, 王雪伟, 杨高尚, 陈希阳. 靶向炎症细胞因子治疗脑卒中的机制:开放全基因组关联研究大数据分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 3198-3216. |
| [13] | 徐 晟, 张稳稳, 张薇薇, 王宏涛, 张 军, 杨瑞盛, 原 媛, 王 丽, 郝海虎. 菟丝子活性成分苦参碱治疗绝经后骨质疏松症:网络药理学分析及实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(11): 2702-2711. |
| [14] | 田明昊, 廖烨晖, 周文洋, 何宝强, 冷叶波, 徐世财, 周佳俊, 李 洋, 唐 超, 唐 强, 钟德君. IRF9基因在脊髓损伤后神经保护中的调控作用:生信分析与实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(11): 2712-2726. |
| [15] | 于漫亚, 崔 兴. 炙甘草汤保护阿霉素诱导心肌损伤的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(11): 2795-2805. |
天然药物(如中草药、植物药)含有多种具有抗肿瘤潜能的活性成分,随着分子生物学与组学技术的不断发展,其作用机制及临床应用价值逐渐受到重视[6]。相比合成化学药物,天然化合物通常具有结构多样、靶点广泛、毒性较低、免疫调节能力强等优势。已有研究表明,多种天然产物中的生物碱、萜类、黄酮类等活性成分,能够通过诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡与分化、抑制血管生成、逆转耐药性、增强免疫功能等多种机制发挥抗肿瘤作用[7-8]。
紫堇灵(Corynoline)是一种来源于中药布氏紫堇(Corydalis yanhusuo)的天然异喹啉类生物碱,具有多种药理学活性,包括抗炎、抗真菌、镇痛、抗氧化及细胞黏附抑制等[9-12],近年来,其抗肿瘤潜力逐渐受到关注。例如,研究显示紫堇灵可通过靶向Pim-3蛋白抑制食管鳞状细胞癌的增殖[13],在三阴性乳腺癌模型中通过抑制增殖与干性、诱导凋亡发挥抗癌效应[14],并可在黑色素瘤中以活性氧依赖性机制介导DNA损伤,抑制其进展[15]。尽管紫堇灵的广谱抗肿瘤效应已被初步证实,但它在急性髓系白血病中的作用及其分子机制尚未见报道。
随着系统生物学与生物信息学的发展,网络药理学成为研究中药复杂成分与作用机制的重要方法。该方法强调“多成分-多靶点-多通路”的整合性理念,与中医“辨证论治”的理论高度契合,可系统性揭示药物、靶点与疾病之间的相互关系[16-17]。此外,分子对接与分子动力学模拟等计算化学技术,已广泛用于小分子药物的先导化合物筛选与机制研究。分子对接可初步预测小分子与蛋白靶点的结合模式与亲和力,而分子动力学模拟可进一步验证其结合的稳定性与动力学特征,为后续的体外实验提供理论支持[18-19]。
此次研究基于网络药理学策略,从多个数据库整合分析紫堇灵潜在抗急性髓系白血病靶点,结合GO与KEGG通路富集、蛋白质相互作用(protein-protein interaction,PPI)网络构建与临床表达预后分析,筛选核心作用靶点,并通过分子对接与分子动力学模拟验证其结合活性与稳定性。随后采用Kasumi-1与MOLM-13细胞模型,开展CCK-8、流式细胞术、qRT-PCR和Western blot实验,从细胞水平与分子水平验证紫堇灵的药理活性及作用机制。与既往局限于单一靶点或实验策略的研究不同,此次研究从系统生物学角度全面揭示紫堇灵在急性髓系白血病治疗中的分子机制,为其作为天然抗急性髓系白血病药物的开发提供理论依据与实验支持。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.2 时间及地点 研究于2023年6月至2024年12月在贵州医科大学医学检验学院与贵州医科大学附属医院临床检验中心联合完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 细胞 人急性髓系白血病细胞系包括Kasumi-1、MOLM-13购自中国科学院细胞库。
