[1] 郭绍彬,唐世杰,张万聪.1990-2019年中国烧伤发病率及死亡率趋势的年龄-时期-队列模型分析[J].中国美容医学, 2023,32(7):9-13.
[2] DA SILVA MMM, TRAVENSOLO CF, PROBST VS, et al. Quantification of changes in functional capacity and muscle strength in patients: a burn intensive care unit cohort study. Burns. 2022;48(4):833-840.
[3] VAN AERDE N, MEERSSEMAN P, DEBAVEYE Y, et al. Five-year impact of ICU-acquired neuromuscular complications: a prospective, observational study. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(6):1184-1193.
[4] CLARK AT, SONG J, YAO X, et al. Muscle Homeostasis Is Disrupted in Burned Adults. J Burn Care Res. 2020;41(1):33-40.
[5] OZKAL O, YURDALAN SU, SEYYAH M, et al. The effect of burn severity on functional capacity in patients with burn injury. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2019;32(2):215-221.
[6] SPRONK I, LEGEMATE CM, POLINDER S, et al. Health-related quality of life in children after burn injuries: A systematic review. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018;85(6):1110-1118.
[7] CUIJPERS MD, BAARTMANS MGA, VAN ZUIJLEN PPM, et al. Children’s growth and motor development following a severe burn: a systematic review. Burns Trauma. 2023;11:tkad011.
[8] POLYCHRONOPOULOU E, HERNDON DN, PORTER C. The Long-Term Impact of Severe Burn Trauma on Musculoskeletal Health. J Burn Care Res. 2018;39(6):869-880.
[9] ARGILÉS JM, CAMPOS N, LOPEZ-PEDROSA JM, et al. Skeletal Muscle Regulates Metabolism via Interorgan Crosstalk: Roles in Health and Disease. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17(9):789-796.
[10] GUPTA K, MEHROTRA M, KUMAR P, et al. Smoke Inhalation Injury: Etiopathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2018;22(3):180-188.
[11] JESCHKE MG, CHINKES DL, FINNERTY CC, et al. Pathophysiologic response to severe burn injury. Ann Surg. 2008;248(3):387-401.
[12] ELNAGGAR RK, OSAILAN AM, MAHMOUD WS, et al. Beyond the Acute Phase: Understanding Relationships Among Cardiorespiratory Response to Exercises, Physical Activity Levels, and Quality of Life in Children After Burn Injuries. J Burn Care Res. 2022;43(4):827-833.
[13] SULLI D, DHOPTE A, AGRAWAL K. Impact of burn contractures of chest wall and their surgical release on pulmonary function. Burns. 2019;45(4):929-935.
[14] KANBAY M, SIRIOPOL D, COPUR S, et al. Effect of Bimagrumab on body composition: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024;36(1):185.
[15] 伍朝明,孙君志.下肢抗阻训练对老人步行能力及平衡能力影响的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(26):4257-4264.
[16] DOMBRECHT D, VAN DAELE U, VAN ASBROECK B, et al. Molecular mechanisms of post-burn muscle wasting and the therapeutic potential of physical exercise. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14(2): 758-770.
[17] 霍婷,徐向阳,谢卫国,等.运动康复训练在小儿烧伤康复中应用的研究进展[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2023, 39(3):275-279.
[18] FLORES O, TYACK Z, STOCKTON K, et al. Exercise training for improving outcomes post-burns: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(6):734-746.
[19] GITTINGS PM, GRISBROOK TL, EDGAR DW, et al. Resistance training for rehabilitation after burn injury: A systematic literature review & meta-analysis. Burns. 2018;44(4): 731-751.
[20] 杨莎,邱林.抗阻训练对烧伤患儿康复效果影响的研究进展[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2021,37(9):895-899.
[21] YANG S, QIU L, XIAO J, et al. The effects of resistance training on children with burns: a meta-analysis. Pediatr Surg Int. 2021;37(10):1323-1332.
[22] SUMAN OE, SPIES RJ, CELIS MM, et al. Effects of a 12-wk resistance exercise program on skeletal muscle strength in children with burn injuries. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2001;91(3):1168-1175.
[23] SUMAN OE, THOMAS SJ, WILKINS JP, et al. Effect of exogenous growth hormone and exercise on lean mass and muscle function in children with burns. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2003;94(6):2273-2281.
[24] WON YH, CHO YS, JOO SY, et al. The effect of a pulmonary rehabilitation on lung function and exercise capacity in patients with burn: a prospective randomized single-blind study. J Clin Med. 2020;9(7):2250.
