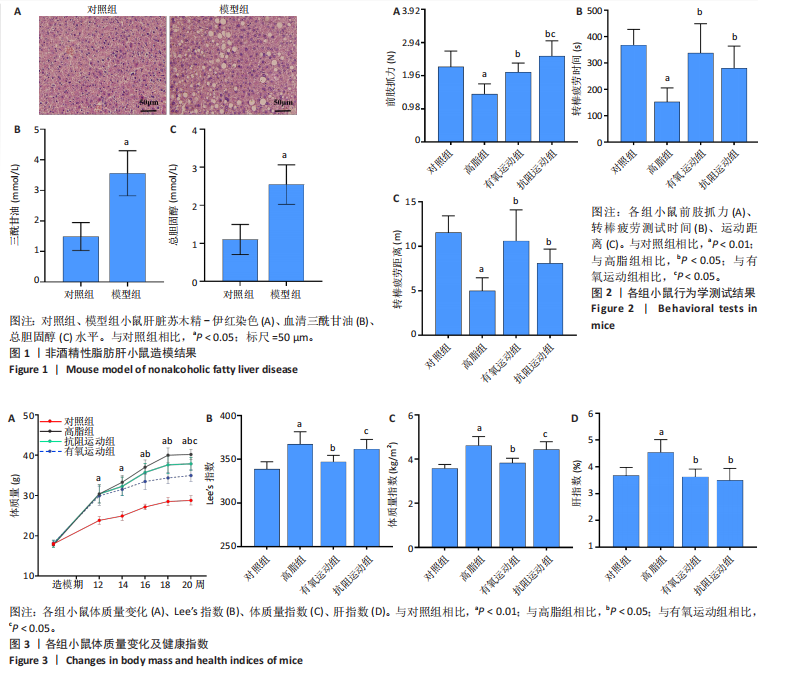
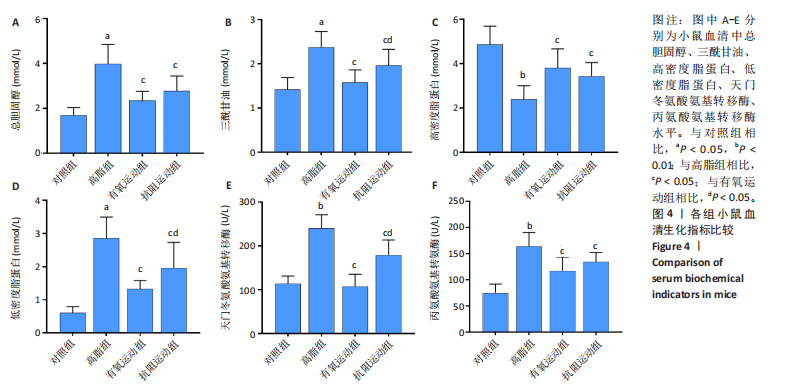
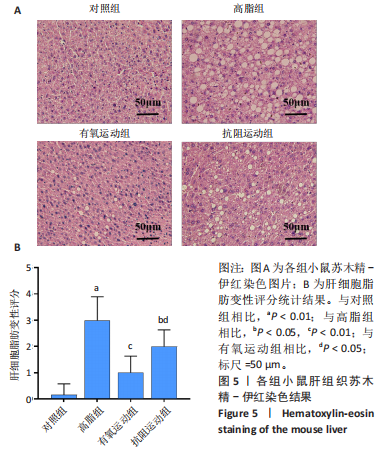
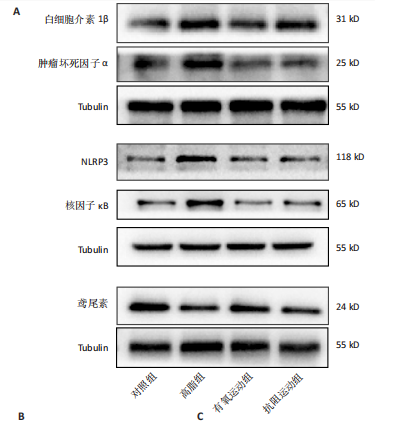
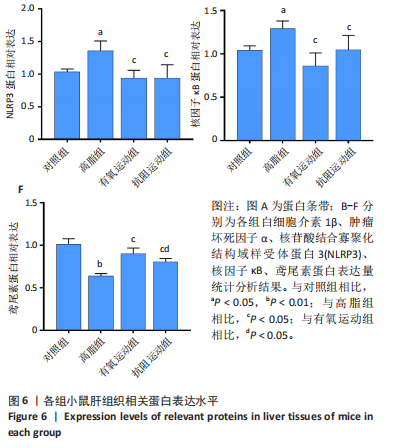
