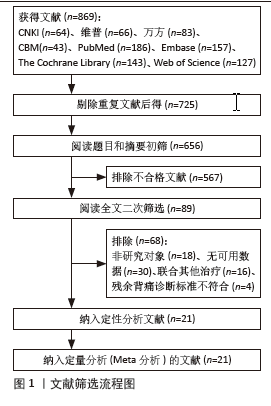
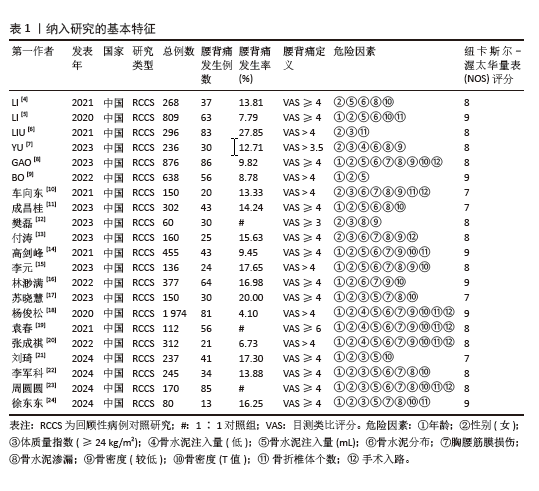
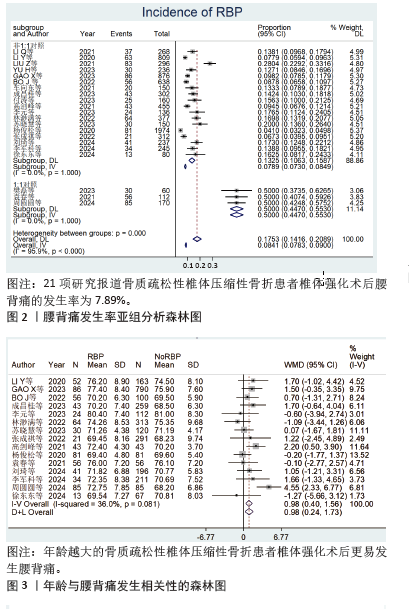
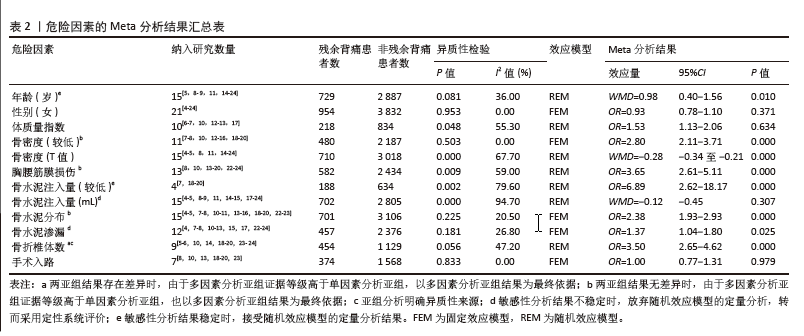
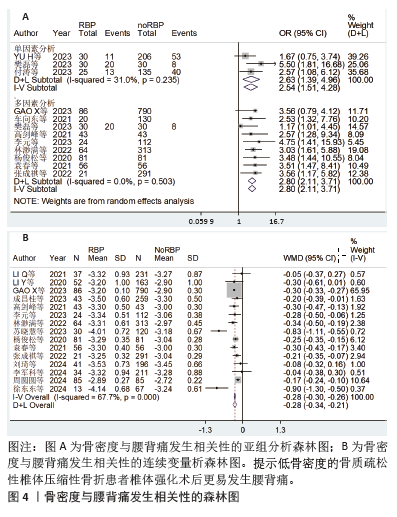
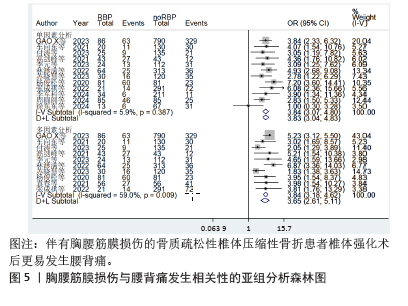
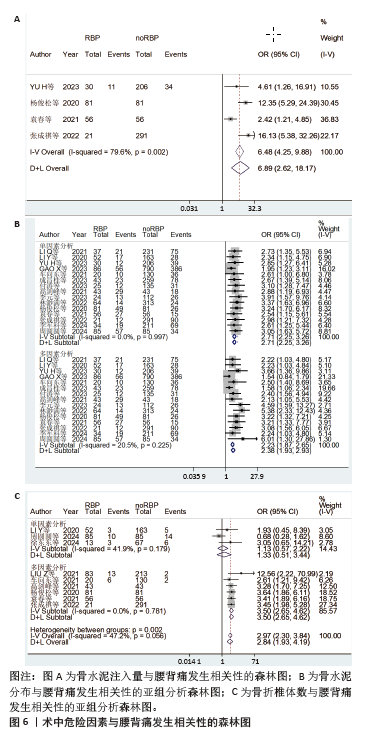
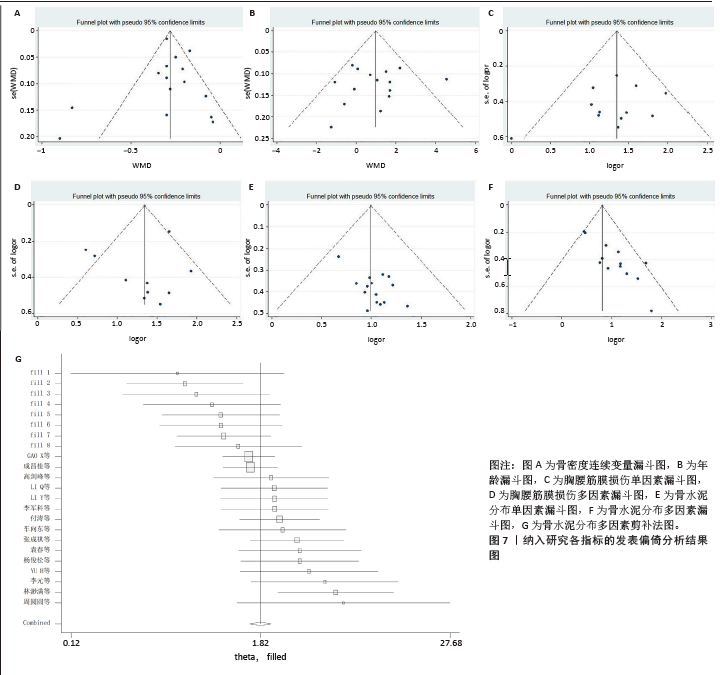
[1] 丁悦, 张嘉, 岳华,等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折诊疗与管理专家共识[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2018,11(5):425-437.
[2] 杜宇康, 廖瑛扬, 肖淼盛,等. 经皮椎体成形术与经皮椎体后突成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效对比分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(10):946-948.
[3] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605.
[4] LI Q, SHI L, WANG Y, et al. A Nomogram for Predicting the Residual Back Pain after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Res Manag. 2021;2021:3624614.
[5] LI Y, YUE J, HUANG M, et al. Risk factors for postoperative residual back pain after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(10):2568-2575.
[6] LIU Z, ZHANG X, LIU H, et al. A nomogram for short-term recurrent pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2022; 33(4):851-860.
[7] YU H, LUO G, WANG Z, et al. Predictors of residual low back pain in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures following percutaneous kyphoplasty. Front Surg. 2023;10:1119393.
[8] GAO X, DU J, HAO D, et al. Risk factors for residual back pain following percutaneous vertebral augmentation: the importance of paraspinal muscle fatty degeneration. Int Orthop. 2023;47(7):1797-1804.
