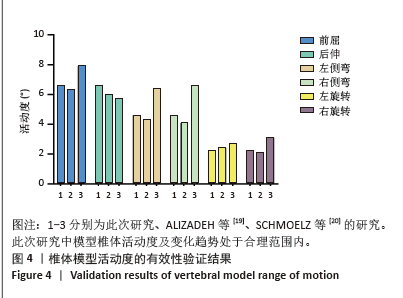
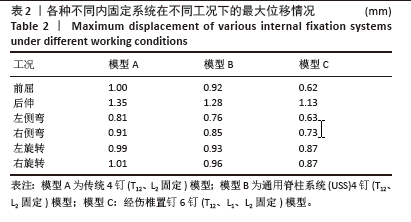
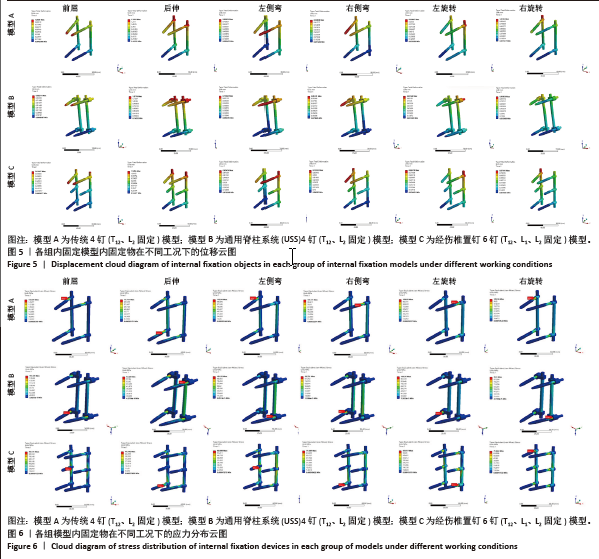
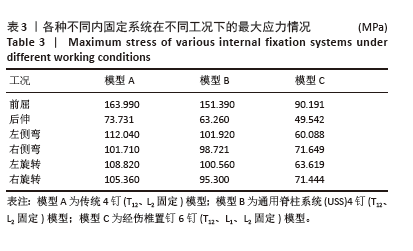
[1] 苏林涛,余秋宇,马俊,等. 胸腰椎骨折椎体水肿对经皮椎弓钉固定疗效的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(20):1852-1857.
[2] HUANG L, XIONG C, GUO Z, et al. Comparison of monoplanar and polyaxial screw fixation systems in percutaneous intermediate fixation for thoracolumbar fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1): 172.
[3] 程明煌,胡侦明,江维,等. 胸腰椎爆裂骨折治疗的研究进展[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2023,26(4):598-602.
[4] LI WJ, GUO LX. Influence of different postures under vertical impact load on thoracolumbar burst fracture. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2020; 58(11):2725-2736.
[5] SHEN J, YANG Z, FU M, et al. The influence of topical use of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss on early operation for thoracolumbar burst fracture: A randomized double-blinded controlled study. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(10):3074-3080.
[6] YU D, DA F, JUN C, et al. Anonymous, Anterior, posterior and anterior-posterior approaches for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Invest Surg. 2024;37(1):2301794.
[7] XU L, LIN X, WU C, et al. Is unilateral pedicle screw fixation as effective as bilateral pedicle screw fixation in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(2):700-711.
[8] ALIMOHAMMADI E, BAGHERI SR, JOSEPH B, et al. Analysis of factors associated with the failure of treatment in thoracolumbar burst fractures treated with short-segment posterior spinal fixation. J Orthop Surg. 2023;18(1):690.
[9] YANG S, SHANG DP, LU JM, et al. Modified Posterior Short-Segment Pedicle Screw Instrumentation for Lumbar Burst Fractures with Incomplete Neurological Deficit. World Neurosurg. 2018;119:977-985.
[10] ALANAY A, ACAROGLU E, YAZICI M, et al. Short-segment pedicle instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: does transpedicular intracorporeal grafting prevent early failure? Spine. 2001;26(2): 213-217.
[11] CHOU KN, WANG PW, CHUNG MH, et al. Hybrid kyphoplasty with short-versus intermediate- and long-segment pedicle screw fixations for the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):203.
[12] LI C, ZHOU Y, WANG H, et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar fractures through short segment pedicle screw fixation techniques using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture: a finite element analysis. PloS One. 2014;9(6):99156.
[13] 赵豪,高山,陈文恒,等. 经伤椎与跨伤椎固定胸腰椎爆裂骨折的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(22):2039-2044.
[14] 王越,李良生,陈建泉,等.后路短节段经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折术中应用横连接的必要性[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2024,22(3):170-175.
[15] WU W, HAN Z, HU B, et al. A graphical guide for constructing a finite element model of the cervical spine with digital orthopedic software. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(2):169.
