中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 721-730.doi: 10.12307/2026.528
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用与展望
管昱杰1,赵 彬 2
- 1黑龙江中医药大学研究生院,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150040;2黑龙江中医药大学附属第二医院肌肉骨骼疼痛诊室,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150001
-
收稿日期:2024-12-22接受日期:2025-02-20出版日期:2026-01-28发布日期:2025-07-07 -
通讯作者:赵彬,博士,副主任医师,黑龙江中医药大学附属第二医院肌肉骨骼疼痛诊室,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150001 -
作者简介:管昱杰,男,2000年生,山东省淄博市人,汉族,黑龙江中医药大学在读硕士,主要从事肌肉骨骼康复相关研究。 -
基金资助:黑龙江省博士后基金项目(LBH-Z22290),项目负责人:赵彬
Application and prospect of artificial intelligence in screening and diagnosis of scoliosis
Guan Yujie1, Zhao Bin2
- 1Graduate School, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Musculoskeletal Pain Clinic, Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-22Accepted:2025-02-20Online:2026-01-28Published:2025-07-07 -
Contact:Zhao Bin, MD, Associate chief physician, Musculoskeletal Pain Clinic, Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Guan Yujie, Master candidate, Graduate School, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:Heilongjiang Province Postdoctoral Fund Project, No. LBH-Z22290 (to ZB)
摘要:
文题释义:
脊柱侧弯:是一种常见的脊柱疾病,主要表现为脊柱三维方向的畸形,使背部呈现C形或S形曲线,其发病原因复杂,各类型脊柱侧弯的病因各异,并随年龄增加症状逐渐加剧,严重者影响呼吸、心脏功能,甚至出现脊髓压迫及瘫痪现象。人工智能:一个以计算机科学为基础,通过模拟人类的思维方式和思考过程,做出与人类智能相似的行为反应,目前正应用于医学的各个领域。
摘要
背景:脊柱侧弯是脊柱侧向弯曲和旋转的三维畸形,其发病年龄覆盖整个生命周期,成为威胁人们健康的重要卫生问题。随着计算机科学的发展不断进步,目前人工智能在医学诊治方面有着巨大的应用潜力,也逐渐被应用于脊柱侧弯的筛查和诊断中。
目的:全面梳理人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用,多方面阐述近年来的应用进展,并对其创新点进行展望,为未来智能化的趋势提供参考。
方法:检索覆盖PubMed、IEEE Xplore、中国知网、万方数据库,英文检索词为“scoliosis,artificial intelligence,machine learning,screen,diagnosis”等,中文检索词为“脊柱侧弯、人工智能、机器学习、筛查、诊断”等,结合布尔逻辑以优化检索策略。纳入与人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中应用研究直接相关的文章,排除关联性不强、陈旧、实验设计不严谨或可信度差的文献,最终纳入83篇文献进行分析。
结果与结论:①人工智能在脊柱侧弯的初期筛查、胸片筛查、智能手机筛查、X射线片诊断、CT和MRI诊断、脊柱三维图像的重建等多个领域均展现出独特的应用价值和发展前景;②人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断领域的应用可提高效率、降低误诊率、减轻医护人员负担,便于早期发现并确诊脊柱侧弯,为脊柱健康保驾护航。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
管昱杰, 赵 彬 . 人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 721-730.
Guan Yujie, Zhao Bin. Application and prospect of artificial intelligence in screening and diagnosis of scoliosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 721-730.
