3.1 文章结果分析 该组病例为反复轻微外伤或者无明显外伤至同一椎体骨折迁延不愈,病程均大于6个月,平均(8.50±10.99)个月;其中L1椎体骨折5例,L2椎体骨折1例,L3椎体骨折3例。与文献报道相似[6,9-10],符合骨质疏松性腰椎压缩骨折的流行病学特点[3,6]。
研究提示,陈旧性OVCF术椎再骨折发生于患有骨质疏松症的老年人群[5,11],X射线平片中的椎体内真空裂隙、椎体前缘“开口”现象以及MRI检查中的双线征均可用来辅助诊断。随着人口老龄化进展,此病发病率明显升高,并显著降低了患者生活质量和预期寿命,引起学者的广泛重视以及深入的研究。
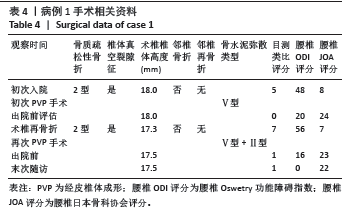
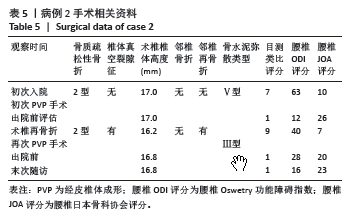
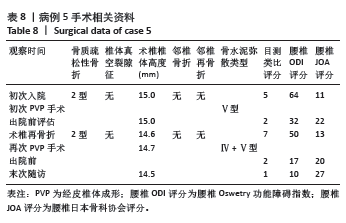
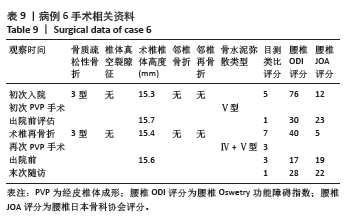
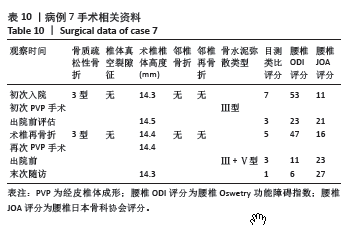
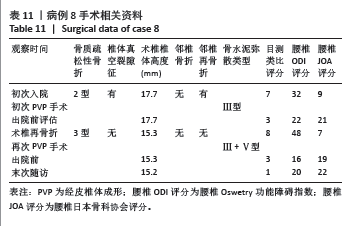
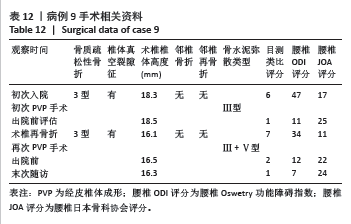
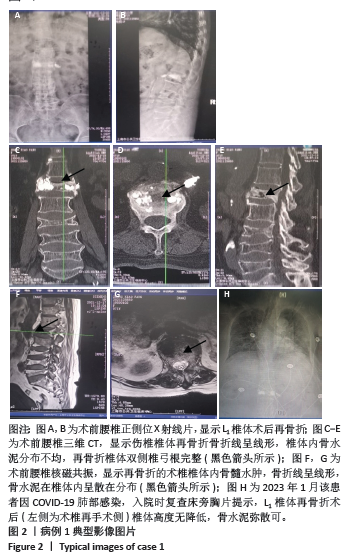
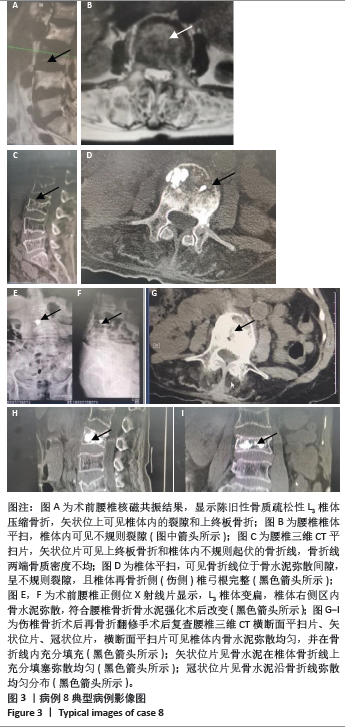
此组9例患者符合骨质疏松性椎体骨折的诊断特点,再骨折术椎的X射线片、三维CT特点:伤椎体内骨水泥分布不均,其中散在的骨水泥周围小梁骨连续性中断;矢状位片可见骨折线呈现明显裂隙征,再骨折椎体前缘可伴有或不伴有高度降低;皮质骨边缘变薄,可伴有或不伴有连续性中断。核磁共振成像显示骨折线为明显裂隙征,裂隙周围骨髓水肿明显。
3.2 术椎再骨折患者的腰椎生物力学特点 有学者观察到,脊柱的生物力学结构的改变是随着人体老化过程[12-13],保证脊柱生物力学特性的一种结构改变(符合Roussouly分型特点),也就是通过改变脊柱的生理曲度[脊柱侧弯、侧方倾斜;脊柱生理曲度增加(前凸增大)、生理曲度变直(前凸减小)],甚至通过骨盆的倾斜程度(骨盆入射角的改变)保证脊柱整体力学结构稳定性不变,这种情况下,则会导致原本在脊柱上均匀分散的应力在某一节段(水平)集中,形成剪切力,进一步加重脊柱力学结构的变化,最终以某一节段(水平)结构的破坏而达成整体脊柱生物力学结构稳定性的重建。
OVCF与腰椎滑脱存在共同的危险因素,如脊柱-骨盆影像学参数异常、雌激素水平降低以及骨密度减少
