1.1 设计 利用网络药理学分析韭菜子在少弱精子症中的主要作用靶点及通路,通过分子对接技术验证核心靶点,最后通过动物实验验证韭菜子改善雷公藤多苷片诱导少弱精子症大鼠模型精子生成及质量的作用机制。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2024年5-8月在宁夏医科大学科技楼完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 网络药理学数据库及分析工具 TCMSP数据库(https://old.tcmsp-e.com/tcmsp.php);Swiss Target Prediction数据库(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/);GeneCards 数据库(https://www.genecards.org/);DisGeNET数据库(https://disgenet.com/);UniProt数据库(https://www.UniProt.org/UniProt/);OMIM数据库(https://www.omim.org/);DrugBank数据库(https://www.drugbank.ca/);STRING数据库 (https://cn.string-db.org/);RCSB PDB数据库 (https://www.rcsb.org/);PubChem数据库(https:// pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/);Venny 2.1制图平台(https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/);DAVID平台(https:// david.ncifcrf.gov/);微生信平台(http://www.bioinformatics. com.cn/);CB-DOCK2网站(https://cadd.labshare.cn/cb-dock2/php/index.php);Cytoscape软件;Graphpad prism软件。
TCMSP(https://old.tcmsp-e.com/tcmsp.php)数据库全称中药系统药理学数据库,来源于中国,由秦岭七药研发中心搭建了完善的技术服务平台,结合系统药理学分析,以动物模型为核心,为科研、医学转化、新药研发等生物技术领域提供一站式专业服务。此次分析应用TCMSP数据库获得韭菜子的4个活性成分,48个有效成分靶点。中药智能新药开发平台TCMSP为国际上第一个大数据+AI的中药新药开发平台。该平台利用人工智能和系统科学理论,构建了模拟人体代谢全过程的中药功效成分数字化ADME/t技术,可以准确实现药代层次功效成分的组合设计。涵盖了人体全景多维靶点辨识技术以及机体全维网络分析技术,实现了基于靶点和作用网络的功效成分智能组合设计。建立了分析中药/复方多点微效、协同整合、级联放大等效应机制的优化评价体系,突破基于协同整合分析的功效成分智能组合设计的瓶颈;完成了多成分协同分析工具及其量-效关系评价新方法,实现定性、定量阐明成分之间的协同关系,用于智能组方的质量控制和量效关系优化。