1.3.2 试剂和仪器 RPMI-1640培养液购自美国Gibco公司;依科赛胎牛血清购自上海吉泰生物科技有限公司;青霉素-链霉素混合液购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;紫堇灵及CCK-8细胞活力检测试剂盒购自美国MedChemExpress公司;Annexin V-APC/Cyanine7/7-AAD细胞凋亡检测试剂盒购自上海普诺赛生命科技有限公司;细胞周期分析试剂盒购自上海七海复秦生物科技有限公司;BCA蛋白浓度检测试剂盒购自上海碧云天生物技术研究所;RIPA裂解液购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;ECL化学发光试剂购自美国Millipore公司;RNA提取试剂(TRIzol)购自美国赛默飞公司;cDNA反转录试剂盒与qRT-PCR反应试剂购自日本Takara公司;PCR引物购自上海生工生物工程有限公司;GAPDH抗体购自南京巴傲得生物科技有限公司;鼠双微体基因2(murine double mimute 2,MDM2)抗体购自沈阳万类生物技术有限公司;磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶
(phos-phoinositide 3-kinase,PI3K)及磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶抗体购自上海艾比玛特医药科技有限公司;蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,AKT)、磷酸化蛋白激酶B、Bax、增殖细胞核抗原(proliferating cell nuclear antigen,PCNA)及p53抗体购自武汉三鹰生物技术有限公司;HRP标记羊抗兔IgG与羊抗鼠IgG二抗均购自南京巴傲得生物科技有限公司。
普通PCR扩增仪、Nanodrop One微量分光光度计、酶标仪、ABI7500实时荧光定量PCR仪均购自美国Thermo Fisher公司;FACSCantoⅡ流式细胞仪购自美国BD公司;凝胶成像分析仪购自美国BIO-RAD公司。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 细胞培养 将人急性髓系白血病细胞株Kasumi-1与MOLM-13接种于含体积分数10%胎牛血清与1%青霉素-链霉素混合液的RPMI-1640培养基中,在37 ℃、体积分数5% CO2饱和湿度条件下恒温培养。每两三天更换细胞培养基并进行传代,以维持其稳定增殖状态。
1.4.2 CCK-8法检测细胞活力 取状态良好的Kasumi-1和MOLM-13细胞计数后,以1×104 /孔密度接种于96孔板中,90 μL/孔,分别加入不同浓度(4,6,8 μmol/L)紫堇灵(10 μL/孔),以二甲基亚砜作为对照。将细胞于37 ℃、体积分数5% CO2培养箱中孵育24 h后,每孔加入10 μL CCK-8试剂继续孵育3 h。采用酶标仪检测450 nm处吸光度(A)值,计算细胞相对生长率:相对生长率(%)=[处理组A值-空白组A值]/[对照组A值-空白组A值] ×100%。使用GraphPad Prism9.0软件计算紫堇灵的半数抑制浓度(50% concentration of inhibition,IC50)值。进一步设置低、中、高浓度(4,6,8 μmol/L)紫堇灵处理细胞,分别培养24,48,72 h后重复上述检测流程,评估细胞活力时间依赖性变化。
1.4.3 流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率和细胞周期
(1)细胞凋亡检测:取对数生长期Kasumi-1和MOLM-13细胞,计数后以 5×10⁵ /孔密度接种于6孔板中,2 mL/孔,分别加入终浓度为4,6,8 μmol/L的紫堇灵溶液,二甲基亚砜为对照组,处理24 h。收集细胞,PBS冲洗2次后用100 μL 1×Binding Buffer重悬,加入5 μL Annexin V-APC与5 μL 7-AAD染料,室温避光孵育20 min。最后加入400 μL 1×Binding Buffer重悬后,使用BD FACSCantoⅡ流式细胞仪分析细胞凋亡率。
(2)细胞周期检测:Kasumi-1和MOLM-13细胞以1×106 /孔密度接种于6 cm培养皿,4 mL/孔,分别加入4,6,8 μmol/L紫堇灵孵育24 h。收集细胞,PBS冲洗后用体积分数70%预冷乙醇固定于4 ℃超过24 h。固定结束后去除乙醇、PBS洗涤细胞,用含碘化丙啶(PI)的染色液重悬,避光孵育30 min。使用流式细胞仪检测细胞周期分布比例。