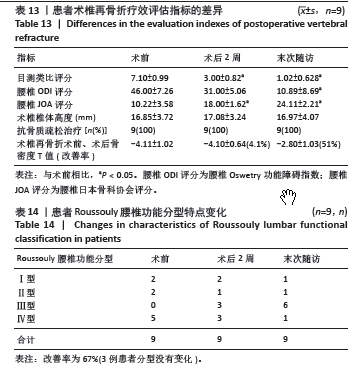
等[14-19]。与以往文献报道相似[20],该组中的9例患者具有鲜明的特征,所有患者的伤椎(骨折椎体)位于Roussouly分型顶椎位置,且在疾病治疗和随访过程中(初次椎体骨折)腰椎的Roussouly分型未发生改变,也就是应力集中的水平未出现上移或者下移,应力大小也未得到分散分解,进而发生伤椎术后出现再骨折情况。此组病例的伤椎-腰椎生物力学特点:符合Roussouly腰椎功能分型,术前为Ⅰ型2例,Ⅱ型2例,Ⅳ型5例;术后给予合适的腰背肌群康复训练,末次随访:Ⅰ型1例,Ⅱ型1例,Ⅲ型6例,Ⅳ型1例,术后末次随访最长时间为术后27个月,改善率为67%。与之相对应患者的目测类比评分、ODI指数、JOA评分术前与末次随访数据比较差异均有显著性意义。
3.3 经皮椎弓根穿刺技术在术椎再骨折手术中的应用特点 在陈旧性椎体压缩骨折骨不连术后术椎再骨折患者中,部分患者因为前次手术中的骨水泥注入使再手术时经椎弓根穿刺变成不可能,也就是常规的椎弓根入路及椎弓根外侧入路无法达到靶点位置,给手术的效果带来了不确定性,也有医生在常规入路PVP无法到达靶点位置时选择经椎间孔入路[21],或者经椎弓根旁入路或者经肋横突入路等都不失是一良好选择[22-23],术后效果满意,未见明显不良反应及相关并发症。也有患者因多次反复多椎体压缩骨折导致脊柱结构发生明显变化,如出现角状后凸等,需要做脊柱截骨矫形手术和使用骨水泥螺钉内固定手术。
此组病例中未发现腰椎后凸畸形患者,以及椎体压缩骨折后出现的脊柱失稳或者二柱和三柱骨折等不稳定性骨折患者;都保留了穿刺的椎弓根完整性,能够做再次的经椎弓根穿刺手术。所有病例选择经术椎椎弓根穿刺单侧入路PVP技术。分析术椎再骨折时前次术椎PVP手术时骨水泥弥散分型:Ⅴ型5例,Ⅲ型4例;考虑是由于单侧骨水泥注入量过少,或者双侧经椎弓根穿刺,两侧骨水泥注入量不平衡,导致术椎的抗压强度和刚度不能承受患者术后必须的功能和活动量,在任意时间节点上,任意外伤都导致患者的腰背部疼痛加重,和原陈旧性椎体压缩骨折部位的再骨折。
在再骨折后的翻修手术中,首先,在术前向患者详细交代术中可能出现的反应和相对应椎体内的改变,让患者有充分的知情和思想准备,并同意配合手术。其次,手术计划制定过程中设计了再骨折区靶向穿刺技术和骨水泥注入时选择在骨水泥黏丝期与成团期之间的时间段。骨水泥注入过程中,由于骨水泥的性质是黏弹性物质,密度较椎体内疏松小梁骨和小梁骨间的炎性肉芽组织和凝血块的密度大,因此在注入过程中的压力检测主要是根据术中患者对骨水泥压力产生的疼痛反应确定,并根据患者术中针对疼痛产生的反应以及术中生命体征监测结果来判断骨水泥注入量和骨水泥推注速度,而不是追求所有再骨折术椎都注入≥3 mL的骨水泥注入量。