GeneCards数据库(https://www.genecards.org/)是人类基因数据库,此次分析应用Gene Cards数据库搜索少弱精子症相关靶点。GeneCards数据库由以色列魏茨曼科学研究所与LifeMap科学联合开发。该知识库自动整合了来自200个Web来源的以基因为中心的数据,包括基因组、转录组、蛋白质组、遗传、临床和功能信息。
DisGeNET数据库(https://www.disgenet.com/)是一个专注于基因-疾病关联的权威生物信息学数据库。此次分析应用DisGeNET数据库搜索少弱精子症相关靶点。DisGeNET是由西班牙巴塞罗那超级计算中心(BSC)和生物医学信息学研究组(GRIB)开发和维护的基因-疾病关联知识平台。它通过整合多来源数据、标准化疾病术语、提供证据评分和强大分析工具,成为研究疾病遗传基础、发现生物标志物和药物靶点的核心资源,尤其适用于复杂疾病机制解析和临床基因组学解读。
OMIM数据库(https://www.omim.org/)中文名为人类在线孟德尔遗传,此次分析应用OMIM数据库搜索少弱精子症相关靶点。该数据库由VictorA.McKusick博士于1960年代初期发起,作为孟德尔特征和疾病的目录,在线版本OMIM于1985年由美国国家医学图书馆和约翰霍普金斯大学的WilliamH.Welch医学图书馆合作创建。OMIM中引用的全文概览信息包含所有已知的孟德尔疾病和超过16 000个基因,侧重于表型和基因型之间的关系。
DrugBank数据库(https://www.drugbank.ca/)于2006年在阿尔伯塔大学DavidWishart博士的实验室成立。此次分析通过DrugBank数据库补充临床用于治疗少弱精子症的常用西药的作用靶点。DrugBank数据库是一个全面的、免费访问的在线数据库,包含有关药物和药物靶点的信息。作为生物信息学和化学信息学资源,将详细的药物(即化学、药理学和制药)数据与全面的药物靶点(即序列、结构和途径)信息相结合。
STRING数据库(https://cn.string-db.org/)由加州大学圣地亚哥分校的生物信息学中心开发。此次分析利用韦恩图得到的共同靶点导入STRING平台,构建蛋白质互作网络。STRING数据库是一个基于公共数据库和文献信息的蛋白质相互作用网络数据库。它收集了多个公共数据库,包括UniProt、KEGG、NCBI和Gene Ontology等,整合这些数据并生成一个全面的蛋白质相互作用网络数据库。STRING数据库不仅提供了蛋白质相互作用网络的可视化,还能够提供蛋白质家族、途径和亚细胞定位等信息。除此之外,STRING数据库还提供了一些分析工具,如聚类分析和基因本体富集分析等,帮助用户更好地分析网络图,并找到有意义的生物学命题。
UniProt数据库(https://www.UniProt.org/UniProt/)是蛋白质序列和注释数据的综合资源。此次分析利用UniProt数据库对基因信息名称进行基因Uniprot ID转换。UniProt数据库为科学界提供全面、高质量且可免费访问的蛋白质序列和功能信息资源。