DUNN等[6]系统回顾了1966-2016年关于脊柱侧弯筛查的研究,共筛查了448 276名青少年,肯定了筛查有助于早期发现脊柱侧弯的作用,验证了广泛筛查的重要性。目前医护人员以Adam’s前屈试验为检查方式,以躯干旋转角度≥5°为疑似脊柱侧弯阈值[14],并根据其严重程度做出适当建议。以机器学习、深度学习为代表的人工智能和带有特定程序的智能手机越来越多的应用于脊柱侧弯的筛查中,其阳性率高、操作简单、院外可访问的特点[15],使得广泛的脊柱筛查成为可能,让更多的脊柱侧弯患者早发现、早诊断、早治疗。
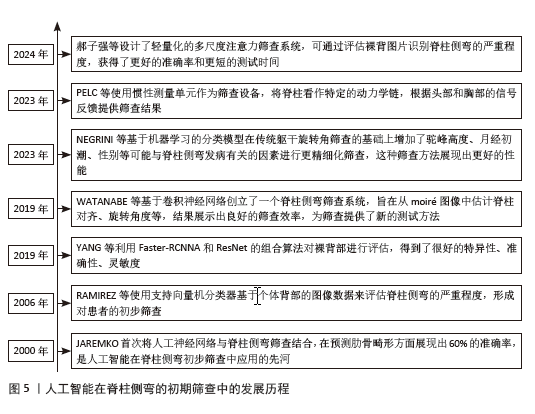
2.1.1 人工智能在脊柱侧弯初期筛查中的应用 基于机器学习和深度学习进行脊柱侧弯的初期筛查是使用神经网络提取人体背部的重点特征,并将其传入分类器中进行处理,得到最后的脊柱侧弯程度,完成脊柱侧弯筛查。2000年JAREMKO等[16]首次将人工神经网络和脊柱侧弯研究相结合,在预测肋骨畸形方面显示人工神经网络平均60%的正确率,高于线性回归分析的34%,为人工神经网络技术应用于脊柱侧弯的筛查提供了方向,此后人工智能越来越多的应用于脊柱侧弯的筛查中。RAMIREZ等[17]采用支持向量机分类器基于个体背部的图像数据,来评估AIS的严重程度。但为了实现更细化的分类,需要使用多个支持向量机组合策略。YANG等[18]开发了深度学习算法模型,利用Faster-RCNNA和ResNet的组合算法对裸背部进行评估,提取二元分类和多类分类的高级特征,其准确性、灵敏度、特异性和PPV均达到理想状态。WATANABE等[19]创建了一个脊柱侧弯筛查系统,该系统基于卷积神经网络从moiré图像中估计脊柱对齐、Cobb角和脊柱旋转,识别定位了12个胸椎、5个腰椎、17个棘突并计算了每个椎骨的旋转角度,为筛查提供了新的测试方法。在筛查的过程中NEGRINI等[20]利用机器学习的分类模型,在传统躯干旋转角度筛查基础上增加了驼峰高度(mm)、性别、年龄、月经初潮、肩胛骨和肩膀的不对称等预测因素,平均预测准确率为80%,灵敏性和特异性分别为95%和83%,为建立多因素脊柱侧弯筛查模型开创先河。提示为了提高筛查的准确性,不仅要关注躯干旋转角度还要关注更多可预测因素,为未来开发更准确且易使用的筛查模型打下基础。PELC等[21]使用低成本的惯性测量单元作为筛查设备,将脊柱看作特定的动力学链并自动跟据头部、胸部区域的信号提供筛查结果,但是该研究仅初步使用模拟测试的方法测试了设备的可执行性,未来研究应纳入真实患者,完善惯性测量单元在筛查中的使用。郝子强等[22]对ResNet50 进行改进并设计了轻量化的多尺度注意力筛查系统,提出了多尺度残差特征提取模块(MRFEM)和多层次特征融合模块(MFFM),在通过裸背图像识别脊柱侧弯严重程度上相比ResNet50总体准确率提高了11.19%,测试时长减少了2 s。
自2000-2024年,人工智能技术在脊柱侧弯早期筛查领域经历了显著的发展,发展流程见图5。在此期间,技术的不断进步和算法的持续优化显著提高了筛查的准确性;迭代、创新筛查方法和建立健全筛查系统提高了筛查的应用效率;筛查过程中的多因素综合分析提高了筛查灵敏性。尽管如此,目前早期筛查工作仍然是劳动密集型的,主要依赖于临床医护人员。展望未来,期待人工智能在脊柱侧弯早期筛查领域得到更广泛的应用。
