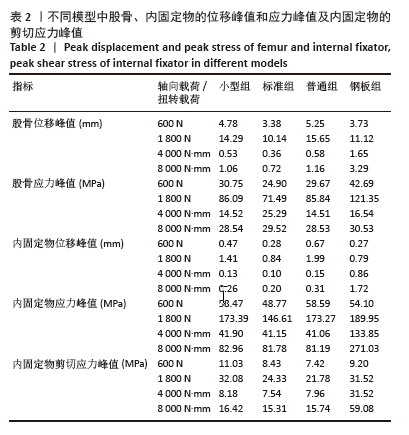
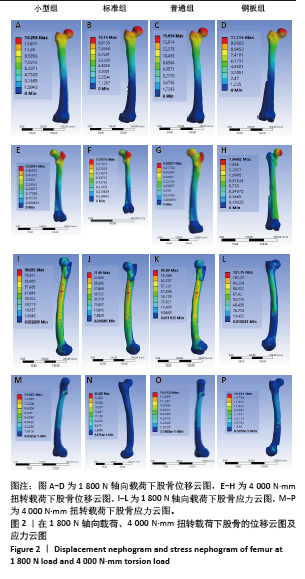
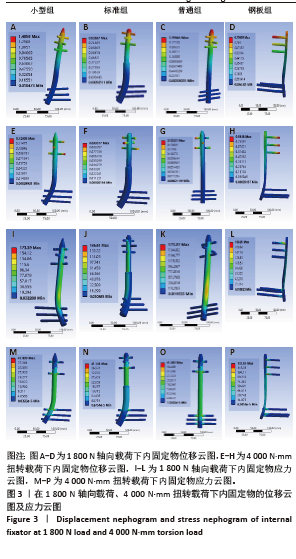
1] NESTER M, BORRELLI J JR. Distal femur fractures management and evolution in the last century. Int Orthop. 2023;47(8):2125-2135.
[2] 安晋宇,文会龙,高立波,等.桥接系统两种构型固定股骨远端骨折比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(22):2029-2034.
[3] 许铎,孙锐坚,王天宇,等.基于有限元生物力学分析的股骨远端A型骨折探索与再思考[J]. 中华外科杂志,2019,57(11):812-817.
[4] 史金友,肖玉周.锁定钢板治疗股骨远端粉碎性骨折的现状与进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(10):1352-1356.
[5] 贾小阳,强敏菲,贾更新,等.计算机辅助术前计划在AO/OTA C型股骨远端骨折治疗中的应用价值[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2024,44(7): 456-462.
[6] 潘汝南,唐承杰,李峰,等.两种复位方式锁定加压钢板内固定治疗老年股骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2024,27(5): 712-716.
[7] 段旭洲,王光超. 逆行交锁髓内钉与锁定钢板内固定治疗AO-A型股骨远端骨折疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2023,38(6): 623-625.
[8] 戴冠东,耿冰雨,罗丽丹,等.磁力导航逆行带锁髓内针远端锁钉技术治疗股骨骨折的应用[J].临床外科杂志,2020,28(4):316-318.
[9] 胡鹏,李铭雄,魏志勇,等. 顺行与逆行髓内针治疗股骨中下段骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(12):17-20.
[10] CHEN SH, TAI CL, YU TC, et al. Modified fixations for distal femur fractures following total knee arthroplasty: a biomechanical and clinical relevance study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24(10):3262-3271.
[11] 李光晟,林伟民,张申申,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉联合前外侧重建钢板修复不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(36):5753-5759.
[12] 黄华健.股骨颈前倾角改变对转子间骨折PFNA固定术后的力学稳定性影响的有限元分析[D].广州:南方医科大学,2020.
[13] 李正刚,尚学红,吴张,等.不同载荷条件下三种内固定方式治疗PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(3):455-463.
[14] 艾克白尔·吐逊,阿吉木·克热木,谢增如,等. 两种内固定方式固定青壮年不稳定型股骨颈骨折生物力学特性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(9):793-798.
[15] 汪金平,杨天府,钟凤林,等.股骨生物力学特性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志 ,2005,7(10):931-934.