[9] BO J, ZHAO X, HUA Z, et al. Impact of sarcopenia and sagittal parameters on the residual back pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):111.
[10] 车向东, 李茂山, 张战峰. PKP术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折残余腰背疼痛的危险因素分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2021,42(1):63-65+69.
[11] 成昌桂, 高增鑫, 陈优民,等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折经皮椎体成形术后残余腰背痛风险列线图模型的构建与验证[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2023,27(12):38-43.
[12] 樊磊. 骨质疏松性椎体骨折PKP术后残留疼痛程度的影响因素分析[J]. 系统医学,2023,8(14): 85-88.
[13] 付涛, 钟炎伟, 于金华. 骨质疏松性腰椎骨折PVP术后慢性腰痛危险因素调查[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2023,44(4):672-673+676.
[14] 高剑峰, 袁景, 沈文东,等. 经皮椎体后凸成形术后残余腰背痛的危险因素分析[J]. 现代医学,2021,49(11):1297-1302.
[15] 李元, 李立平, 李强. PKP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折早期疼痛缓解不佳相关因素分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2023,29(5):390-394.
[16] 林渺满, 文雪梅, 黄宗伟,等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折椎体强化术后残余腰背痛风险预测模型的构建与验证[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2022,32(8):720-728.
[17] 苏晓慧, 芮晶晶, 陈文月,等. 骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体强化术后并发残余腰背痛的危险因素[J]. 临床与病理杂志,2023,43(7): 1384-1391.
[18] 杨俊松, 陈浩, 刘鹏,等. 经皮椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折疗效不佳的多因素分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(1): 45-52.
[19] 袁春, 缪伟, 唐文凯,等. PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折术后持续腰背疼痛的影响因素分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(9): 956-958.
[20] 张成祺, 裴济民, 赵永辉,等. PVP术后早期残留腰背痛的风险因素分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2022,43(2):204-207.
[21] 刘琦, 钱军, 张岚,等. OVCF患者PVP术后肌肉减少和矢状面参数对残余背痛的影响[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2024,45(2):311-314.
[22] 李军科, 马续彬, 李亮,等. 预测骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术后残余背痛的列线图[J]. 中国骨伤,2024,37(6):553-559.
[23] 周圆圆, 张玲敏, 袁之木. 老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折患者术后残余腰背痛影响因素及预测模型的构建分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2024, 45(1): 101-106.
[24] 徐东东, 张坚若, 何戟锋. 经皮椎体强化治疗胸腰椎OVCF患者术后残余痛发生危险因素分析[J]. 浙江创伤外科,2024,29(5):857-859.
[25] 陈莹, 盛珺, 刘达,等. 唑来膦酸改善骨质疏松患者后路腰椎椎间融合术后腰痛[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2019,17(5):319-323.
[26] 李智斐, 付拴虎, 张家立,等. 椎体成形术后再骨折相关因素分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(9):790-794.
[27] 金军伟, 赵刚, 胡付立. 唑来膦酸静脉滴注联合仙灵骨葆胶囊和醋酸钙胶囊口服对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮椎体成形术后疗效和安全性的影响[J]. 中医正骨,2019,31(7):15-20.
[28] 杨鑫, 皮文杰, 李素铠. 经皮穿刺椎体成形术后余椎新发骨折的风险因素分析[J]. 重庆医学, 2024,53(18):2793-2798,2803.
[29] PRESTWOOD KM, KENNY AM. Osteoporosis: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment in older adults. Clin Geriatr Med. 1998;14(3):577-599.
[30] 钟远鸣, 张翼升, 李智斐,等. 胸腰椎骨质疏松骨折时间与PVP术后临床疗效相关性的研究[J]. 重庆医学,2018,47(32):4134-4138.
[31] YAN Y, XU R, ZOU T. Is thoracolumbar fascia injury the cause of residual back pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty? A prospective cohort study. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(3): 1119-1124.