SwissTargetPrediction数据库(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/)是由瑞士生物信息学研究所(SIB)和日内瓦大学分子模拟组开发的小分子靶点预测平台。此次分析利用SwissTargetPrediction数据库对韭菜子进行成分靶点预测。SwissTargetPrediction
数据库通过融合化学相似性分析与结构反向对接技术,高效预测化合物可能作用的蛋白质靶点,为药物发现、化学生物学及机制研究提供关键计算支持。
RCSB PDB数据库(https://www.rcsb.org/)全称Protein Data Bank,此次分析利用RCSB PDB数据库下载核心靶点蛋白结构文件。PDB数据库是美国Brook haven国家实验室于1971年创建的,由结构生物信息学研究合作组织(Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics)维护。PDB数据库是生物大分子的原子坐标以及描述蛋白质和其他重要生物大分子相关信息的存储库。结构生物学家使用X射线晶体学、核磁共振光谱和冷冻电子显微镜等方法来确定分子中每个原子相对于彼此的位置,然后存储这些信息,并由PDB数据库注释并公开发布到档案中。
PubChem数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)是美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)的一个开放化学数据库。此次分析利用PubChem数据库下载韭菜子核心靶点蛋白结构文件。PubChem主要包含小分子,也包含较大的分子,例如核苷酸、碳水化合物、脂质、肽和化学修饰的大分子。数据库收集有关化学结构、标识符、化学和物理特性、生物活性、专利、健康、安全、毒性数据等信息。
此研究所用数据均来源于国际公认的公开科研数据库,均通过合法渠道获取,数据访问符合各平台许可协议。人类数据已去标识化,分析过程遵循最小必要原则,原始数据未离开受控研究环境。
1.3.2 主要试剂与设备 韭菜子(宁夏康泰隆中医饮片有限公司,批号:2403001);左卡尼汀口服液(东北制药集团,批号231105,规格:10 mL ∶1 g);雷公藤多苷片(浙江得恩德制药股份有限公司,批号: Z33020422,规格:10 mg);电泳缓冲液(武汉塞维尔生物科技有限公司,货号G2081-1L);BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(凯基生物公司,货号20240308);ELISA试剂盒(南京博研生物,卵泡刺激素:货号BY-ER334438;黄体生成素:货号BY-ER330447;睾酮:货号BY-JZF0458);β-actin抗体(北京LABLEAD公司,货号A0101);磷脂酰肌醇3激酶抗体(北京Immunoway公司,货号YT6156);磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