[25] 邱卓英,王朴,王博.《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》的发展和应用进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2008(1):85-86.
[26] 王国祥,姜静远,邱卓英,等.康复体育政策架构、优先领域及其核心内容:基于WHO康复政策内容分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(12):1380-1389.
[27] 刘兴朝,胡通,马艳,等.康复机器人训练脑性瘫痪患者:改善下肢运动功能效果的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(18):3925-3933.
[28] PAGE MJ, MOHER D, BOSSUYT PM, et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021; 372:n160.
[29] ABDELBASSET WK, ELSAYED SH, NAMBI G, et al. Optimization of pulmonary function, functional capacity, and quality of life in adolescents with thoracic burns after a 2-month arm cycling exercise programme: a randomized controlled study. Burns. 2022;48(1):78-84.
[30] ALI ZM, EL-REFAY BH, ALI RR. Aerobic exercise training in modulation of aerobic physical fitness and balance of burned patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(3):585-589.
[31] ALLAM NM, BADAWY MM, ELIMY DA. Effect of Pilates exercises on pulmonary function, respiratory muscle strength, and functional capacity in patients with inhalation injury after flame thermal burn: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Burns. 2024; 50(9):107284.
[32] AL-MOUSAWI AM, WILLIAMS FN, MLCAK RP, et al. Effects of exercise training on resting energy expenditure and lean mass during pediatric burn rehabilitation. J Burn Care Res. 2010;31(3):400-408.
[33] BADAWY MM, ALLAM NM. Impact of Adding Protein Supplementation to Exercise Training on Lean Body Mass and Muscle Strength in Burn Patients. J Burn Care Res. 2021;42(5):968-974.
[34] BASHA MA, ABOELNOUR NH, ALY SM, et al. Impact of Kinect-based virtual reality training on physical fitness and quality of life in severely burned children: a monocentric randomized controlled trial. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2022;65(1):101471.
[35] CHAO T, PARRY I, PALACKIC A, et al. The effects of short bouts of ergometric exercise for severely burned children in intensive care: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2022;36(8):1052-1061.
[36] ÇINAR MA, BAYRAMLAR K, ERKILIC A, et al. Effect of three different exercise trainings on functional capacity in early stage severe burn patients: a randomized controlled trial. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2024; 30(8):562-270.
[37] ÇINAR MA, ERKILIÇ A. Effect of aerobic exercise on neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio, and lymphocyte-monocyte ratio in burn patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2024;95:199-206.
[38] CUCUZZO NA, FERRANDO A, HERNDON DN. The effects of exercise programming vs traditional outpatient therapy in the rehabilitation of severely burned children. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2001;22(3):214-220.
[39] DE LATEUR BJ, MAGYAR-RUSSELL G, BRESNICK MG, et al. Augmented exercise in the treatment of deconditioning from major burn injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(12 Suppl 2):S18-23.
[40] EBID AA, ATTALLA AF, IBRAHIM AR, et al. Effect of anti-gravity treadmill (Alter G) training on gait characteristics and postural stability in adult with healed burns: a single blinded randomized controlled trial. Burns. 2024;50(1):106-114.
[41] EBID AA, EL-SHAMY SM, AMER MA. Effect of vitamin D supplementation and isokinetic training on muscle strength, explosive strength, lean body mass and gait in severely burned children: a randomized controlled trial. Burns. 2017;43(2):357-365.
[42] EBID AA, EL-SHAMY SM, DRAZ AH. Effect of isokinetic training on muscle strength, size and gait after healed pediatric burn: a randomized controlled study. Burns. 2014;40(1):97-105.
[43] EBID AA, OMAR MT, ABD EL BAKY AM. Effect of 12-week isokinetic training on muscle strength in adult with healed thermal burn. Burns. 2012;38(1):61-68.
[44] ELNAGGAR RK, OSAILAN AM, ALSUBAIE SF, et al. Graded aerobic exercise (GAEx): an effective exercise regimen to improve cardio-respiratory fitness and physical and psychosocial functioning in children with burn sequelae of the chest. Burns. 2022;48(2):337-344.
[45] GITTINGS PM, WAND BM, HINCE DA, et al. The efficacy of resistance training in addition to usual care for adults with acute burn injury: a randomised controlled trial. Burns. 2021;47(1):84-100.
[46] HARDEE JP, PORTER C, SIDOSSIS LS, et al. Early rehabilitative exercise training in the recovery from pediatric burn. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;46(9):1710-1716.