[16] LIU J, YANG S, ZHOU F, et al. The feasibility of short-segment Schanz screw implanted in an oblique downward direction for the treatment of lumbar 1 burst fracture: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg. 2020;15(1):537.
[17] MCCORMACK T, KARAIKOVIC E, GAINES RW. The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine. 1994;19(15):1741-1744.
[18] XU G, FU X, DU C, et al. Biomechanical comparison of mono-segment transpedicular fixation with short-segment fixation for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: a finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng. 2014;228(10):1005-1013.
[19] ALIZADEH M, KADIR MRA, FADHLI MM, et al. The use of X-shaped cross-link in posterior spinal constructs improves stability in thoracolumbar burst fracture: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Res Off Publ Orthop Res Soc. 2013;31(9):1447-1454.
[20] SCHMOELZ W, SCHASER KD, KNOP C, et al. Extent of corpectomy determines primary stability following isolated anterior reconstruction in a thoracolumbar fracture model. Clin. Biomech. Bristol Avon. 2010;25(1):16-20.
[21] CHOU TY, TSUANG FY, HSU YL, et al. Surgical versus non-surgical treatment for thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurological deficit: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Glob Spine J. 2024; 14(2):740-749.
[22] DVORAK MF, ÖNER CF, SCHNAKE K, et al. From Radiographic Evaluation to Treatment Decisions in Neurologically Intact Patients With Thoraco-lumbar Burst Fractures. Glob Spine J. 2024;14:4-7.
[23] GREINER PERTH AK, WILKE HJ, LIEBSCH C. Which spinal fixation technique achieves which degree of stability after thoracolumbar trauma? A systematic quantitative review. Spine J Off J North Am Spine Soc. 2024;S1529-9430(24)1095-7.
[24] HASHIMURA T, ONISHI E, OTA S, et al. Correction loss following short-segment posterior fixation for traumatic thoracolumbar burst fractures related to endplate and intervertebral disc destruction. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):174.
[25] YADAV SK, RAJNISH RK, KANTIWAL P, et al. Short segment posterior fixation of unstable thoracolumbar vertebral fractures with fractured vertebra augmentation with intermediate pedicle screw - a clinicoradiological analysis. Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2024;13(1):1-6.
[26] RISPOLI R, ABOUSAYED M, HAMED AA, et al. Long versus short segment with intermediate screw fixation for burst fractures of thoracolumbar junction: Radiological and clinical results. J Neurosurg Sci. 2024;68(5): 567-573.
[27] ZHANG G, LI J, ZHANG L, et al. Biomechanical effect of different posterior fixation techniques on stability and adjacent segment degeneration in treating thoracolumbar burst fracture with osteoporosis: A finite element analysis. Spine. 2024;49(15):229-238.
[28] ZHANG G, DU Y, JIANG G, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of different posterior fixation techniques for treating thoracolumbar burst fractures of osteoporosis old patients: A finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1268557.
[29] LIAO JC, CHEN WP, WANG H. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by short-segment pedicle screw fixation using a combination of two additional pedicle screws and vertebroplasty at the level of the fracture: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017; 18(1):262.
[30] AONO H, TOBIMATSU H, ARIGA K, et al. Surgical outcomes of temporary short-segment instrumentation without augmentation for thoracolumbar burst fractures. Injury. 2016;47(6):1337-1344.
[31] CAI P, XI Z, DENG C, et al. Fixation-induced surgical segment’s high stiffness and the damage of posterior structures together trigger a higher risk of adjacent segment disease in patients with lumbar interbody fusion operations. J Orthop Surg. 2023;18(1):371.
[32] CUI X, ZHU J, YANG W, et al. Finite element study of sagittal fracture location on thoracolumbar fracture treatment. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1229218.
[33] XILONG C, JUNHUN Z, YULIANG S, et al. Biomechanical comparison of different treatment strategies for thoracolumbar burst fracture: A finite element study. World Neurosurg. 2023;180:429-439.
[34] LI Q, LI X, LIU Y, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar fracture with pedicle screws at injury level: a biomechanical study based on three-dimensional finite element analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol Orthop Traumatol. 2013;23(7):775-780.
[35] MAHAR A, KIM C, WEDEMEYER M, et al. Short-segment fixation of lumbar burst fractures using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture. Spine. 2007;32(14):1503-1507.
[36] DICK JC, JONES MP, ZDEBLICK TA, et al. A biomechanical comparison evaluating the use of intermediate screws and cross-linkage in lumbar pedicle fixation. J Spinal Disord. 1994;7(5):402-407.
[37] MULLER U, BERLEMANN U, SLEDGE J, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit by indirect reduction and posterior instrumentation: Bisegmental stabilization with monosegmental fusion. Eur Spine J. 1999;8(4):284-289.
[38] SCHOMIG F, PALMOWSKI Y, NIKIFOROV I, et al. Burst fractures lead to a fracture-associated intervertebral vacuum phenomenon: a case series of 305 traumatic fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(10):3068-3073. |