3激酶抗体(上海Abmart公司,货号TA32425);蛋白激酶B抗体(北京Immunoway公司,货号YT0185);磷酸化蛋白激酶B抗体(北京Immunoway公司,货号YP0006);B细胞淋巴瘤2抗体(武汉Abclonal公司,货号A20777);TUNEL试剂盒(南京诺威赞生物科技有限公司,货号A112-02);石蜡切片机(德国LEICA公司,型号:RM2235);电子分析天平[华志(福建)电子科技有限公司,型号:PTX-FA220S];倒置荧光显微镜(德国LEICA公司,型号:DM2000/DFC450C)。
1.4 实验方法
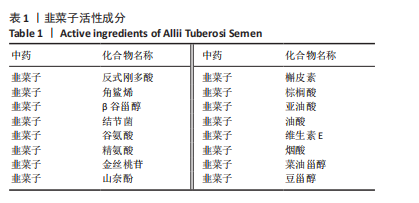
1.4.1 韭菜子有效活性成分的筛选 登录中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP数据库),按照生物利用度≥30%且类药性≥0.18的标准进行筛选,获得韭菜子的有效成分;通过PubChem数据库检索韭菜子有效成分的SMILES分子结构,将其导入Swiss Target Prediction数据库获得成分靶点。利用UniProt数据库将靶标转换成geneSymbol。
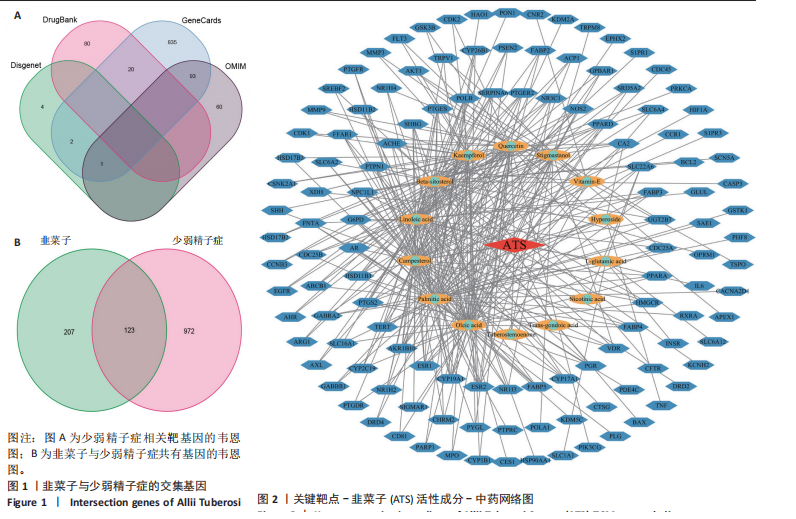
1.4.2 少弱精子症疾病靶点获取 依据关键词“oligoasthenozoospermia”“oligospermia” “deficiency of spermmotility”“spermatogenic dysfunction”“asthenospermia”“low sperm counts/motility”,在Genecards数据库、DisGeNET数据库、DrugBank数据库和OMIM数据库搜索疾病相关靶点,并通过DrugBank数据库补充临床用于治疗少弱精子症的常用西药的作用靶点,删除重复值,合并4个数据库所获得的数据得到与疾病有关的靶基因。
1.4.3 构建“关键靶点-活性成分-中药”网络 将韭菜子活性成分及靶点基因导入Cytoscape软件,构建药物-有效成分-靶点疾病网络。
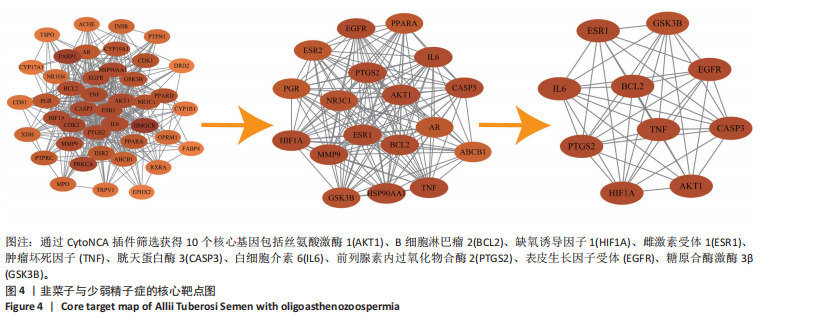
1.4.4 蛋白质互作网络构建 选取韭菜子和少弱精子症交集基因制作韦恩图,将韦恩图得到的共同靶点导入String平台,设置最低置信度为0.4,构建蛋白质互作网络。将靶点基因导入Cytoscape软件进行可视化展示,根据Degree值筛选出核心靶点。
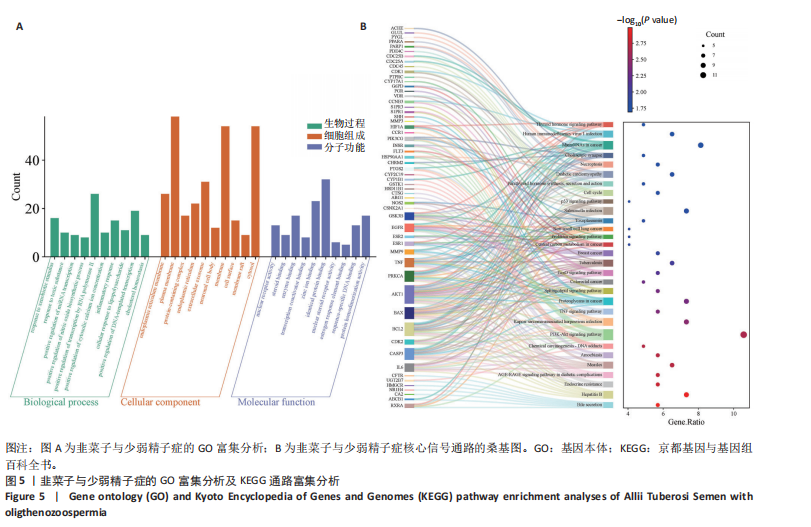
1.4.5 基因本体(gene ontology,GO)和京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)富集分析 将交集靶点导入DAVID数据库,获得韭菜子干预少弱精子症可能的生物过程和主要的信号通路,设定阈值P < 0.05,利用微生信可视化平台对核心靶点基因可视化处理。