2.1.2 人工智能在胸片筛查中的应用 在健康体检时常用胸片来检查肺部结构[23],胸片在显影肺的同时还能显影脊柱,因此在体检时通过胸片初步筛查脊柱侧弯成为一种省时省力的方法。XIE等[24]开发了包含一个学习模块和一个推理模块的人工智能自动程序,该研究使用96张图像用于程序训练,491张图像用于测试,结果显示人工智能诊断脊柱侧弯的准确率为98.37%,特异性98.73%,灵敏度88.24%;和5°躯干旋转角度特异性100%、灵敏度47%相比[25],有着稍低的特异性,但灵敏性远高于5°躯干旋转角度。LEE等[26]研究开发了一种基于深度学习并整合生成对抗网络的半监督学习模式,是用于胸片中的脊柱侧弯筛查工具。研究共纳入512名受试者,结果显示该工具的特异性达到98.5%,而灵敏度为28.5%,虽然特异性略有提高,但这种提升是以牺牲灵敏度为代价的,导致许多非脊柱侧弯患者需要接受额外的X射线检查以进行进一步诊断,从而增加了不必要的辐射暴露风险。LEE等[27]在LEE等[26]的研究基础上增加了简单多层感知器对胸片进行分析,经过内部和外部数据的验证,显示出良好的接收器操作特性,当灵敏度固定在0.9时,模型的特异性在内部数据集为69.7%,在外部数据集中为64.6%。胸部X射线片可显示整个胸椎和上腰椎,虽然腰部曲线看不到,但研究验证了人工智能应用于胸部X射线片可以在筛查时达到良好的特异性和敏感性,是脊柱侧弯筛查的可行方法。
2.1.3 智能手机在筛查中的应用 随着互联网的快速发展,手机的智能化和普及率逐年增高,因其廉价、高效、使用方便等特点被人们越来越多的应用于脊柱侧弯的筛查中。手机在脊柱侧弯筛查中的应用方法大致分为2类:①分析裸背图片的应用程序;②平替旋转角度尺的应用程序。ZHANG等[15]研发了由 ScolioNets 深度学习模型支持的AlignProCARE应用程序,旨在通过上传单张裸背照片至该程序来评估AIS的严重程度、曲线类型和进展风险。研究证明了该团队研发的程序在评估患者裸背照片时有着较高的灵敏度和阴性预测值,该应用程序具有院外可访、无辐射、接入方便等优点,既可以方便医生做出有效的管理决策,还能帮助患者进行足不出户、可信赖的线上筛查。VAN WEST等[28]同样使用智能手机参与AIS检查,不同的是该研究使用的是Scolioscreen(带有倾斜度计应用和保护外壳的智能手机),以骨科医生使用旋转角度尺测量的躯干旋转角度平均值为标准来检验Scolioscreen的准确性。结果显示Scolioscreen精度高、操作简单,可以作为居家筛查的工具,但该研究样本量较小(AIS 50例),未来应该纳入更大样本量进一步验证该模型的有效性。有趣的是QIAO等[29]、BALG等[30]使用没有保护外壳的智能手机进行研究,灵敏度和精确度反而提高。VAN WEST等[28]、DRISCOLL等[31]、IZATT等[32]却认为带有保护外壳的智能手机在筛查中的表现更优。由于关于该问题的研究过少,无法判定孰是孰非,需在未来持续研究。