[32] YANG JS, LIU JJ, CHU L, et al. Causes of Residual Back Pain at Early Stage After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A Retrospective Analysis of 1,316 Cases. Pain Physician. 2019;22(5):E495-E503.
[33] 万广, 杨慧, 吴大鹏,等. 脊柱-骨盆参数对椎体成形术效果的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2020,28(16):1472-1476.
[34] 董洲, 陶晖, 刘艺明,等. 脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡状态与骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形效果的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(29):4635-4640.
[35] 刘长枫, 宋文慧, 刘昌文,等. 经皮椎体成形术骨水泥分布评价及影响因素分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(11):1001-1008.
[36] WIGGINS MC, SEHIZADEH M, PILGRAM TK, et al. Importance of intravertebral fracture clefts in vertebroplasty outcome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(3):634-640.
[37] 付兆宗, 陈忠羡, 秦英,等. 骨水泥分布指数对椎体成形术后症状性邻近节段骨折的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2017,37(7):947-951.
[38] 蔡明, 戚颖, 刘肃,等. 骨水泥不同分布对骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的生物力学影响:三维有限元分析[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2022,39(6):771-777.
[39] LIU H, ZHANG J, LIANG X, et al. Distribution Pattern Making Sense: Patients Achieve Rapider Pain Relief with Confluent Rather Than Separated Bilateral Cement in Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e1190-e1196.
[40] BRIGGS AM, WRIGLEY TV, VAN DIEËN JH, et al. The effect of osteoporotic vertebral fracture on predicted spinal loads in vivo. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15(12):1785-1795.
[41] HE X, LI H, MENG Y, et al. Percutaneous Kyphoplasty Evaluated by Cement Volume and Distribution: An Analysis of Clinical Data. Pain Physician. 2016;19(7):495-506.
[42] HUANG S, ZHU X, XIAO D, et al. Therapeutic effect of percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with anti-osteoporosis drug on postmenopausal women with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture and analysis of postoperative bone cement leakage risk factors: a retrospective cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):452.
[43] FU Z, HU X, WU Y, et al. Is There a Dose-Response Relationship of Cement Volume With Cement Leakage and Pain Relief After Vertebroplasty? Dose Response. 2016;14(4):1559325816682867.
[44] REN HL, JIANG JM, CHEN JT, et al. Risk factors of new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures in osteoporotic patients undergone percutaneous vertebroplasty. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(4):750-758.
[45] LI K, YAN J, YANG Q, et al. The effect of void creation prior to vertebroplasty on intravertebral pressure and cement distribution in cadaveric spines with simulated metastases. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:20.
[46] LIEBSCHNER MA, ROSENBERG WS, KEAVENY TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26(14):1547-1554.
[47] LUO J, DAINES L, CHARALAMBOUS A, et al. Vertebroplasty: only small cement volumes are required to normalize stress distributions on the vertebral bodies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(26):2865-2873.
[48] ZHU SY, ZHONG ZM, WU Q, et al. Risk factors for bone cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective study of four hundred and eighty five patients. Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1205-1210.
[49] MANSOORINASAB M, ABDOLHOSEINPOUR H. A review and update of vertebral fractures due to metastatic tumors of various sites to the spine: Percutaneous vertebroplasty. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2018;10(1):1-6.
[50] KIM WJ, MA SB, SHIN HM, et al. Correlation of Sagittal Imbalance and Recollapse after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Multivariate Study of Risk Factors. Asian Spine J. 2022;16(2):231-240.
[51] AHMADI SA, TAKAHASHI S, HOSHINO M, et al. Association between MRI findings and back pain after osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a multicenter prospective cohort study. Spine J. 2019;19(7):1186-1193.
[52] 王华锋, 叶小伟, 周福山,等. PVP术后有症状椎管内骨水泥渗漏的诊治并文献回顾[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(5):499-501. |