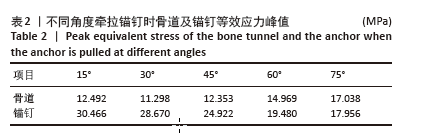
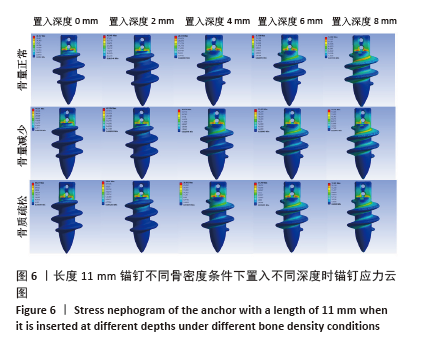
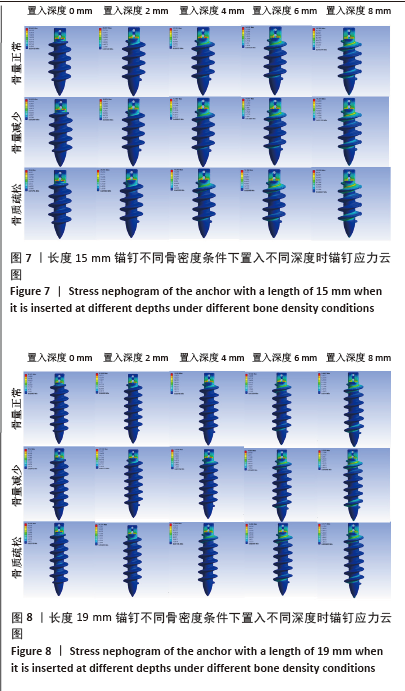
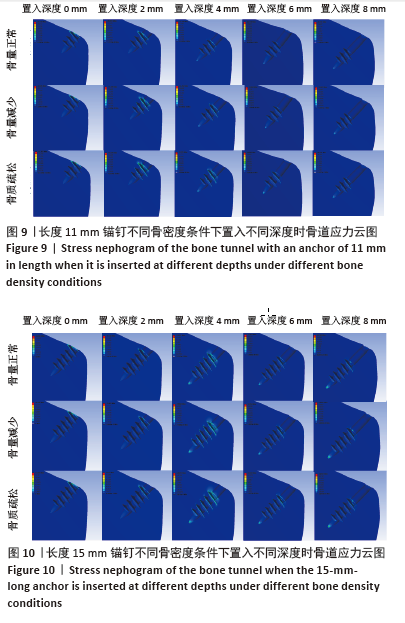
[1] YOO TH, KIM SJ, CHOI YR, et al. Age, tear size, extent of retraction, and fatty infiltration associated with a high chance of a similar rotator cuff tear in the contralateral shoulder regardless of symptoms in patients undergoing cuff repair in the index shoulder. Arthroscopy. 2023;39(7): 1611-1617.
[2] DEWAN EMH, DHAKAL RO, HOUGHTON AJ, et al. Treatment options for massive irreparable rotator cuff tears: a review of arthroscopic surgical options. EFORT Open Rev. 2023;8(1): 11-10.
[3] MORAN TE, WERNER BC. Surgery and rotator cuff disease: a review of the natural history, indications, and outcomes of nonoperative and operative treatment of rotator cuff tears. Clin Sports Med. 2023;42(1): 21-24.
[4] BEDI A, BISHOP J, KEENER J, et al. Rotator cuff tears. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024;10(1): 8.
[5] LANZAFAME GU, MARCOLONGO A, MARCHETTI F, et al. Histological, radiological and clinical analysis of the supraspinatus tendon and muscle in rotator cuff tears. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1): 127-127.
[6] GUPTA A, MIGLIORINI F, MAFFULLI N. Management of rotator cuff injuries using allogenic platelet - rich plasma. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024; 19(1):165.
[7] DEMETRACOPOULOS A, DILLINGHAM M. Rotator Cuff Disease: Treatment Options and Considerations. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2018; 26(3): 129-133.
[8] MENEKSE S. Comparison of Outcomes between Open and Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair. Adv Orthop. 2024;2024(1):5575404.
[9] HSU KL, KUAN FC, GARCIA AV, et al. Factors association with reparability of rotator cuff tears: A systematic review and meta - analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024;33(9):465-477.
[10] MACLEAN IS, BROCKMEIER SF. Failed and revision rotator cuff repair. Clin Sports Med. 2023;42(1):141-155.
[11] PIATTI M, GORLA M, ALBERIO F. Comparison of all - suture anchors with metallic anchors in arthroscopic cuff repair: Structural and functional properties and clinical suitability. J Orthop. 2023;39:66-69.
[12] HOFFMAN TR, LAMPLOT JD, MCCLISH SJ, et al. Three medial all suture anchors improves contact force compared to two hard body anchors in a biomechanical two-tendon rotator cuff tear model. Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2022;4(5):e1601-e1607.
[13] CLEVENGER TA, BEEBE MJ, STRAUSS EJ. The effect of insertion angle on the pullout strength of threaded suture anchors: a validation of the deadman theory. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(8):900-905.
[14] KAWAKAMI J, YAMAMOTO N, NAGAMOTO H, et al. Minimum Distance of Suture Anchors Used for Rotator Cuff Repair Without Decreasing the Pullout Strength: A Biomechanical Study. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(2): 377-385.
[15] 周恩昌,殷浩,唐萍,等.锚钉数量及位置对肩关节Bankart损伤修复强度影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨伤,2018,31(12):1136-1139.
[16] LI XW, XU YJ, HAN S, et al. Risk Factors and Corresponding Management for Suture Anchor Pullout during Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair. J Clin Med. 2022;11(22):6870-6870.