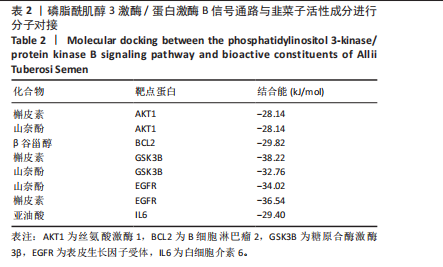
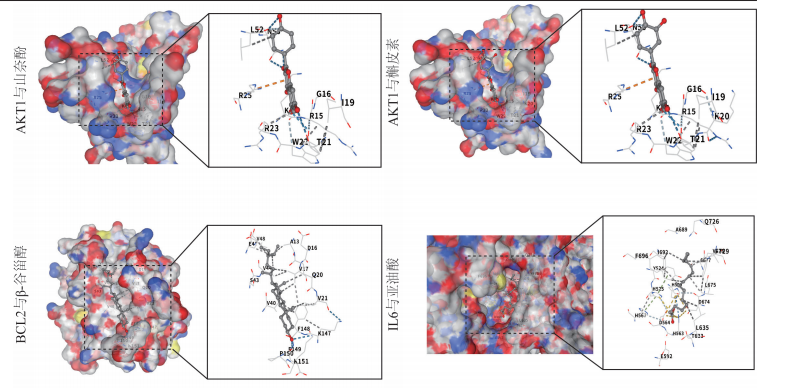
1.4.6 分子对接 利用PDB数据库下载核心靶蛋白3D结构,作为受体。通过PubChem数据库下载关键成分结构文件,作为配体。利用CB-Dock2在线网站进行分子对接计算动力结合能。
1.5 动物实验
1.5.1 实验动物 SPF级SD雄性大鼠46只,6-8周龄,体质量180-200 g,购自宁夏医科大学动物实验中心,动物许可证号为SYXK(宁)2020-0001;饲养于宁夏医科大学SPF级动物房,温度为(23±3) ℃,相对湿度53%-58%,每日12 h光照,通风良好,自由饮食、摄水。此研究获得宁夏医科大学动物伦理委员会的批准,伦理批号:IACUC-NYLAC-2021-0721。
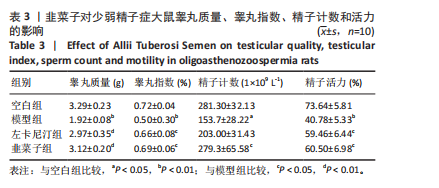
1.5.2 分组、造模、给药处理 取SPF级46只SD雄鼠随机分为空白组(n=13)和模型组(n=33),动物适应性饲养7 d后开始造模,参照孙天松等[15-16]造模方法,模型组灌胃40 mg/(kg·d)雷公藤多苷片4周构建少弱精子症大鼠模型。造模结束后,从空白组与模型组大鼠中各随机选取3只大鼠,腹腔注射2.5%戊巴比妥钠麻醉后,取睾丸组织进行苏木精-伊红染色,镜下睾丸组织整体结构异常,睾丸曲细精管生精细胞排列紊乱,部分生精细胞脱落坏死,曲细精管精子数量急剧减少,符合少弱精子症诊断标
准[16],表明造模成功。空白组剩余10只,模型组剩余30只。将剩余30只造模成功大鼠按随机数字法再分成3组,分别为模型组、韭菜子组、左卡尼汀组,每组10只。左卡尼汀组大鼠灌胃100 mg/(kg·d)左卡尼汀,给药28 d;韭菜子组按照人临床每日剂量为9 g以及人与大鼠体质量折算选择0.81 g/(kg·d)灌胃[17],给药28 d;正常组和模型组大鼠灌胃等剂量的生理盐水。观察各组大鼠进食、活动、毛发光泽度及脱落情况。给药结束后,腹腔注射2.5%戊巴比妥钠麻醉,经心脏穿刺采血,分离血清并于-80 ℃保存;取睾丸组织置于40 g/L多聚甲醛固定液中固定24 h,用于制备石蜡切片。

1.6 主要观察指标
1.6.1 计算睾丸脏器系数 脏器系数(%)=睾丸脏器质量/体质量×100%。
1.6.2 精液质量测定 选取大鼠右侧附睾,剪碎使精液流出,用预热的37 ℃生理盐水润洗,滤纸滤干后称质量,再放入盛有2 mL PBS已预热至37 ℃的Ep管中,用手术剪剪碎,摇匀,37 ℃条件下恒温孵育15 min,使附睾内储存的生精细胞充分游离到培养液中,孵育结束后,用玻璃棒搅拌均匀,制备精子悬液,取10 μL精子悬液加注至精子计数板,覆盖盖玻片,利用计算机辅助精液分析系统对精子质量进行检测[20]。
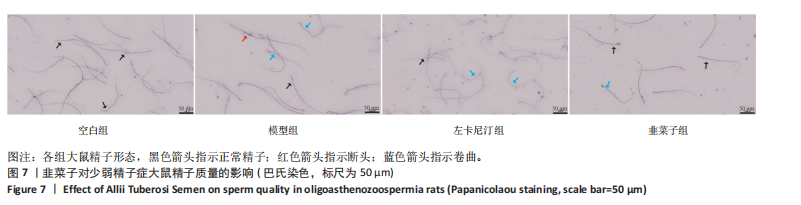
1.6.3 精子形态学观察 待精液标本完全液化后,洗涤并涂片,待玻片干燥后,用梯度乙醇脱水,使用巴式法对标本进行染色后封固,置于显微镜下观察。