[47] NAMBI G, ABDELBASSET WK, ELSHEHAWY AA, et al. Yoga in Burn: role of pranayama breathing exercise on pulmonary function, respiratory muscle activity and exercise tolerance in full-thickness circumferential burns of the chest. Burns. 2021;47(1):
206-214.
[48] OTHMAN EM, TOSON RA. Response of bone mineral density and balance performance in post-burn patients with selected Qigong training: a single-blind randomized controlled trial. Burns. 2024;50(2):495-506.
[49] PARATZ JD, STOCKTON K, PLAZA A, et al. Intensive exercise after thermal injury improves physical, functional, and psychological outcomes. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(1):186-194.
[50] PRZKORA R, HERNDON DN, SUMAN OE. The effects of oxandrolone and exercise on muscle mass and function in children with severe burns. Pediatrics. 2007;119(1):e109-116.
[51] RADWAN NL, IBRAHIM MM, MAHMOUD WS. Effect of Wii-habilitation on spatiotemporal parameters and upper limb function post-burn in children. Burns. 2021;47(4):828-837.
[52] SCHIEFFELERS DR, DOMBRECHT D, LAFAIRE C, et al. Effects of exercise training on muscle wasting, muscle strength and quality of life in adults with acute burn injury. Burns. 2023;49(7):1602-1613.
[53] SUMAN OE, HERNDON DN. Effects of cessation of a structured and supervised exercise conditioning program on lean mass and muscle strength in severely burned children. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(12 Suppl 2):S24-29.
[54] SUMAN OE, MLCAK RP, HERNDON DN. Effect of exercise training on pulmonary function in children with thermal injury. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2002;23(4):288-293; discussion 287.
[55] VOIGT CD, FONCERRADA G, PEÑA R, et al. Effects of Community-Based Exercise in Adults With Severe Burns: a Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(1S):S36-S41.
[56] WURZER P, VOIGT CD, CLAYTON RP, et al. Long-term effects of physical exercise during rehabilitation in patients with severe burns. Surgery. 2016;160(3):781-788.
[57] 霍婷,阮晶晶,蒋梅君,等.居家弹力带抗阻训练对严重烧伤患儿肌肉功能和步行能力影响的前瞻性研究[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2023,39(12):1131-1139.
[58] 茹天峰,李菲虹,谢卫国,等.平衡训练联合常规治疗对严重烧伤后下肢运动及平衡功能障碍患者影响的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华烧伤杂志,2021,37(4): 312-318.
[59] 茹天峰,李菲虹,袁林,等.阿基米德悬吊系统在深度烧伤后膝关节屈曲功能障碍康复中的临床效果[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2019,35(6):428-433.
[60] 孙天宝,郭钦,王俊,等.有氧训练对大面积烧伤患者康复早期心肺功能的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(2):182-184.
[61] 吴坤平,陈佩,茹天峰,等.功率自行车康复训练对大面积烧伤致下肢功能障碍患者股四头肌和步行能力影响的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022,38(5):447-453.
[62] 谢肖霞,刘付明英,彭冲,等.早期卧位踏车训练对下肢重度烧伤患者的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(5):603-606.
[63] 赵海洋,刘佳琦,韩军涛,等.渐进式核心肌群训练联合下肢智能康复训练对烧伤患者下肢功能障碍影响的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志, 2022,38(12):1117-1125.
[64] KONOPKA AR, ASANTE A, LANZA IR, et al. Defects in mitochondrial efficiency and H2O2 emissions in obese women are restored to a lean phenotype with aerobic exercise training. Diabetes. 2015; 64(6):2104-2115.
[65] RIVAS E, HERNDON DN, CAMBIASO-DANIEL J, et al. Quantification of an Exercise Rehabilitation Program for Severely Burned Children: The Standard of Care at Shriners Hospitals for Children®-Galveston. J Burn Care Res. 2018;39(6): 889-896.
[66] 胡玲玉.功率自行车对脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢肌张力及平衡功能的影响[J].医疗装备,2020,33(1):193-194.
[67] LEE SY, SEO J, SEO CH, et al. Gait Performance and Brain Activity Are Improved by Gait Automatization during Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Patients with Burns: A Prospective, Randomized, Single-Blinded Study. J Clin Med. 2024; 13(16):4838.
[68] CAMBIASO-DANIEL J, RIVAS E, CARSON JS, et al. Cardiorespiratory Capacity and Strength Remain Attenuated in Children with Severe Burn Injuries at Over 3 Years Postburn. J Pediatr. 2018;192:152-158.
