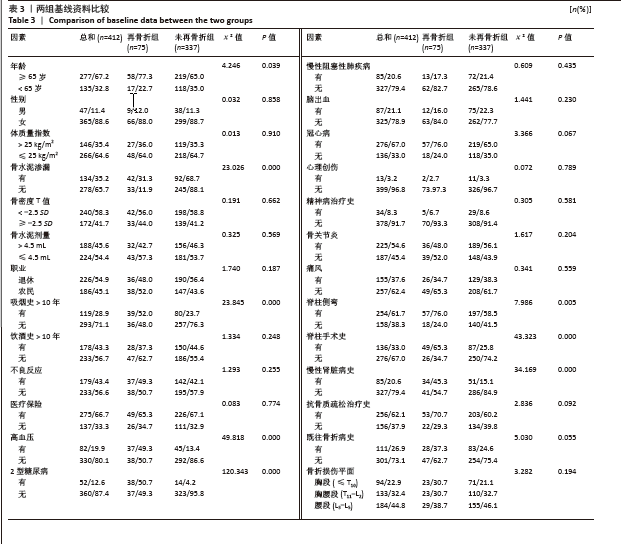
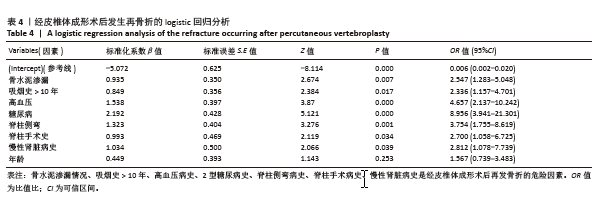
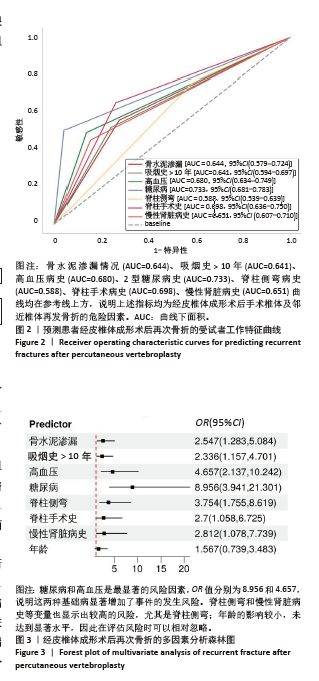
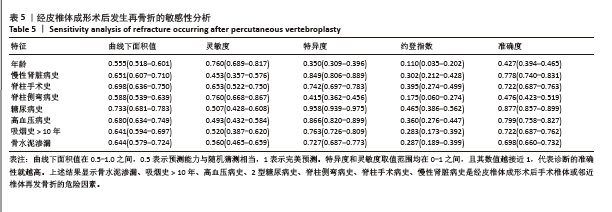
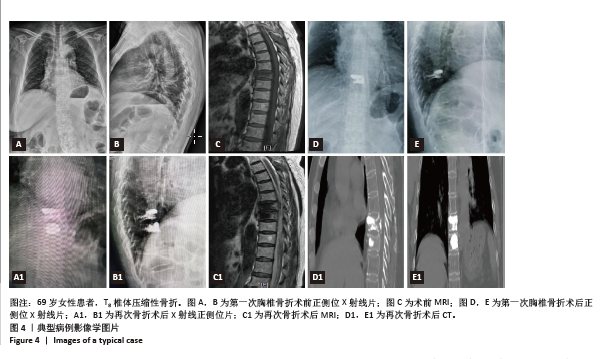
[1] 阿卜杜吾普尔·海比尔,阿里木江·玉素甫,林航,等. 经皮椎体成形术中骨水泥分布对手术及邻近椎体再发骨折的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(29):4657-4662.
[2] CAREY JJ, CHIH-HSING WU P, BERGIN D. Risk assessment tools for osteoporosis and fractures in 2022. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2022;36(3):101775.
[3] LIU AF, GUO TC, FENG HC, et al. Efficacy and safety of early versus delayed reconstruction for anterior cruciate ligament injuries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee. 2023;44:43-58.
[4] 朱洁云,高敏,宋秋韵,等.中国老年人骨质疏松症患病率的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(3):346-353.