2.2 人工智能在脊柱侧弯诊断中的应用 目前影像学识别已经成为脊柱侧弯诊断的重要方法[33],医生不仅仅直观看到脊柱的结构变化,还能测量相关脊柱参数来量化脊柱疾病的严重程度。目前人工智能与脊柱侧弯诊断的联系越来越密切,基于机器学习的卷积神经网络技术广泛应用于图像识别、物体检测、信息判断等领域。该技术可以根据输入的全脊柱X射线片、CT或MRI中自动分析脊柱、测量相关参数、重建三维图像、分型脊柱侧弯并预测进展风险等,呈现智能化、准确化的趋势。另外开源人工智能也可以辅助脊柱侧弯的诊断。
2.2.1 人工智能在X射线片中诊断脊柱侧弯的应用 在筛查中发现的疑似侧弯患者通常建议去医院拍摄全脊柱X射线片,通过Cobb角的测量评估脊柱侧弯的严重程度。自1948年起Cobb角被用于评估脊柱侧弯,之后一直作为确诊脊柱侧弯的金标准。目前Cobb角的测量主要依赖于医护工作者,是一项劳动密集型的工作,其内部一致性较低。应用人工智能技术自动测量Cobb角可以提高诊断精度、简化评估流程、降低主观性、减轻医疗负担等[34]。
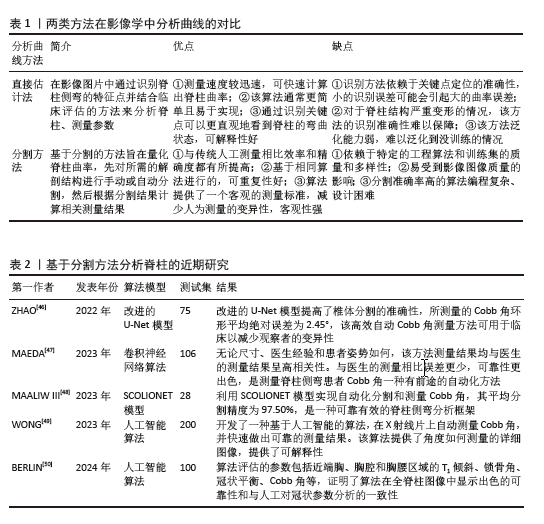
目前人工智能在影像图像中分析脊柱曲线的方法大概分为2类[35]:①直接估计;②分割方法,两种方法的对比解读见表1。
直接估计法是人工智能通过识别图像的关键部位(地标)进而测量脊柱侧弯的各项参数。2017年WU等[36]设计了BoostNet架构来识别地标并测量Cobb角,并且通过嵌入判别功能模块,提高识别脊柱地标的稳健性。但由于椎体结构紧密相连,单视图往往有着对脊柱特征展示不全的缺点,次年WU等[36]团队设计了多视图网络(MVC-Net)架构,进一步提高了所测Cobb角的准确性[35]。WANG等[37]同样基于多视图分析椎体特征识别脊柱地标,但在Wu等[36]的基础上改进了损失函数,并使用外推获得了更准确的Cobb角度,在正视图参数测量的平均绝对误差为8.81°,侧视图平均绝对误差为6.26°。GALBUSERA等[38]根据全脊柱X射线图像建立了卷积神经网络模型,通过识别锥体的单个中心点,并由此中心点画一条对角线来确定椎骨,进而测量Cobb角,结果所有测量结果都与金标准相关。WU等[39]基于深度学习研发了一种多阶段集成网络系统(MSE-Net)来自动评估AIS全脊柱 X射线图像,测量Cobb角和其他相关参数,结果显示测量参数平均绝对误差为1.07°、灵敏度高达97.35%。与GALBUSERA等[38]相比,WU等[39]的研究样本量更大,创新之处是选择4个关键点来定位椎骨,提高终椎选择的准确性。ZOU等[40]提出了一种椎骨定位和倾斜估计网络(VLTENet)的深度学习架构,该模型创新性地结合了深度高分辨率网络(HRNet)和全卷积U-Net架构,还提出了特征融合通道注意力(FFCA)模块,使其关注更多重要的脊柱特征;此外,还设计了联合脊柱损失函数(JS-Loss)来考虑脊柱形状和其他空间约束,使其关注更多重要的区域。RAHMANIAR等[41]基于卷积神经网络设计了自动测量Cobb模型Auto-CA,通过识别17块椎骨上的4个角和中点并定位上下终板来测量Cobb角,Cobb角测量值与真实值的中值差异< 5°,对称平均绝对百分比误差为5.27% 。CHEN等[42]开发软件IB Lab SQUIRREL,可通过3个步骤自动测量全脊柱X射线片上的Cobb角和冠状平衡,Cobb角测量结果为(0.16±0.35)°,组内相关系数为0.97,准确率为88.58%。