1.4.4 紫堇灵潜在靶点预测 为获取紫堇灵的潜在药物作用靶点,首先在PubChem 数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)中检索并下载其化学结构信息[20]。将该化合物结构输入以下数据库进行靶点预测:PharmMapper(www.lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmapper/)[21]、SwissTargetPrediction(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/index.php)和TCMSP(https://www.tcmsp-e.com/)数据库[22-23],经 UniProt(http://www.uniprot.org/) 数据库标准化处理[24],统一命名并去重,获得紫堇灵药物作用相关靶点。急性髓系白血病的疾病靶点从OMIM(https://omim.org/)[25]、Drugbank(https://go.drugbank.com/)[26]、Genecards(https://www.genecards.org/)数据库中检索[27],将3个数据库中检索到的基因集合合并、去重,形成急性髓系白血病相关靶点集。使用Venny 2.1(在线韦恩图工具)对紫堇灵药物靶点与急性髓系白血病疾病靶点进行交集分析,筛选出紫堇灵治疗急性髓系白血病的潜在共同作用靶点。
1.4.5 “药物-疾病-靶点”网络的构建 将上述药物-疾病共同靶点利用Cytoscape 3.9.1软件构建“药物-疾病-靶点”网络并进行可视化。
1.4.6 蛋白-蛋白相互作用网络分析 将上述药物-疾病共同靶点导入到STRING数据库(https://string-db.org/)中进行检索,设置蛋白种类为“Homo sapiens”,设置最小交互阈值为0.9,获取蛋白间相互作用关系,并导入Cytoscape 3.9.1进行网络可视化。使用其插件MCODE(Molecular Complex Detection)对蛋白质相互作用网络进行模块聚类分析,以识别潜在的功能模块与核心靶点。
1.4.7 GO和KEGG富集分析 使用David数据库(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/)对交叉靶点进行GO与KEGG富集分析[28]。利用R语言(ggplot2包)进行结果可视化,绘制气泡图以展示富集的生物过程、细胞组分、分子功能及相关信号通路。
1.4.8 核心靶点基因表达和总生存分析 在 GEPIA2平台(http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/index.html)中对核心靶点在急性髓系白血病患者与正常个体之间的表达差异进行分析[29]。利用Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库 (https://www.kmplot.com/analysis/index)分析各核心靶点的表达水平与患者总生存期之间的关系[30],以评估其作为预后标志物的潜在价值。
1.4.9 分子对接分析 该步骤旨在评估紫堇灵与急性髓系白血病核心靶点蛋白之间的结合能力与结合模式,探讨其潜在的分子作用基础。①配体准备:从PubChem数据库下载紫堇灵的化合物结构文件(SDF格式),导入ChemDraw 3D软件中,通过MM2力场对其进行能量最小化,获得能量最低的稳定构象,并保存为mol2文件。随后使用AutoDockTools 1.5.6对配体进行预处理[31],包括添加氢原子、赋予Gasteiger电荷、检测配体的root位置、定义可旋转键,并最终保存为pdbqt文件。②受体准备:从RCSB PDB 数据库(www.rcsb.org)下载核心靶点蛋白的三维晶体结构[32],利用PyMOL软件去除蛋白结构中的水分子与配体杂原子,再通过AutoDockTools对蛋白加氢、计算电荷并设置为受体,保存为pdbqt文件。③对接过程与可视化:采用 AutoDock Vina 1.1.2 软件进行分子对接,通过设定网格框中心与尺寸,完成配体与受体的对接过程。使用PyMOL软件对接后的复合物进行可视化展示与分析,评估其结合模式、关键氢键及疏水相互作用。
1.4.10 分子动态模拟 使用Gromacs 2023对复合物进行100 ns 分子动力学模拟。蛋白质采用CHARMM 36力场参数[33],配体拓扑结构由GAFF2力场参数构建。采用周期性边界条件,将蛋白质-配体复合物放置在立方盒中。采用TIP3P水模型将水分子填充到盒子中[34]。使用粒子网格Ewald算法和Verlet算法分别处理静电相互作用。随后进行100 000 步的等温等容系综平衡和等温等压系综平衡,耦合常数为0.1 ps,持续时间为100 ps 模拟。范德华和库仑相互作用均使用 1.0 nm 的截止值计算。最后,系统在恒定温度(300 K)和恒压(0.1 MPa)下利用Gromacs 2023进行了分子动力学模拟,共计时长100 ns。