3.4 伤椎骨水泥注入量和伤椎内骨水泥分布特点 文献报道,伤椎椎体成形术后椎体前缘高度存在不同程度的丢失,导致患者出现椎体塌陷,或称为术椎再骨折、术椎再压缩等[9,24],他们认为骨水泥的分布位置与术后椎体塌陷密切相关,研究认为分布于椎体中央、团块状的骨水泥更容易出现应力集中,骨水泥应向椎体的前缘弥散,以强化椎体的前缘。此组病例观察椎体内原有骨水泥分布多为单侧Ⅴ型骨水泥分布,且骨水泥的边缘有裂隙征或真空征存在,这可能是再骨折后疼痛加重的主要原因。在再骨折的术椎中注入骨水泥使之弥散到骨折区域,能够达到减少骨折椎体内骨折区域微动、稳定骨折端、重建脊柱稳定性、迅速缓解疼痛、改善生活质量的目的[25-29]。
BELKOFF等[30]在椎体压缩骨折生物力学的研究中发现,2 mL的骨水泥灌注即可恢复压缩椎体的强度。有利用尸体进行研究发现至少需要灌注椎体容积 15%的骨水泥,才能恢复椎体的抗压强度,也就是说在胸腰段PVP手术中需要注入4-6 mL骨水泥才有理想的生物力学效应[31]。
SUN等[22]采用三维有限元模拟力学实验,表明椎体刚度的恢复与注入骨水泥剂量密切相关,1 cm³骨水泥(填充率14%)可恢复小于15%的椎体初始刚度,3.5 cm³骨水泥(填充率50%)可有效恢复上椎的初始刚度,7 cm³骨水泥(填充率98%)可使椎体刚度增加50%。田云虎等[23]发现骨水泥的灌注剂量与骨折椎体刚度的恢复呈正相关关系。且目前多数研究一致认为,没有必要过分追求椎体刚度的恢复,通过治疗使椎体的生物力学重新稳定即可。
随着陈旧性OVCF骨不连患者的逐渐增多,更多的观察结果指向陈旧性椎体压缩骨折骨不连现象一般发生在椎体的上缘,骨折线也在椎体靠近上终板的上部分,而随着抗骨质疏松治疗的深入,如双膦酸盐类药物使用的增加,在陈旧性骨折骨不连椎体体现出骨折线真空征下方骨呈硬化骨改变[4-5]。因此骨水泥弥散需要分布在骨折线周围,也就是对骨折线周围进行骨水泥强化即可[5,10],而不追求全椎体的骨水泥强化,或全椎体骨水泥弥散,或大部弥散。这就要求注入适当的骨水泥量,而不是最大量。
此组病例特点为术椎再骨折患者,伤椎内有部分骨水泥存在,再注入骨水泥的目的是使骨水泥在骨折线周围弥散,并于椎体内原有骨水泥相粘连,此组病例中伤椎骨水泥注入量为1.5-4.5 mL。