上述研究采用的是通过识别椎体进行脊柱侧弯分析的直接估计法,该方法在评估脊柱侧弯图像中有着较高的性能,能减少人力提高效率。近年来通过软件系统不断创新,测量准确率逐步提升,随着系统对椎体的定位、识别等性能的提高,未来有望代替医生进行诊断。但系统识别依赖于高质量的影像学图像,未来仍需持续改进人工智能模型,使其在普通的图像中达到较高的效能。
分割方法是人工智能在影像图像中将识别椎骨、分割脊柱和分析脊柱相结合,然后通过脊柱中线拟合或角度回归网络计算Cobb角,达到诊断的目的。ANITHA等[43-44]在2012年和2014年分别使用active contouring和filtering来识别椎体并分割脊柱关键区域,实现了全自动测量脊柱曲率,但测量值易发生偏差。SARDJONO等[45]使用physics models实现了对脊柱X射线片进行分割并全自动测量曲率,但不够灵活。这些传统的分割方法在分割脊柱的过程中可能会产生偏差,易受到图像质量的影响。分割方法通过人工智能系统实现对脊柱侧弯的精准诊断主要依赖于该系统能够准确对脊柱进行识别、分割、测量。近年来由于人工智能系统的迭代更新,诊断水平从灵活性、准确性、高效性逐步提高,近期研究汇总见表2。ZHAO等[46]使用改进的U-Net模型实现多尺度特征提取,提高分割椎骨的准确性,测量Cobb角的环形平均绝对误差为2.45°,低于手动测量的5°-7°。MAEDA等[47]研发了一种卷积神经网络框架,该框架既可用于脊柱分割和椎骨检测的预处理,还可以自动测量脊柱侧弯患者的Cobb角,不管患者姿势如何,几秒钟就可以完成对脊柱的分割并测量Cobb角,可以在大量的分割任务中减少医生的工作量。MAALIW III[48]利用卷积神经网络设计了SCOLIONET架构,该架构的平均分割精度为97.50%(索伦森-骰子系数)和96.30%(联合交叉),平均误差为2.86°,表明该模型在分割脊柱、测量Cobb角方面很成熟,该架构可以帮助医生快速且一致地评估脊柱情况,提高了脊柱侧弯的诊断效能。WONG等[49]开发了2个卷积神经网络(一个用于分割脊柱、一个用于分割椎体)以级联方式定位椎体并导出它们的边界框倾斜角度以自动测量Cobb角,该研究使用130个数据集用于人工智能模型开发,200个数据集用于验证模型测量Cobb角的准确性,其组内相关系数为 0.92、标准误为0.79°,获得了出色的可靠性。BERLIN等[50]基于卷积神经网络开发了一种人工智能算法,能够检测并分割需要的解剖结构并全自动计算与脊柱相关的基本放射学参数,如T1倾斜、锁骨角、冠状平衡、腰椎代偿值以及Cobb 角。以100 张 X 射线图像为测试集,结果显示算法的准确率和内部一致性高,且平均需要 15 s来分析1个图像,而临床医生分析同一图像要花费3-7 min,证明了人工智能算法可以准确且高效地测量术前全脊柱图像中的冠状参数。
上述研究采用的是分割方法,该方法依赖于计算机算法模型,可以实现识别椎骨、分割脊柱和测量Cobb角相结合,目前,在X射线片图像质量良好的基础上,通过近几年不断创新与更新,分割人工智能在测量Cobb角准确性、应用灵活性、分析全面性等方面都已经得到迅猛发展,基本能完成测量任务。但分割过程中由于不标准脊柱形态及测量姿势可能会产生偏差,所以未来人工智能分割方法的发展方向应该为精准、普适、自动。