[16] 周龙,王亮,徐锐,等.股骨转子间骨折不同外侧壁分型髓内钉治疗的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(29): 4652-4657.
[17] 葛志强,罗伟.股骨干骨折钢板内固定术后骨折部位生物力学改变的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2023,38(10): 1106-1108.
[18] 段卓岳.股骨头坏死旋转截骨术的术前评估及其有限元分析[D].包头:内蒙古科技大学,2023.
[19] ROLLICK NC, GADINSKY NE, KLINGER CE, et al. The effects of dual plating on the vascularity of the distal femur. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(4):530-538.
[20] 李华平,赵世杰,姚裴,等.锁定钢板与逆行髓内钉固定股骨远端骨折比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(18):1654-1659.
[21] 谢威,黄子阳,黄泽茂,等.微创内固定系统与逆行髓内钉内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的Meta分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2022,37(4):355-358.
[22] THOMSON AB, DRIVER R, KREGOR PJ, et al. Long-term functional outcomes after intra-articular distal femur fractures: ORIF versus retrograde intramedullary nailing. Orthopedics. 2008;31(8):748-750.
[23] HEINEY JP, BARNETT MD, VRABEC GA, et al. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of trigen retrograde intramedullary (i.m.) nail, dynamic condylar screw (DCS), and locking compression plate (LCP) condylar plate. J Trauma. 2009;66(2):443-449.
[24] 史方石,袁维.有限元法在骨科器械和植入物中的应用综述[J].科学技术与工程,2023,23(30):12775-12785.
[25] 胡浩,陆骅.有限元分析在股骨远端骨折内固定中的应用研究进展[J].实用临床医药杂志,2023,27(6):145-148.
[26] 邹诚实,李开成,张兆国,等.股骨远端骨折髓内钉与锁定钢板内固定方式的有限元分析[J]. 浙江医学,2016,38(18):1507-1509,1518.
[27] DEMIRTAŞ A, AZBOY I, ÖZKUL E, et al. Comparison of retrograde intramedullary nailing and bridge plating in the treatment of extra-articular fractures of the distal femur. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(5):521-526.
[28] 张权.股骨远端骨折治疗进展[J].上海医药,2024,45(5):1-4+8.
[29] 周飞虎,王岩,周勇刚.国人正常股骨远端三维模型及骨形态测量研究[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(6):62-63+65.
[30] 曾蜀雄,伍国胜,董喜乐,等.膝关节腓侧副韧带的解剖学观察及其临床意义[J].解剖学报,2011,42(4):513-516.
[31] 叶俊武,李箭.膝关节后外侧复合体重建术的应用解剖学及生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(10):1199-1203.
[32] 徐洪伟.正常成人股骨内外侧髁侧面地形学研究[D].张家口:河北北方学院,2015.
[33] PENG B, WAN T, TAN W, et al. Novel Retrograde Tibial Intramedullary Nailing for Distal Tibial Fractures. Front Surg. 2022;9:899483.
[34] 熊远飞,刘晖,许遵营,等.胫骨逆行髓内钉在高危人群胫骨远端关节外骨折中的应用研究[J].骨科,2024,15(1):71-75.
[35] 王义昌,林文杰,林涛,等.胫骨远端骨折三种内固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(36):5760-5765.
[36] 张金辉,刘晖,徐维臻,等.三种内固定方式治疗AO/OTA A3型股骨远端骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(27):5728-5734.
[37] 陈丁,于娇娜,于洋,等.有限元分析3种内固定方式治疗伴有内侧骨缺损的C3型股骨远端骨折[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2023,48(11): 1711-1720.
[38] 胡浩,陆骅.有限元分析在股骨远端骨折内固定中的应用研究进展[J].实用临床医药杂志,2023,27(6):145-148.
[39] SAKTHIVELNATHAN V, PURUDAPPA PP, MOUNASAMY V, et al. Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing and Locked Plating for the Treatment of Periprosthetic Supracondylar Femur Fractures: A Meta-Analysis and Quantitative Review Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2022;10(5): 395-402.
[40] PIETRINI SD, LAPRADE RF, GRIFFITH CJ, et al. Radiographic identification of the primary posterolateral knee structures. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(3): 542-551. |