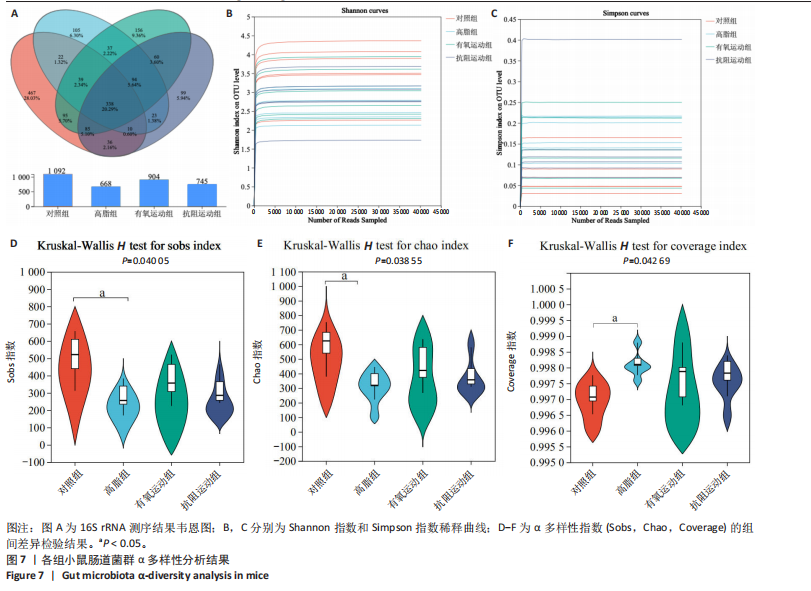
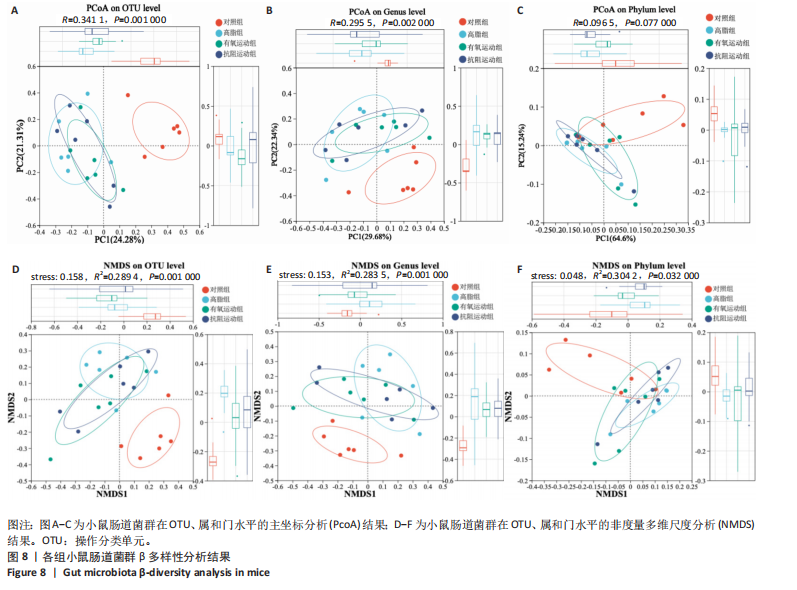
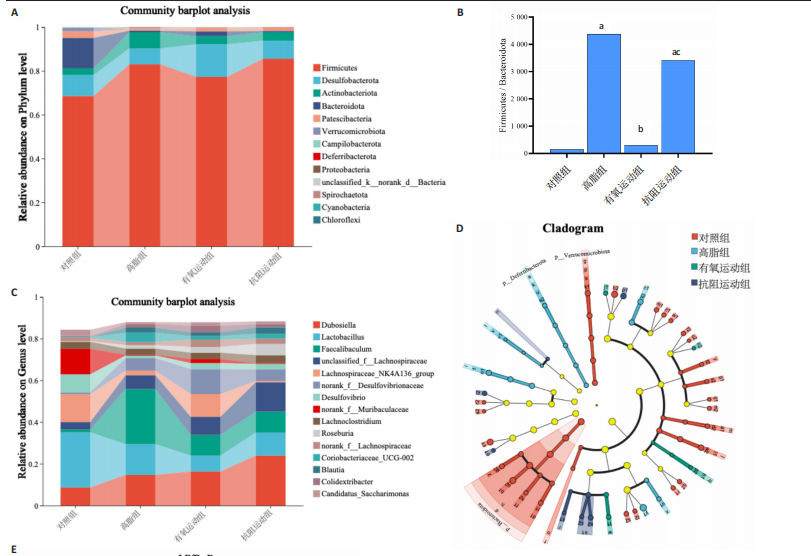
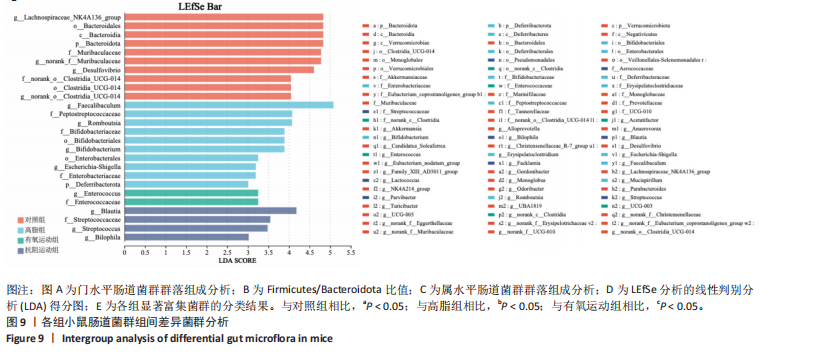
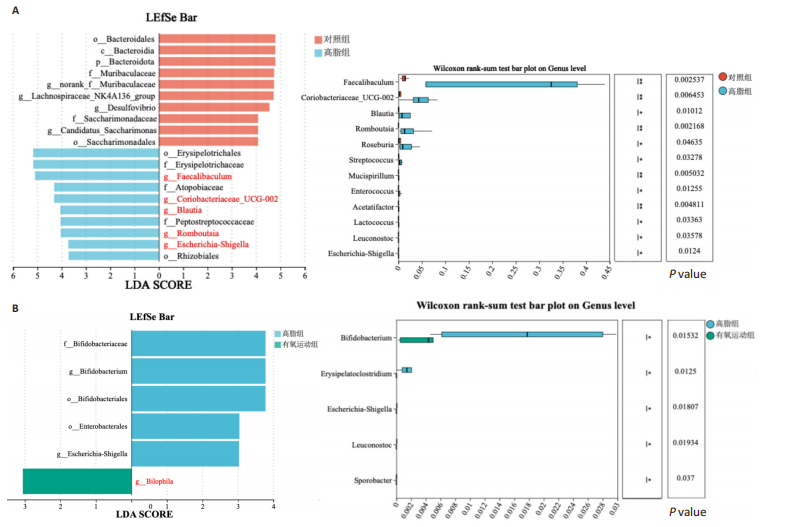
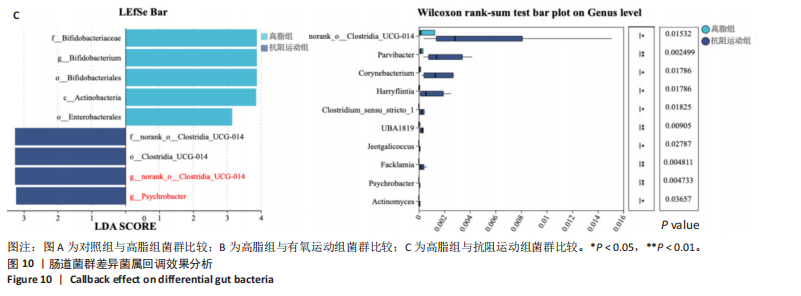
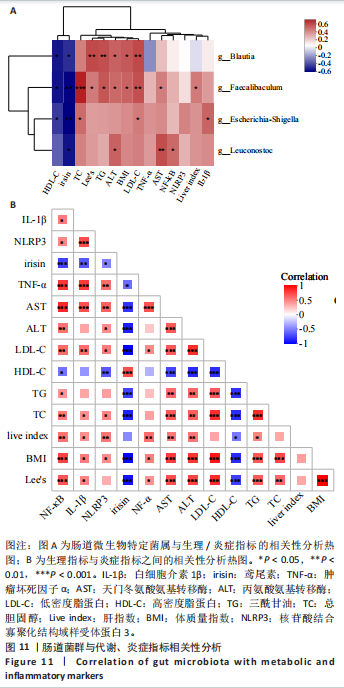
[1] WANG S, YIN J, LIU Z, et al. Metabolic disorders, inter-organ crosstalk, and inflammation in the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Life Sci. 2024;359:123211.