1.4.11 实时定量聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)分析靶点基因表达 提取紫堇灵处理后MOLM-13细胞的总RNA,使用TRIzol试剂提取并测定浓度,取1 μg反转录合成cDNA。qRT-PCR采用SYBR Green Master Mix,使用ABI7500实时荧光定量PCR仪完成反应。GAPDH作为内参基因,采用2-ΔΔCt方法计算相对表达水平。所用引物序列见表 1。
4 ℃ 条件下超声破碎并 12 000×g 离心 15 min,取上清测定蛋白浓度。加上样缓冲液混匀,于100 ℃加热10 min,取等量蛋白(30 μg)进行 SDS-PAGE电泳。转膜后以5%脱脂奶粉封闭2 h,放入相应的一抗中,GAPDH(1∶10 000)、鼠双微体基因2、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、蛋白激酶B、磷酸化蛋白激酶B(均1∶1 000)、Bax、增殖细胞核抗原、p53(均1∶2 000),于4 ℃孵育过夜后使用 1×TBST 洗膜3次,放入二抗(HRP标记羊抗兔IgG与羊抗鼠IgG二抗均1∶10 000稀释)中,室温孵育1 h后使用 1×TBST 洗膜3次,用ECL化学发光试剂显影,图像使用ImageJ软件分析条带灰度值。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①紫堇灵对Kasumi-1与MOLM-13细胞增殖的影响;②紫堇灵对细胞生长、细胞周期分布及细胞凋亡的影响;③紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病的药物靶点预测;④紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病靶点基因的GO与KEGG分析;⑤核心靶点的筛选;⑥核心基因在急性髓系白血病中表达和生存分析;⑦药物与核心靶点分子对接结果;⑧紫堇灵与靶蛋白复合物分子动力学模拟结果;⑨紫堇灵调控鼠双微体基因2-p53轴及磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路抗急性髓系白血病的作用。
1.6 统计学分析 所有实验独立重复3次,数据以x±s表示。统计分析使用GraphPad Prism 9.0软件完成。组间两两比较采用t检验,多组数据比较采用单因素方差分析,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义,以P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1表示差异的显著性水平。文章统计学方法已经通过贵州医科大学统计学专家审核。
中药具有药理机制新颖、毒副作用小等优点。已有研究证实,几种中药生物活性成分对急性髓系白血病具有良好的疗效,在急性髓系白血病治疗中展现出潜力[42]。三氧化二砷是传统中药砒石的主要成分,在白血病的治疗方面也取得了突破性进展[43]。早期研究证明三氧化二砷联合全反式维甲酸治疗的M3型急性髓系白血病患者中估计5年无事件生存率和总生存期率分别为89.2%和91.7%[44]。三氧化二砷最初用于急性髓系白血病复发患者,随后被美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)和欧洲药品管理局(EMA)批准用于全反式维甲酸复发患者的挽救治疗,三氧化二砷最近作为单一药物或全反式维甲酸±化疗联合用于急性早幼粒白血病的一线治疗。在美国进行的一项初步研究后[45],两项随机试验的结果将这种方法确定为至少对中低风险患者的新治疗标准,允许单独使用靶向药物治愈急性早幼粒白血病,而无需化疗[46-47]。除此之外,报道显示黄芩素[48]、黄芩苷和黄曲霉素等中药活性成分在抗急性髓系白血病方面也具有重要作用[18,49]。然而,由于中药化学成分复杂,研究中药的具体作用机制存在一定挑战。随着网络药理学的不断发展,为探索中药的作用机制提供了重要推动[50]。
该研究采用网络药理学方法,获得了紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病的102个潜在治疗靶点,通过对蛋白质相互作用网络的聚类分析确定了紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病核心交叉靶点蛋白酪氨酸激酶2、视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14。基于核心交叉靶点的表达和临床预后分析确认视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14在急性髓系白血病中发挥重要作用。