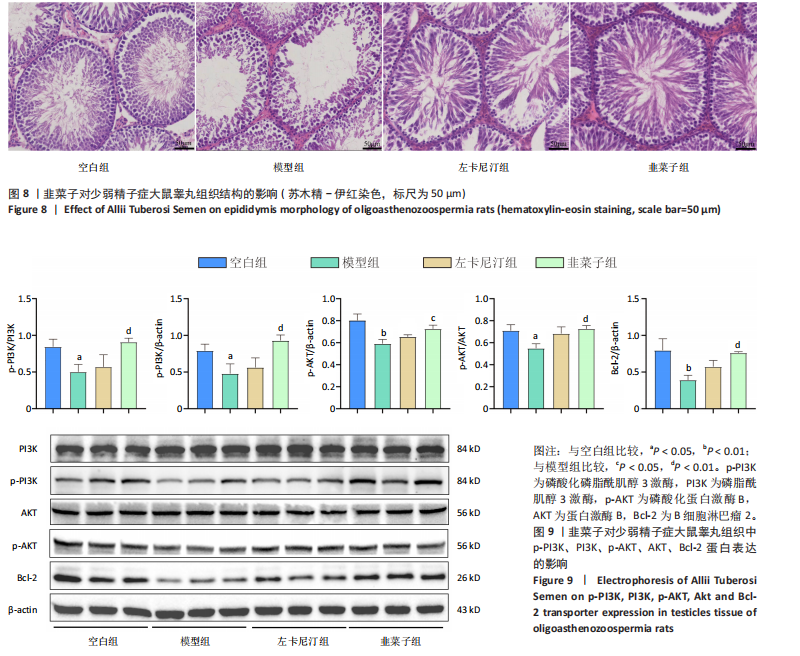
1.6.4 苏木精-伊红染色观察睾丸组织病理形态 取大鼠睾丸组织,置于40 g/L多聚甲醛溶液中固定≥24 h,确保充分固定。经脱水、透明化处理后,石蜡包埋,制备4.0-5.0 μm厚度切片,60 ℃烘箱烤片2 h,增强切片附着力。二甲苯Ⅰ、Ⅱ各脱蜡
10 min,梯度乙醇(体积分数100%→95%→80%)至水化,蒸馏水浸洗5 min;浸染1 min,流水冲洗;PBS返蓝30 s,流水冲洗,快速脱水(体积分数95%→100%乙醇各30 s),二甲苯透明10 min×2次,中性树胶封固。光学显微镜下观察睾丸组织完整性,重点评估生精小管结构、间质细胞分布及基底膜状。
1.6.5 酶联免疫吸附法测定睾酮、黄体生成素和卵泡刺激素水平 按照标准操作流程对大鼠睾丸组织进行匀浆处理,并依据ELISA试剂盒说明书检测睾酮、黄体生成素和卵泡刺激素水平。
1.6.6 蛋白免疫印迹法(Western blot)检测大鼠睾丸组织磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3激酶、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶、磷酸化蛋白激酶B、蛋白激酶B、B细胞淋巴瘤2蛋白水平 取50 mg睾丸组织裂解后离心,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,经SDS-PAGE电泳、转膜、封闭后,以β-actin(1∶8 000)为内参,分别用特异性磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3激酶、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶、磷酸化蛋白激酶B、蛋白激酶B、B细胞淋巴瘤2一抗(1∶1 000)4 ℃孵育过夜,TBST洗涤后加入二抗(1∶10 000)孵育1 h,ECL化学发光显影,最后使用化学发光成像仪采集图像并用ImageJ 1.8.0软件进行定量分析。
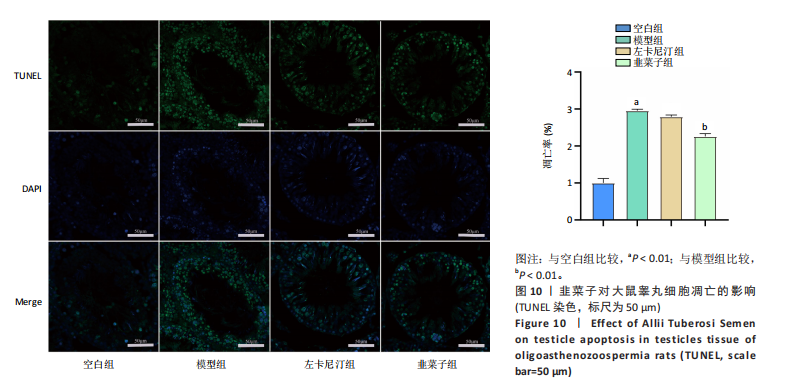
1.6.7 TUNEL检测大鼠睾丸细胞凋亡情况 按照常规方法对睾丸组织切片进行TUNEL染色,DAPI将细胞核染成蓝色,凋亡细胞产生绿色荧光。在荧光显微镜波长为488 nm下对切片进行拍照分析。
1.7 统计学分析 采用SPSS 24.0软件进行统计分析:多个样本均数间比较采用完全随机设计资料的单因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA),当各组方差齐时,多个样本均数之间的多重比较采用LSD-t检验,组间比较经方差齐性检验后采用成组t检验;当各组方差不齐时用Dunnett法进行均数间的两两比较,检验水准为α=0.05,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经通过宁夏医科大学公共卫生与管理学院统计学专家审核。