[5] YIN P, ZHU SQ, ZHANG YS, et al. The clinical effect of percutaneous curved kyphoplasty for osteoporosis vertebral compression fractures. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;59(6):458-463.
[6] CHEN H, PAN W, ZHANG Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics analysis of 681 cases of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022;36(7):873-880.
[7] SYU DK, HSU SH, YEH PC, et al. The association between coronary artery disease and osteoporosis: a population-based longitudinal study in Taiwan. Arch Osteoporos. 2022;17(1):91.
[8] WANG J, XIE X, GOU Y, et al. Forearm bone mineral density as a predictor of adjacent vertebral refracture after percutaneous kyphoplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a retrospective analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):788.
[9] QI B, KONG X, MENG C, et al. Analysis of the impact of underlying diseases in the elderly on postoperative re-fractures after osteoporotic compression fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):556.
[10] TANG J, WANG S, WANG J, et al. Risk factors for secondary vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebral augmentation: a single-centre retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):797.
[11] WANG R, XU Y, MA X. Risk factors and strategies for recovery quality, postoperative pain, and recurrent fractures between percutaneous kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty in elderly patients with thoracolumbar compression fractures: a retrospective comparative cohort study. Ann Transl Med. 2023;11(2):122.
[12] 包志强,陈扬.经皮椎体成形术后再发骨折的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(2):150-155.
[13] DEPALMA MJ, KETCHUM JM, FRANKEL BM, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the nonagenarians: a prospective study evaluating pain reduction and new symptomatic fracture rate. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(4):277-282.
[14] CHIN KY. A review on the performance of osteoporosis self-assessment tool for Asians in determining osteoporosis and fracture risk. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(7):734-746.
[15] IMAI K. Vertebral fracture risk and alendronate effects on osteoporosis assessed by a computed tomography-based nonlinear finite element method. J Bone Miner Metab. 2011;29(6):645-651.
[16] SYED MI, PATEL NA, JAN S, et al. Intradiskal extravasation with low-volume cement filling in percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(9):2397-2401.
[17] 阿卜杜吾普尔·海比尔,阿里木江·玉素甫,麦麦提敏·阿卜力米提,等.经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥量和分布对手术椎体及邻近椎体再发骨折的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(10):1586-1591.
[18] GAO C, ZONG M, WANG WT, et al. Analysis of risk factors causing short-term cement leakages and long-term complications after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Acta Radiol. 2018;59(5):577-585.
[19] ZHOU C, HUANG S, LIAO Y, et al. Correlation analysis of larger side bone cement volume/vertebral body volume ratio with adjacent vertebral compression fractures during vertebroplasty. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1072087.
[20] KOMEMUSHI A, TANIGAWA N, KARIYA S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture: multivariate study of predictors of new vertebral body fracture [J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2006;29(4):580-585.
[21] 李涛,于涛.吸烟性骨质疏松症发病机制研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(5):381-386.
[22] 杨波,陈晓峰,段媛媛,等.结合吸烟与遗传因素交互作用鉴定骨质疏松症易感基因[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2018,39(4): 589-596.
[23] COSTA-RODRIGUES J, ROCHA I, FERNANDES MH. Complex osteoclastogenic inductive effects of nicotine over hydroxyapatite. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(2):1029-1040.
[24] JOEHANES R, JUST AC, MARIONI RE, et al. Epigenetic Signatures of Cigarette Smoking. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2016;9(5):436-447.
[25] KIYOTA Y, MURAMATSU H, SATO Y, et al. Smoking cessation increases levels of osteocalcin and uncarboxylated osteocalcin in human sera. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):16845.
[26] ILIĆ K, OBRADOVIĆ N, VUJASINOVIĆ-STUPAR N. The relationship among hypertension, antihypertensive medications, and osteoporosis: a narrative review. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;92(3):217-227.
[27] MASUGATA H, SENDA S, INUKAI M, et al. Association between bone mineral density and arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2011;223(2):85-90.
[28] VESTERGAARD P, REJNMARK L, MOSEKILDE L. Hypertension is a risk factor for fractures. Calcif Tissue Int. 2009;84(2):103-111.
[29] BONUCCI E, BALLANTI P. Osteoporosis-bone remodeling and animal models. Toxicol Pathol. 2014;42(6):957-969.
