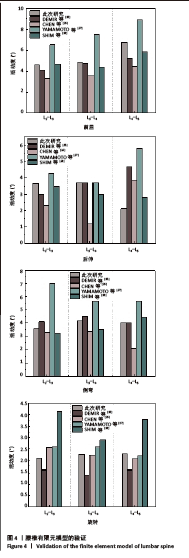
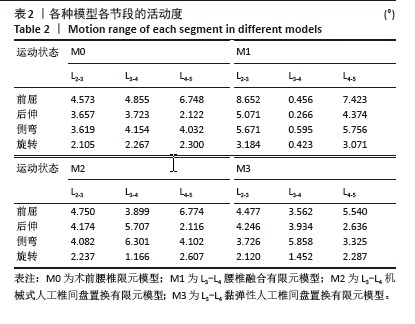
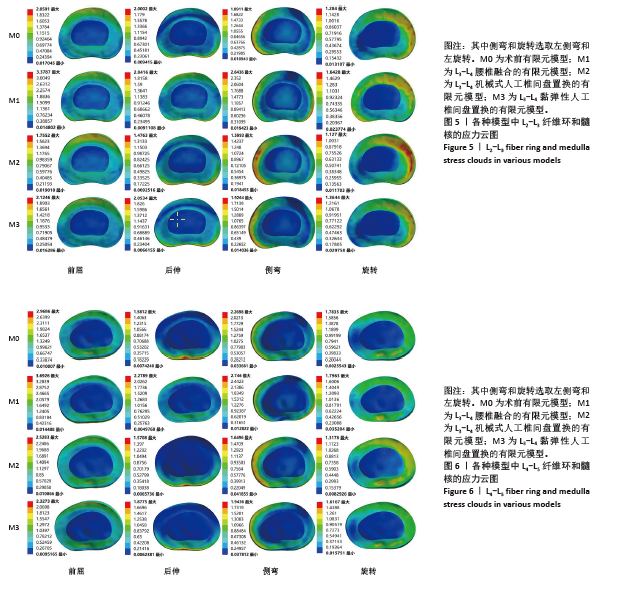
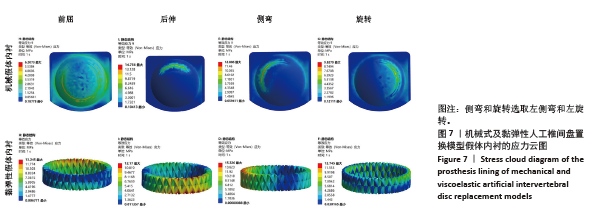
[1] RAVINDRA VM, SENGLAUB SS, RATTANI A, et al. Degenerative lumbar spine disease: estimating global incidence and worldwide volume. Glob Spine J. 2018;8(8):784-794.
[2] 舒建川, 杨程显, 李淳德, 等. MIS-TLIF治疗腰椎退行性疾病研究现状及展望[J]. 重庆医学, 2023,52(13):2056-2062+2071.
[3] 邹海波, 王宇鸣. 腰椎后路椎体间融合方式对术中出血量及术后引流量的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(2):145-148.
[4] MA XL, ZHAO XW, MA JX, et al. Effectiveness of surgery versus conservative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis: a system review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 2017;44: 329-338.
[5] YU Q, LU HG, PAN XK, et al. Unilateral biportal endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus conventional interbody fusion for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spine disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bmc Musculoskel Dis. 2023; 24(1):838.
[6] 张振军, 孙艺萄, 廖振华, 等. 有限元法在腰椎融合术与置换术生物力学研究中应用进展[J]. 医用生物力学,2022,33(1):82-88.
[7] 付坤飞, 林福, 全仁夫, 等. 有限元法在腰椎融合术生物力学研究中的应用进展[J]. 中医正骨 ,2022,34(4):46-50+54.
[8] LI XF, LV ZD, YIN HL, et al. Impact of adjacent pre-existing disc degeneration status on its biomechanics after single-level anterior cervical interbody fusion. Comput Meth Prog Bio. 2021;209:106355.
[9] CAI XY, SUN MS, HUANG YP, et al. Biomechanical effect of L4–L5 intervertebral disc degeneration on the lower lumbar spine: a finite element study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):917-930.
[10] MARAGKOS GA, MOTIEI-LANGROUDI R, FILIPPIDIS AS, et al. Factors predictive of adjacent segment disease after lumbar spinal fusion. World Neurosurg. 2020;133:e690-e694.
[11] 吴佳源, 田伟. 腰椎人工椎间盘置换术的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(3):268-274.
[12] JANSSEN M, GARCIA R, MILLER L, et al. Challenges and solutions for lumbar total disc replacement implantation. Spine. 2017;42:S108-S111.
[13] CHENG XL, QU Y, DONG RP, et al. A comparison of long-term efficacy of K-rod-assisted non-fusion operation and posterior lumbar interbody fusion for single-segmental lumbar disc herniation. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;95:1-8.
[14] ZIGLER JE, BLUMENTHAL SL, GUYER RD, et al. Progression of Adjacent-level Degeneration After Lumbar Total Disc Replacement: Results of a Post-hoc Analysis of Patients With Available Radiographs From a Prospective Study With 5-year Follow-up. Spine. 2018;43(20): 1395-1400.