[69] RIVAS E, HERNDON DN, BECK KC, et al. Children with Burn Injury Have Impaired Cardiac Output during Submaximal Exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017; 49(10):1993-2000.
[70] CLAYTON RP, WURZER P, ANDERSEN CR, et al. Effects of different duration exercise programs in children with severe burns. Burns. 2017;43(4):796-803.
[71] TAPKING C, POPP D, HERNDON DN, et al. Cardiovascular Effect of Varying Interval Training Frequency in Rehabilitation of Severely Burned Children. J Burn Care Res. 2019;40(1):34-38.
[72] PALACKIC A, SUMAN OE, PORTER C, et al. Rehabilitative Exercise Training for Burn Injury. Sports Med. 2021;51(12):2469-2482.
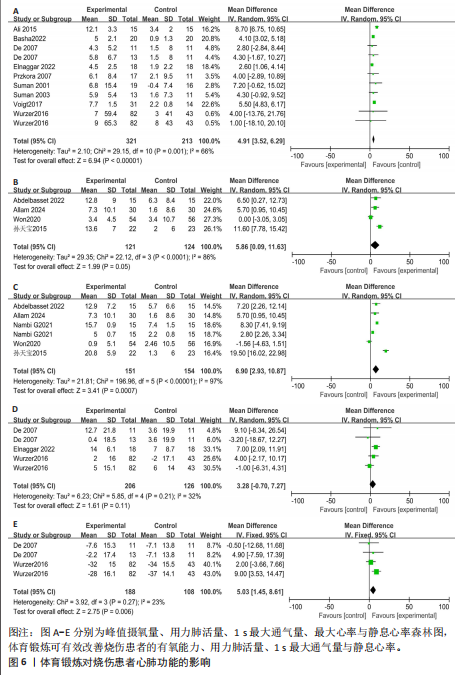
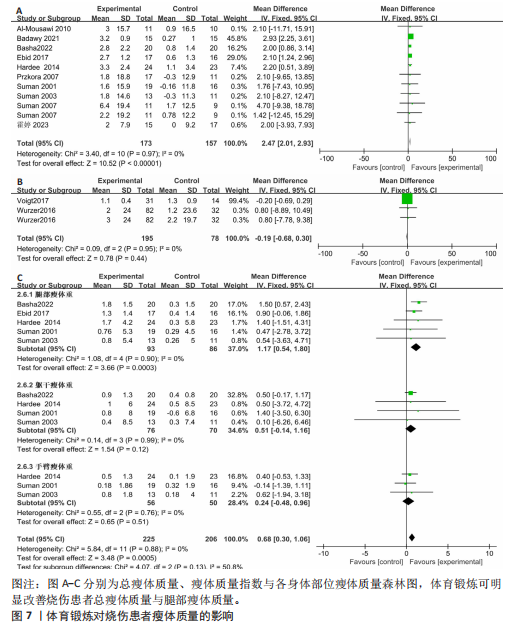
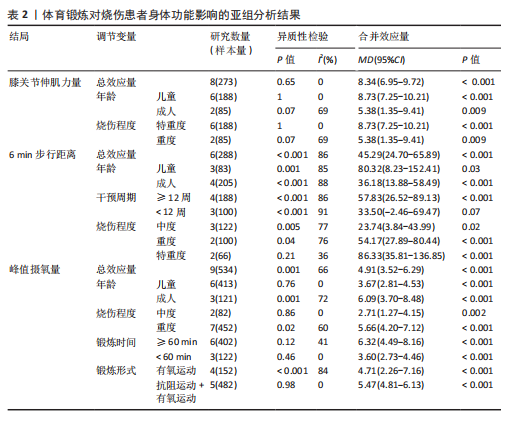
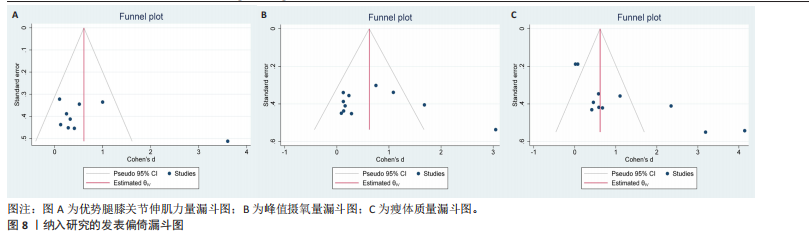
|