[30] PEETERS G, VAN SCHOOR NM, LIPS P. Fall risk: the clinical relevance of falls and how to integrate fall risk with fracture risk. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2009;23(6):797-804.
[31] MAUREL DB, BOISSEAU N, BENHAMOU CL, et al. Alcohol and bone: review of dose effects and mechanisms. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(1): 1-16.
[32] BOTOLIN S, FAUGERE MC, MALLUCHE H, et al. Increased bone adiposity and peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma2 expression in type I diabetic mice. Endocrinology. 2005;146(8):3622-3631.
[33] SCHWARTZ AV, SELLMEYER DE, ENSRUD KE, et al. Older women with diabetes have an increased risk of fracture: a prospective study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(1):32-38.
[34] ZHANG ZL, YANG JS, HAO DJ, et al. Risk Factors for New Vertebral Fracture After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16:1193-1200.
[35] FROTZLER A, CHEIKH-SARRAF B, POURTEHRANI M, et al. Long-bone fractures in persons with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2015;53(9): 701-704.
[36] YAN J, LIAO Z, YU Y. Finite element analysis of dynamic changes in spinal mechanics of osteoporotic lumbar fracture. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):142.
[37] KIM JE, YOO HS, CHOI DJ, et al. Comparison of Minimal Invasive Versus Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Single-level Lumbar Disease. Clin Spine Surg. 2021;34(2):E64-E71.
[38] 廖芝富,匡中强,曲诗言,等.经皮椎体成形术后邻近椎体继发骨折危险因素分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2023,12(4):296-301.
[39] 李文乐,王浩胜,宁丽俊,等.经皮椎体成形术后新发椎体压缩骨折临床预测模型的建立与验证[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021, 27(12):1804-1809.
[40] ZUO XH, ZHU XP, BAO HG, et al. Network meta-analysis of percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous kyphoplasty, nerve block, and conservative treatment for nonsurgery options of acute/subacute and chronic osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) in short-term and long-term effects. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(29):e11544.
[41] MIGLIORINI F, MAFFULLI N, SPIEZIA F, et al. Biomarkers as therapy monitoring for postmenopausal osteoporosis: a systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):318.
[42] MITTALHENKLE A, GILLEN DL, STEHMAN-BREEN CO. Increased risk of mortality associated with hip fracture in the dialysis population. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44(4):672-679.
[43] NICKOLAS TL, MCMAHON DJ, SHANE E. Relationship between moderate to severe kidney disease and hip fracture in the United States. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(11):3223-3232.
[44] 袁群生,李雪梅.2017年KDIGO关于慢性肾脏病矿物质及骨异常临床实践指南更新与解读[J].协和医学杂志,2018,9(3):213-218.
45] MILLER PD, ADACHI JD, ALBERGARIA BH, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Romosozumab Among Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis and Mild-to-Moderate Chronic Kidney Disease. J Bone Miner Res. 2022;37(8):1437-1445.
[46] HSU S, BANSAL N, DENBURG M, et al. Risk factors for hip and vertebral fractures in chronic kidney disease: the CRIC study. J Bone Miner Res. 2024;39(4):433-442.
[47] BOVER J, GÓMEZ-ALONSO C, CASADO E, et al. Osteoporosis management in patients with chronic kidney disease (ERCOS Study): A challenge in nephrological care. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2024;44(2): 241-250.
[48] KUAN V, DENAXAS S, PATALAY P, et al. Identifying and visualising multimorbidity and comorbidity patterns in patients in the English National Health Service: a population-based study. Lancet Digit Health. 2023;5(1):e16-e27.
[49] SABAGHIAN T, DELKASH P, RAHMANNIA M, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Anti-Osteoporotic Agents across CKD Stages: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2024;49(1): 581-587.
[50] GOTO NA, WESTSTRATE ACG, OOSTERLAAN FM, et al. The association between chronic kidney disease, falls, and fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(1):13-29.
[51] PIMENTEL A, BOVER J, ELDER G, et al. The Use of Imaging Techniques in Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorders (CKD-MBD)-A Systematic Review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(5):772.
[52] KIM CS, CHOI HS, BAE EH, et al. Weight change and fracture risk in patients with diabetic kidney disease: A nationwide population-based study. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:912152. |