分子对接结果提示紫堇灵与视黄酸受体β、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14结合活性强。已有研究报道,在TBL1XR1-RARB融合的急性早幼粒细胞白血病样急性髓系白血病中,该融合基因与全反式维甲酸治疗耐药及不良预后密切相关,提示视黄酸受体β异常在髓系分化阻断和急性髓系白血病发病机制中具有重要意义[51]。过氧化物合酶2(即环氧化酶2)在部分急性髓系白血病亚型患者与细胞系中高表达,其产物前列腺素E2与骨髓炎症微环境增强相关,提示环氧化酶2抑制剂可能作为辅助治疗手段。鼠双微体基因2过表达可通过抑制p53通路功能促进肿瘤细胞存活,是复发/难治性急性髓系白血病的重要治疗靶点。多项研究显示,鼠双微体基因2拮抗剂能够激活p53介导的细胞周期阻滞和凋亡,在临床前和临床试验中均表现出良好的抗肿瘤潜力[52-53]。此外,丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14[又称p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38MAPK)]在急性髓系白血病细胞中高表达,与其对氧化应激与化疗耐受能力增强密切相关。临床前研究显示,小分子抑制剂(如SB203580)靶向丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14可显著增强急性髓系白血病细胞对常规化疗药物(如高三尖杉酯碱和5-氟尿苷)的敏感性[54]。综上所述,这些核心靶点在急性髓系白血病的发生、发展及治疗反应中均发挥重要作用,进一步验证了紫堇灵通过多靶点机制干预急性髓系白血病进程的科学依据。
紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病的102个潜在治疗靶点的GO和KEGG通路分析显示,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路在紫堇灵诱导细胞凋亡中发挥关键作用。磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路在细胞生理过程中扮演着关键角色,包括细胞周期的调控、细胞分化、转录和翻译过程、细胞凋亡以及代谢调节等[55]。在急性髓系白血病中,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路被认为参与细胞增殖、凋亡和转移的主要信号传导通路。通过抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路可有效抑制急性髓系白血病细胞的增殖并促进凋亡过程[56];并可通过抑制鼠双微体基因2蛋白介导p53的激活来抑制乳腺癌、胃癌、肝癌等癌症的进展[57-59]。
鼠双微体基因2是一种由491个氨基酸组成的调节蛋白,具有多种功能结构域,包括一个N端的p53结合域、一个核定位信号(NLS)、一个核输出信号(NES)、一个酸性结构域、一个锌指结构域和一个C端的RING-finger结构域。核定位信号和核输出信号对于鼠双微体基因2在细胞核与细胞质之间的转运至关重要。在酸性结构域内,特定氨基酸残基的磷酸化过程促进了p53的降解。此外,C端的RING-finger结构域作为E3泛素连接酶,能够在鼠双微体基因2与p53相互作用后诱导p53的泛素化[60]。
现有研究表明,鼠双微体基因2在急性髓系白血病及多种肿瘤中具有促癌作用,其机制主要通过降低p53的丰度和功能来介导,导致肿瘤细胞在发生DNA损伤时无法有效阻止细胞周期进程,从而引发持续的凋亡过程[61-63]。p53作为细胞内重要的转录因子,在多种肿瘤中存在基因突变,p53突变不仅损害其抗肿瘤活性,还赋予突变 p53 蛋白致癌特性,进而参与肿瘤的进展[64]。p53的激活可通过调控下游靶基因p21、Bax、p48等多种基因的表达阻止肿瘤细胞周期、促进细胞凋亡和参与细胞DNA损伤修复进程[65]。同时,p53的激活可负反馈调节鼠双微体基因2的转录,发挥抑癌作用[66]。
