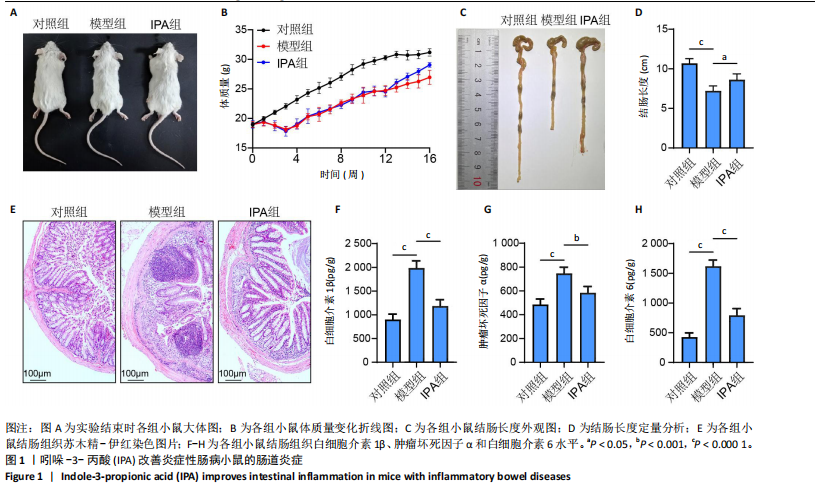
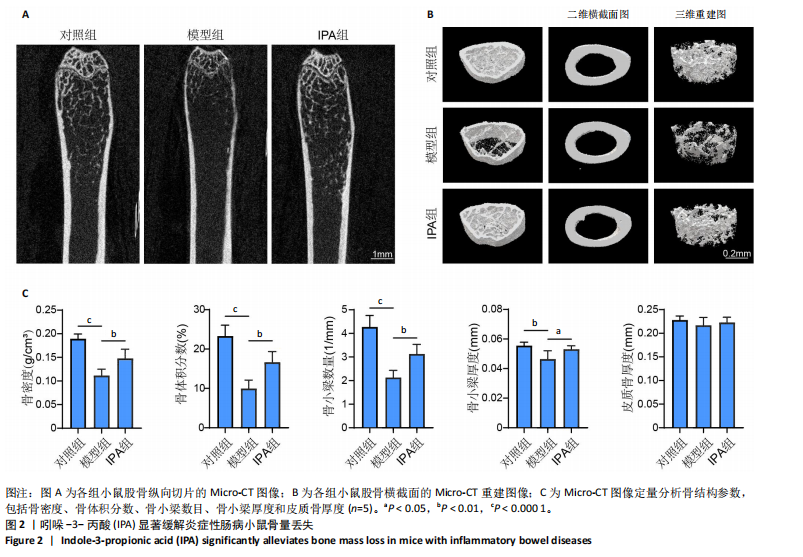
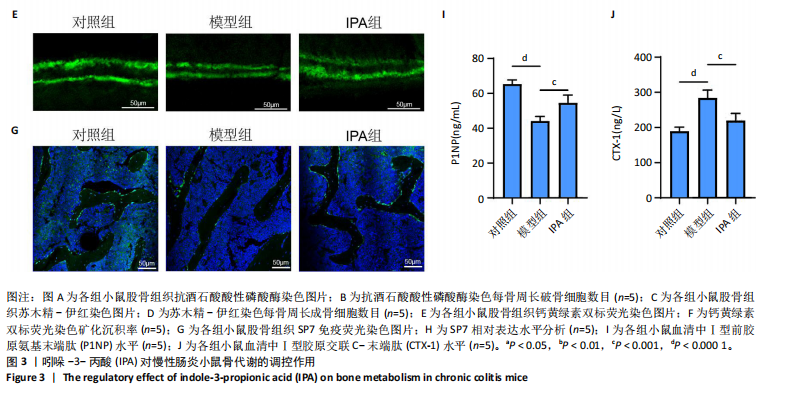
| [1] MOLODECKY NA, SOON IS, RABI DM, et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(1):46-54.e42.
[2] NG SC, SHI HY, HAMIDI N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390(10114):2769-2778.
[3] AGRAWAL M, CHRISTENSEN HS, BØGSTED M, et al. The Rising Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Denmark Over Two Decades: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(6):1547-1554.e5.
[4] GILLILAND A, CHAN JJ, DE WOLFE TJ, et al. Pathobionts in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Origins, Underlying Mechanisms, and Implications for Clinical Care. Gastroenterology. 2024;166(1):44-58.
[5] SINGH N, BERNSTEIN CN. Environmental risk factors for inflammatory bowel disease. United European Gastroenterol J. 2022;10(10):1047-1053.