[2] GU Y, GUO C, LIU Z, et al. The trend in incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its impact on cirrhosis and liver cancer: An analysis from Global Burden of Disease 2021. Public Health. 2025;242:79-86.
[3] KAN C, ZHANG K, WANG Y, et al. Global burden and future trends of metabolic dysfunction-associated Steatotic liver disease: 1990-2021 to 2045. Ann Hepatol. 2025;30(2):101898.
[4] WAYAL V, WANG SD, HSIEH CC. Novel bioactive peptides alleviate Western diet-induced MAFLD in C57BL/6J mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis via TLR4/NF-κB and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025;148: 114177.
[5] ZHOU M, LV J, CHEN X, et al. From gut to liver: Exploring the crosstalk between gut-liver axis and oxidative stress in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Ann Hepatol. 2025;30(1):101777.
[6] GERBER L, OTGONSUREN M, MISHRA A, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with low level of physical activity: a population-based study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;36(8):772-781.
[7] CHEN M, ZHU JY, MU WJ, et al. Cdo1-Camkk2-AMPK axis confers the protective effects of exercise against NAFLD in mice. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):8391.
[8] 雷森林,李先辉,伍方佳.脂噬在非酒精性脂肪性肝病中的作用及运动调节机制的研究进展[J].中国病理生理杂志,2025,41(1):165-172.
[9] FARZANEGI P, DANA A, EBRAHIMPOOR Z, et al. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur J Sport Sci. 2019;19(7):994-1003.
[10] YE X, SUN P, LAO S, et al. Fgf21-Dubosiella axis mediates the protective effects of exercise against NAFLD development. Life Sci. 2023;334: 122231.
[11] GU X, YUAN L, GAN L, et al. Understanding the Role of Exercise and Probiotic Interventions on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Alleviation in Zebrafish: Dialogue Between the Gut and Liver. Int J Mol Sci. 2025; 26(3):1360.
[12] KOVYNEV A, YING Z, ZHANG S, et al. Timing Matters: Late, but Not Early, Exercise Training Ameliorates MASLD in Part by Modulating the Gut-Liver Axis in Mice. J Pineal Res. 2024;76(8):e70003.
[13] DE CÓL JP, DE LIMA EP, POMPEU FM, et al. Underlying Mechanisms behind the Brain-Gut-Liver Axis and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(7):3694.
[14] ZHU W, SAHAR NE, JAVAID HMA, et al. Exercise-Induced Irisin Decreases Inflammation and Improves NAFLD by Competitive Binding with MD2. Cells. 2021;10(12):3306.
[15] HUANGFU LX, CAI XT, YANG JN, et al. Irisin attenuates inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis by altering the intestinal microbiota. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(6):1433.
[16] 王佳倩,蒋昌君,彭毅,等.有氧运动对CNPY2基因调控AKT/GSK3β通路改善非酒精性脂肪肝的作用研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(30):6441-6448.
[17] REYNOLDS JC, LEE C. Mouse Fitness as Determined Through Treadmill Running and Walking. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2144:57-65.
[18] HORNBERGER TA JR, FARRAR RP. Physiological hypertrophy of the FHL muscle following 8 weeks of progressive resistance exercise in the rat. Can J Appl Physiol. 2004;29(1):16-31.