3.5 有效抗骨质疏松治疗 此组患者在发生伤椎再骨折时骨密度在-5.4至-3.3(平均骨密度-4.10±0.64),在骨折椎体术后给予规律抗骨质疏松治疗,末次随访骨密度明显提高:-5.1至-1.6(平均骨密度-2.80±1.03)。这提示骨质疏松同样是伤椎再骨折的必要因素。伴有骨质疏松症的患者多发或者再发术椎、邻椎椎体的压缩骨折,或陈旧性OVCF骨不连首先表现的特点是由于骨密度减低导致的全身骨痛,和椎体骨折引起的翻身、起床、坐起活动时腰疼、背痛的典型症状,其中大部分症状可以通过抗骨质疏松治疗得到缓解。因此,有效规律的抗骨质疏松治疗是充分和必要的。
在早期此组病例中有明显的骨密度减低和反应性的甲状旁腺激素增高,经过系统、规律的抗骨质疏松药物治疗后,全身骨痛症状缓解明显,且骨密度和甲状旁腺激素水平恢复正常。结合指南,课题组给患者进行了三级抗骨质疏松治疗,同时根据患者自身个体差异进行适当调整,其中5例患者服用骨化三醇胶囊±醋酸钙片;2例患者单纯服用钙尔奇D,并进行每日1次的鲑降钙素50 U
规律皮下注射连续2周。所有患者均接受了在院的静脉注射唑来膦酸钠注射液治疗,每年1次。此组患者初次骨折时的骨密度T值为-4.11±1.02,由于不规律的抗骨质疏松治疗,再骨折时骨密度T值平均-4.10±0.64(改善率4.1%),术椎再骨折术后给予规律抗骨质疏松治疗,末次随访时平均骨密度T值为-2.80±1.03(改善率51%)。相对应的患者末次随访时的目测类比评分、ODI指数和JOA评分都有不同程度的改善。
3.6 研究局限性和展望 此组病例数较少,观察内容和范围覆盖面窄,并不能全面、充分反映陈旧性OVCF不连伤椎术后再骨折的病例特点,还需要大样本量、多中心研究才能更充分地体现这一疾病的特点,获得更多的治疗方法和拥有更多的适应证选择范围。同时,作者也在思考:由于这类患者大都伴随肌少症,导致初次椎体压缩骨折未得到及时治疗,骨质疏松未得到及时控制,而腰椎生物力学结构退变的过程也没有及时阻止,因而发生术椎再骨折。由于再骨折术后课题组给予积极的抗骨质疏松治疗、适度的功能锻炼,调整和改善脊柱生物力学结构,使患者术后的生活质量有明显提高,同时骨密度也得到相应改善。因此,课题组提出在治疗过程中的诊疗思路要更宽阔,术前方案制定要更周详。同样地,此类患者为老年患者,多伴有一种或多种基础疾病,增加的药物和手术治疗的风险,因此手术预案的制定需要规避这些风险。
陈旧性OVCF骨不连伤椎术后再骨折这一类疾病的诊疗,会随着更多的专家学者开展的更多的研究而得到更充分的诠释和获得更多的治疗方法和更好疗效。课题组坚信,随着科学技术的发展,更多、更好的检测手段和治疗方法的出现,会使这类疾病的诊治更科学、更简单、更微创或者无创,使这类人群获益更多。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程