[17] HONG JP, HUANG SW, LEE CH, et al. Osteoporosis increases the risk of rotator cuff tears: a population-based cohort study. J Bone Miner Metab. 2022;40(2):348-356.
[18] KAWASHIMA I, ISHIZUKA S, OBA H, et al. Prevalence and Treatment Rates of Osteoporosis Among Individuals with Rotator Cuff Tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024;33(11):e606-e609.
[19] CHUNG SW, OH JH, GONG HS, et al. Factors affecting rotator cuff healing after arthroscopic repair: osteoporosis as one of the independent risk factors. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(10):2099-2107.
[20] KLAUE C, KLAUE S, SATTLER MC, et al. X-treme CT analysis of cancellous bone at the rotator cuff insertion in human individuals with osteoporosis: superficial versus deep quality. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(3):381-387.
[21] BUENO C, SACRISTÁN H, PÉREZ G, et al. Single-row versus double-row arthroscopic repair in the treatment of rotator cuff tears. A systematic review. Rev Fac Cien Med Univ Nac Cordoba. 2023;80(3):252-274.
[22] BURKHART SS. The deadman theory of suture anchors: observations along a south texas fence line. Arthroscopy. 1995;11(1):119-123.
[23] ABEDI A, FARAHMAND F, ZANJANI OL, et al. Effect of geometrical design variables on implantation configuration and fixation stiffness of titling bone anchors: A parametric finite element study. Med Eng Phys. 2024;129:104191.
[24] HITCHON S, SOLTANMOHAMMADI P, MILNER SJ, et al. Porous versus solid shoulder implants in humeri of different bone densities: A finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2024;42(9):1897-1906.
[25] 王伟斌,袁欣华,扶青松,等.骨质疏松性肱骨近端骨折PMMA骨水泥强化螺钉钢板固定的有限元分析[J].中国骨伤,2023,36(3): 262-267.
[26] DAHAN G, TRABELSI N, SAFRAN O, et al. Finite element analyses for predicting anatomical neck fractures in the proximal humerus. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2019;68:114-121.
[27] RHO JY, HOBATHO MC, ASHMAN RB. Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys. 1995;17(5): 347-355.
[28] WANG H, CHEN L, XU G, et al. Biomechanical effects of deltoid muscle atrophy on rotator cuff tissue: a finite element study. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):17592-17592.
[29] 刘蒙飞,马鹏程,尹灿,等.不同骨密度对膝关节单髁置换后关节内各结构影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(24):3801-3806.
[30] POLIKEIT A, NOLTE LP, FERGUSON SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit: finite - element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(10): 991-996.
[31] 郭文文,刘静,曹慧,等.正常与骨质疏松肱骨的三维重建及有限元分析[J].中国医疗设备,2018,33(4):34-37.
[32] SANO H, IMAGAWA K, YAMAMOTO N, et al. Predicting failures of suture anchors used for rotator cuff repair: A CT-based 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015; 25(4):371-380.
[33] REDEPENNING DH, LUDEWIG PM, LOOFT JM. Finite element analysis of the rotator cuff: A systematic review. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2020;71: 73-85.
[34] 包呼日查, 齐岩松, 陶立元, 等. 肩袖损伤修补金属锚钉置入角度-有限元分析[J]. 中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2019,7(1):56-62.
[35] YAMAURA K, FUJIBAYASHI I, KUROSAWA T, et al. Timing of retears after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair and associated factors: a retrospective analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32(9):1929-1936.
[36] LEE JS, SUH KT, SHIN WC, et al. Socioeconomic and Other Risk Factors for Retear after Arthroscopic Surgery for Nontraumatic Rotator Cuff Tear. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024;60(4):640.
[37] ZHAO J, ZENG L, LIANG G, et al. Risk factors for symptomatic rotator cuff tears: a retrospective case - control study. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;10:1321939-1321939.
[38] TINGART MJ, APRELEVA M, LEHTINEN J, et al. Anchor design and bone mineral density affect the pull-out strength of suture anchors in rotator cuff repair: which anchors are best to use in patients with low bone quality? Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(6):1466-1473.
[39] PATTERSON BM, BOZOGHLIAN MF. Modifiable and Nonmodifiable Risk Factors Associated with the Development of Recurrent Rotator Cuff Tears. Orthop Clin North Am. 2023;54(3):319-326.
[40] YAMAUCHI S, TSUKADA H, SASAKI E, et al. Biomechanical analysis of bioabsorbable suture anchors for rotator cuff repair using osteoporotic and normal bone models. J Orthop Sci. 2022;27(1):115-121.
[41] NAGAMOTO H, YAMAMOTO N, SANO H, et al. A biomechanical study on suture anchor insertion angle: Which is better, 90 degrees or 45 degrees? J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(1): 56-62.
[42] OH JH, JEONG HJ, YANG SH, et al. Pullout strength of all - suture anchors: effect of the insertion and traction angle - a biomechanical study. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(10):2784-2795.
[43] MENG M, WANG J, HUANG H, et al. 3D printing metal implants in orthopedic surgery: Methods, applications and future prospects. J Orthop Translat. 2023;42:94-112.
[44] OMER S, BEDRI K, SOHEIL A, et al. Investigation of lattice infill parameters for additively manufactured bone fracture plates to reduce stress shielding. Comput Biol Med. 2023;161:107062-107062.
[45] YAKACKI CM, POUKALOVA M, GULDBERG RE. The effect of the trabecular microstructure on the pullout strength of suture anchors. J Biomech. 2010;43(10):1953-1959.
[46] MAHAR TA, TUCKER SB, UPASANI VV. Increasing the insertion depth of suture anchors for rotator cuff repair does not improve biomechanical stability. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(6):626-630. |