[19] ZHAO Q, JING Y, JIANG X, et al. SIRT5 safeguards against primate skeletal muscle ageing via desuccinylation of TBK1. Nat Metab. 2025; 7(3):556-573.
[20] 颜惠敏,吕欣晨,宋雯燕,等.姜黄素调控肠道菌群及其代谢物提高小鼠运动表现的研究[J].食品与发酵工业,2025,51(8):37-44.
[21] 张树玲,李军汉,王佳倩,等.有氧运动干预非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠肝脏JAK2/STAT5信号通路的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(17):2690-2695.
[22] WEI S, WANG L, EVANS PC, et al. NAFLD and NASH: etiology, targets and emerging therapies. Drug Discov Today. 2024;29(3):103910.
[23] LIN X, QU J, YIN L, et al. Aerobic exercise-induced decrease of chemerin improved glucose and lipid metabolism and fatty liver of diabetes mice through key metabolism enzymes and proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2023;1868(12):159409.
[24] DINIZ TA, DE LIMA JUNIOR EA, TEIXEIRA AA, et al. Aerobic training improves NAFLD markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-α signaling in obese mice. Life Sci. 2021;266:118868.
[25] FANG C, LIU S, YANG W, et al. Exercise ameliorates lipid droplet metabolism disorder by the PLIN2-LIPA axis-mediated lipophagy in mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024;1870(3):167045.
[26] SANTOS JDM, SILVA JFT, ALVES EDS, et al. Strength Training Protects High-Fat-Fed Ovariectomized Mice against Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(10):5066.
[27] ARRESE M, CABRERA D, KALERGIS AM, et al. Innate Immunity and Inflammation in NAFLD/NASH. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61(5):1294-1303.
[28] FREDRICKSON G, BARROW F, DIETSCHE K, et al. Exercise of high intensity ameliorates hepatic inflammation and the progression of NASH. Mol Metab. 2021;53:101270.
[29] YANG S, XU B, HAN Y, et al. TAF15 exacerbates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis progression by regulating lipid metabolism and inflammation via FASN and p65 NF-κB. Liver Int. 2023;43(9):1920-1936.
[30] HE M, CHIANG HH, LUO H, et al. An Acetylation Switch of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulates Aging-Associated Chronic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2020;31(3):580-591.e5.
[31] LI H, SHEN J, WU T, et al. Irisin Is Controlled by Farnesoid X Receptor and Regulates Cholesterol Homeostasis. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:548.
[32] XIN C, LIU J, ZHANG J, et al. Irisin improves fatty acid oxidation and glucose utilization in type 2 diabetes by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016;40(3):443-451.
[33] LIU Y, JIN Y, LI J, et al. Small Bowel Transit and Altered Gut Microbiota in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis. Front Physiol. 2018;9:470.
[34] XU H, FANG F, WU K, et al. Gut microbiota-bile acid crosstalk regulates murine lipid metabolism via the intestinal FXR-FGF19 axis in diet-induced humanized dyslipidemia. Microbiome. 2023;11(1):262.
[35] HAN H, ZHANG S, WANG M, et al. Retinol metabolism signaling participates in microbiota-regulated fat deposition in obese mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2025;136:109787.
[36] ZHAO J, BAI M, NING X, et al. Expansion of Escherichia-Shigella in Gut Is Associated with the Onset and Response to Immunosuppressive Therapy of IgA Nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022;33(12):2276-2292.
[37] SHANG X, CHE X, MA K, et al. Chronic Cr(VI) exposure-induced biotoxicity involved in liver microbiota-gut axis disruption in Phoxinus lagowskii Dybowski based on multi-omics technologies. Environ Pollut. 2025;368:125759.
[38] LIU X, MAO B, GU J, et al. Blautia-a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes. 2021;13(1):1-21.
[39] SHIBATA M, OZATO N, TSUDA H, et al. Mouse Model of Anti-Obesity Effects of Blautia hansenii on Diet-Induced Obesity. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023;45(9):7147-7160.
[40] ZHAO T, ZHAN L, ZHOU W, et al. The Effects of Erchen Decoction on Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:647529.
|