[15] LEBL DR, CAMMISA FP, GIRARDI FP, et al. In vivo functional performance of failed Prodisc-L devices: retrieval analysis of lumbar total disc replacements. Spine. 2012;37(19):E1209-E1217.
[16] 樊光亚, 苏文硕, 钟木森, 等. 有限元分析在腰椎生物力学方面的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(30):4896-4901.
[17] BISWAS JK, MALAS A, MAJUMDAR S, et al. A comparative finite element analysis of artificial intervertebral disc replacement and pedicle screw fixation of the lumbar spine. Comput Method Biomec. 2022;25(16): 1812-1820.
[18] YU Z, VOUMARD B, SHEA K, et al. Exploration of the influence of different biomimetic designs of 3D printed multi-material artificial spinal disc on the natural mechanics restoration. Mater Design. 2021; 210:110046.
[19] ROSINSKI AA, MITTAL A, ODEH K, et al. Alternatives to traditional pedicle screws for posterior fixation of the degenerative lumbar spine. Jbjs Rev. 2021;9(7):e20.
[20] INYANG AO, VAUGHAN CL. Functional characteristics and mechanical performance of PCU composites for knee meniscus replacement. Materials. 2020;13(8):1886.
[21] ZHANG S, LIU Z, LU C, et al. Oblique lateral interbody fusion combined with different internal fixations for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spine disease: a finite element analysis. Bmc Musculoskel Dis. 2022;23(1):206.
[22] LU T, LU Y. Comparison of biomechanical performance among posterolateral fusion and transforaminal, extreme, and oblique lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019; 129:e890-e899.
[23] LEE SH, IM YJ, KIM KT, et al. Comparison of cervical spine biomechanics after fixed-and mobile-core artificial disc replacement: a finite element analysis. Spine. 2011;36(9):700-708.
[24] HEKIMOĞLU M, BAŞAK A, YILMAZ A, et al. Adjacent Segment Disease (ASD) in incidental segmental fused vertebra and comparison with the effect of stabilization systems on ASD. Cureus. 2021;13(10):e18647.
[25] DEMIR E, ELTES P, CASTRO AP, et al. Finite element modelling of hybrid stabilization systems for the human lumbar spine. P I Mech Eng H. 2020;234(12):1409-1420.
[26] CHEN CS, CHENG CK, LIU CL, et al. Stress analysis of the disc adjacent to interbody fusion in lumbar spine. Med Eng Phys. 2001;23(7): 485-493.
[27] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[28] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine. 2008;33(22):E820-E827.
[29] 欧裕福, 肖增明. 腰椎融合术后邻近节段退变的发生因素及机制研究进展[J]. 医学信息,2024,37(10):165-169.
[30] WANGSAWATWONG P, SAWA AG, DE ANDRADA PEREIRA B, et al. Adjacent-segment effects of lumbar cortical screw–rod fixation versus pedicle screw-rod fixation with and without interbody support. J Neurosurg Spine. 2021;35(3):263-269.
[31] KUMARAN Y, SHAH A, KATRAGADDA A, et al. Iatrogenic muscle damage in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and adjacent segment degeneration: a comparative finite element analysis of open and minimally invasive surgeries. Eur Spine J. 2021;30:2622-2630.
[32] 刘庆涛, 王辉, 许星柱, 等. 腰椎融合术后五年邻近节段退变的危险因素分析[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2023,12(4):248-253.
[33] ALAHMADI H, DEUTSCH H. Outcome of salvage lumbar fusion after lumbar arthroplasty. Eur Spine J. 2014;8(1):13.
[34] FORMICA M, VALLERGA D, ZANIRATO A, et al. Fusion rate and influence of surgery-related factors in lumbar interbody arthrodesis for degenerative spine diseases: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Musculoskelet Surg. 2020;104:1-15.
[35] GUPPY KH, ROYSE KE, NORHEIM EP, et al. Operative nonunion rates in posterolateral lumbar fusions: analysis of a cohort of 2591 patients from a national spine registry. World Neurosurg. 2021;145:e131-e140.
[36] 高志扬, 王京, 黄毓凯, 等. 斜外侧入路腰椎椎间融合术的临床进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2024,34(7):774-779.
[37] 曾忠友, 吴宏飞, 宋永兴, 等. 腰椎退行性疾病两种融合术的并发症比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(3):193-198.
[38] PAN A, HAI Y, YANG J, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar spinal fusion compared with motion-preservation procedures: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25:1522-1532.
[39] MATTEI TA, BEER J, TELES AR, et al. Clinical outcomes of total disc replacement versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion for surgical treatment of lumbar degenerative disc disease. Glob Spine J. 2017; 7(5):452-459.
[40] 李路明, 徐宝山, 朱少文, 等. 腰椎椎体间融合失败因素的研究进展[J]. 天津医科大学学报,2024,30(4):381-384.
[41] SCHÄTZ C, RITTER-LANG K, GÖSSEL L, et al. Comparison of single-level and multiple-level outcomes of total disc arthroplasty: 24-month results. Int J Spine Surg. 2015;9:14.
[42] SANDHU F, BLUMENTHAL S, GRUNCH B, et al. Barriers to and budget impact of lumbar total disc replacement utilization. Spine. 2017;42: S112-S114.
[43] 刘潇, 刘耀升, 刘蜀彬. 有限元法分析腰椎融合与非融合后的应力分布[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(3):409-414. |