[6] CABALLERO-FLORES G, PICKARD JM, NÚÑEZ G. Microbiota-mediated colonization resistance: mechanisms and regulation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023;21(6):347-360.
[7] MIRSEPASI-LAURIDSEN HC, VALLANCE BA, KROGFELT KA, et al. Escherichia coli Pathobionts Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;32(2):e00060-18.
[8] TIE Y, HUANG Y, CHEN R, et al. Current insights on the roles of gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease-associated extra-intestinal manifestations: pathophysiology and therapeutic targets. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(2):2265028.
[9] KNIGHTS D, LASSEN KG, XAVIER RJ. Advances in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: linking host genetics and the microbiome. Gut. 2013;62(10):1505-1510.
[10] BECKER C, NEURATH MF, WIRTZ S. The Intestinal Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ILAR J. 2015;56(2):192-204.
[11] KOSTIC AD, XAVIER RJ, GEVERS D. The microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease: current status and the future ahead. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(6):1489-1499.
[12] 严冰,孙菁.炎症性肠病与代谢综合征关系的研究进展[J].中华炎性肠病杂志,2022,6(1):70-73.
[13] FRIEDRICH M, POHIN M, POWRIE F. Cytokine Networks in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Immunity. 2019; 50(4):992-1006.
[14] WANG L, YU W, YIN X, et al. Prevalence of Osteoporosis and Fracture in China: The China Osteoporosis Prevalence Study. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(8):e2121106.
[15] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(6):573-611.
[16] ABEGUNDE AT, MUHAMMAD BH, ALI T. Preventive health measures in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(34): 7625-7644.
[17] CLYNES MA, HARVEY NC, CURTIS EM, et al. The epidemiology of osteoporosis. Br Med Bull. 2020;133(1):105-117.
[18] LI JY, CHASSAING B, TYAGI AM, et al. Sex steroid deficiency-associated bone loss is microbiota dependent and prevented by probiotics. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(6):2049-2063.
[19] YU M, PAL S, PATERSON CW, et al. Ovariectomy induces bone loss via microbial-dependent trafficking of intestinal TNF+ T cells and Th17 cells. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(4):e143137.
[20] GUO M, LIU H, YU Y, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(1):2190304.
[21] GUAN Z, XUANQI Z, ZHU J, et al. Estrogen deficiency induces bone loss through the gut microbiota. Pharmacol Res. 2023;196:106930.
[22] LIN X, XIAO HM, LIU HM, et al. Gut microbiota impacts bone via Bacteroides vulgatus-valeric acid-related pathways. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):6853.
[23] NI J, WU GD, ALBENBERG L, et al. Gut microbiota and IBD: causation or correlation? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14(10):573-584.
[24] SANTANA PT, ROSAS SLB, RIBEIRO BE, et al. Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenic Role and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3464.
[25] ROGLER G. Resolution of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2(7):521-530.
[26] MIGLIORINI F, COLAROSSI G, ESCHWEILER J, et al. Antiresorptive treatments for corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis: a Bayesian network meta-analysis. Br Med Bull. 2022;143(1):46-56.
[27] MORGAN S, HOOPER KM, MILNE EM, et al. Azathioprine Has a Deleterious Effect on the Bone Health of Mice with DSS-Induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6085.
[28] CHOTIYARNWONG P, MCCLOSKEY EV. Pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and options for treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(8):437-447.
[29] JIA X, YANG R, LI J, et al. Gut-Bone Axis: A Non-Negligible Contributor to Periodontitis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:752708.
[30] ZHANG YW, SONG PR, WANG SC, et al. Diets intervene osteoporosis via gut-bone axis. Gut Microbes. 2024;16(1):2295432.
[31] ZHANG YW, CAO MM, LI YJ, et al. The regulative effect and repercussion of probiotics and prebiotics on osteoporosis: involvement of brain-gut-bone axis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(25):7510-7528.
[32] ZHANG YW, WU Y, LIU XF, et al. Targeting the gut microbiota-related metabolites for osteoporosis: The inextricable connection of gut-bone axis. Ageing Res Rev. 2024;94:102196.
[33] LU Y, YANG W, QI Z, et al. Gut microbe-derived metabolite indole-3-carboxaldehyde alleviates atherosclerosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):378.
[34] ZHAO ZH, XIN FZ, XUE Y, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid inhibits gut dysbiosis and endotoxin leakage to attenuate steatohepatitis in rats. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(9):1-14.
[35] ZHUANG H, REN X, JIANG F, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid alleviates chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via the AhR/NF-κB axis. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):17.
[36] YIN Y, LU X, LI Z, et al. Risk Factors for Worsening of Bone Loss in Patients Newly Diagnosed with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022;2022:1498293. |