体外实验表明,紫堇灵可显著抑制急性髓系白血病细胞增殖、诱导细胞凋亡并干扰细胞周期进程。为阐明其抗急性髓系白血病作用机制,此次研究通过Western blot分析靶向检测磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路关键组分及其相关下游分子,结果显示,紫堇灵处理可显著抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路的激活,表现为磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、蛋白激酶B及磷酸化蛋白激酶B蛋白水平的下调;同时,紫堇灵上调促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达,并降低增殖标志物增殖细胞核抗原的水平。进一步通过qRT-PCR分析紫堇灵作用核心靶点的表达,结果显示鼠双微体基因2 mRNA表达呈浓度依赖性升高尤为显著;然而,Western blot结果显示,随着紫堇灵浓度增加,鼠双微体基因2蛋白水平逐渐降低,而p53蛋白水平相应升高。这种反向调控关系提示,紫堇灵可能通过转录后调控机制拮抗鼠双微体基因2介导的p53抑制,例如促进鼠双微体基因2降解从而重新激活p53信号。分子动力学模拟进一步支持该假说,结果显示紫堇灵与鼠双微体基因2之间存在稳定的结合作用,提示两者可直接相互作用并干扰鼠双微体基因2功能。与p53的重新激活一致,qRT-PCR结果显示其下游靶基因(特别是AIFM2、p21、Bax和p48)均呈现上调趋势,其中p21与Bax的升高幅度最为显著且呈浓度依赖性。上述结果表明,紫堇灵通过激活p53/p21/Bax信号轴触发细胞周期阻滞与凋亡。
尽管此次研究通过整合网络药理学与体外实验初步阐明了紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病作用机制,但仍存在以下局限性:首先,紫堇灵在体内抗急性髓系白血病的药理效应尚未验证,后续研究有必要构建急性髓系白血病异种移植模型或基因工程小鼠模型,以系统评估其在体内的抗肿瘤活性及潜在作用机制;其次,尽管网络药理学、分子对接和分子动力学模拟提示紫堇灵可能通过靶向多个核心靶点发挥作用,但缺乏直接实验证据支持其与这些靶点之间的因果关系,因此,需进一步开展细胞热迁移分析(CETSA)验证紫堇灵与靶点蛋白的结合情况,并结合基因敲除、过表达以及报告基因检测等实验手段,深入解析各信号通路和关键靶点在其抗白血病作用中的具体贡献;第三,目前尚不清楚紫堇灵在体内的药代动力学与药效学特征,包括其代谢稳定性、生物分布及潜在毒性等,这些问题亟待进一步研究,异种移植或人源化模型在此方面将具有重要价值。尽管存在上述局限,此次研究为推进紫堇灵作为急性髓系白血病多靶点治疗候选药物奠定了坚实基础,并为其临床转化提供了理论支持,同时为开发基于p53的靶向治疗策略提供了新视角。
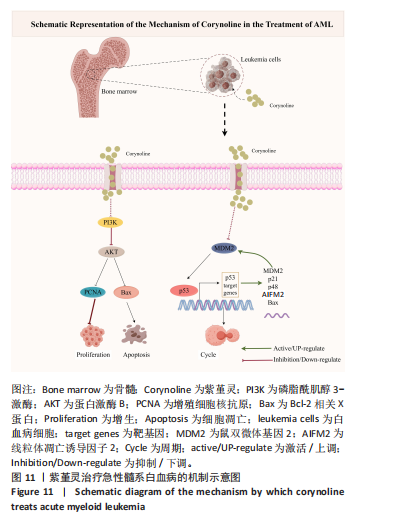
结论:此项研究综合运用网络药理学方法、分子对接技术、分子动力学模拟和实验验证手段,系统阐明紫堇灵在急性髓系白血病治疗中的药理作用及潜在分子机制(图11,基于Figdraw绘制)。具体而言,研究验证了紫堇灵在体外抑制急性髓系白血病肿瘤细胞增殖、诱导细胞凋亡和介导G2/M期细胞周期阻滞方面的药理学潜力,其作用机制一方面通过抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路抑制细胞恶性增殖和诱导细胞凋亡;另一方面紫堇灵通过促进鼠双微体基因2降解,解除对p53的抑制作用,进而激活p53/p21/Bax通路,从而促进细胞周期阻滞与凋亡。这些发现不仅为急性髓系白血病的临床治疗提供了一个新的候选药物,也为天然产物紫堇灵治疗急性髓系白血病潜力提供了分子药理学依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
近年来,天然产物正逐渐成为抗癌药物研发中的“新宠”,尤其在精准治疗时代背景下,中药活性成分的多靶点作用特性引发广泛关注。紫堇灵,作为源自中药布氏紫堇的一种天然生物碱,展现出令人期待的抗肿瘤潜力。在本研究中,作者首次将目光聚焦于紫堇灵在急性髓系白血病中的应用,系统评估其在体外对急性髓系白血病细胞的抑制作用,并通过多维手段解析其作用机制。结果表明,紫堇灵不仅可以通过磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/AKT信号通路抑制急性髓系白血病细胞的异常增殖,还可靶向降解鼠双微体基因2(MDM2),解除对p53的抑制,激活p53/p21/Bax通路,从而诱导凋亡与细胞周期阻滞。更有趣的是,借助网络药理学与分子模拟技术,揭示了紫堇灵与视黄酸受体β(RARB)、过氧化物合酶2、鼠双微体基因2和丝裂原激活蛋白激酶14等多个关键致癌靶点间的稳定结合关系,为其分子作用提供了可信的计算支撑。这种“虚拟靶点+实验验证”的研究范式不仅为紫堇灵抗急性髓系白血病作用提供了坚实的理论基础,也为天然产物的现代化药物开发打开了新路径。未来,紫堇灵或许能作为天然来源的“精准打击手”,在急性髓系白血病等血液肿瘤治疗中发挥更加重要的角色。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||