2.2.5 人工智能在脊柱侧弯分型中的应用 脊柱侧弯的合理分型有助于临床医生制订合理的治疗方案,并预测患者的进展风险和预后。目前脊柱侧弯的分型包括Lenke[69]、King[70]、PUMC等[71]。人工智能提高了脊柱侧弯的分类速度和准确性,减少了误差,成为临床医生制订治疗决策的得力帮手。THONG等[72]基于堆叠自编码器的机器学习算法对663例患者的X射线片进行三维重建并提取重要信息,将信息进行聚类分析,扩展了Lenke分类并研究其子组的存在,使分类更加细致。
RAHMANIAR等[41]不仅设计了一种基于卷积神经网络的脊柱自动检测模型(Auto-CA),还对纳入的脊柱侧弯患者进行了Lenke分型,平均准确率为92.4%,该方法可以辅助医生在临床上诊断脊柱侧弯、完成脊柱侧弯分型、制订手术计划。TINGSHENG等[73]基于卷积神经网络开发了一个新模型,该模型既可实现Cobb角的精确测量也可实现脊柱侧弯的Lenke分型,并基于分析结果输出相应的手术建议,其在对脊柱侧弯进行Lenke分型上展现出高度准确性和高度可靠性(组内相关系数=0.962)。虽然人工智能可以辅助进行脊柱侧弯的分型,但是目前的分型模式对患者其他的脊柱参数考虑较少,未来有望研究设计更多更精细化的脊柱侧弯分型。
2.2.6 人工智能在预测脊柱侧弯进展风险中的应用 脊柱侧弯的进展风险是由多因素决定的,如年龄、性别、骨龄、脊柱侧弯的严重程度等,全方位多因素地对其分析可以提高预测的准确性[74]。预测脊柱侧弯的进展风险可以早期发现高危人群,并将该人群作为重点关注对象为患者提供个性化的管理服务,具体研究汇总见表3。NAULT等[75]设计了脊柱侧弯患者脊柱曲线进展的预测模型,通过侧弯曲线类型、骨骼成熟度和3D脊柱参数来预测骨骼完全成熟时的Cobb角,研究显示显著的预测因子包括骨骼成熟度、曲线类型、冠状面Cobb角、最大曲率平面角和三维扭转偏移参数,该模型可以帮助医生预测进展风险并指导治疗。深度卷积神经网络在模型学习脊柱侧弯的分型中发挥重要的作用。YAHARA等[76]使用深度卷积神经网络将58例AIS患者的肺、腹部、全脊柱作为学习和预测的数据源,模型展现出69%的准确性,高于外科医生47%的准确性。KIM等[77]同样使用深度卷积神经网络设计了可穿戴惯性传感器的步态分析数据来预测患者侧弯进展风险,使用7个惯性测量单元传感器收集38例AIS患者的步态数据,生成代表关节间协调的髋膝环形图进行步态分析,在通过步态分析来预测曲线进展中实现了92%的准确度,但是该研究的样本量较小,未来的研究应该考虑增大样本量对该模型进行进一步的测试验证。与传统方法相比,人工智能模型展现了更高的预测精度,方便对患者进行个性化管理。然而鉴于数据和模型的复杂性,需要进行更全面、更深入的研究,以确保该模型能安全有效地应用于临床实践。
骨龄可以反映一个人的生长潜力,骨龄越低代表生长潜力越大,导致畸形加剧的可能性就越大,所以骨龄是判断脊柱侧弯进展风险的重要指标,对患有脊柱侧弯的年轻患者尤为重要[78-79]。人工智能可以提高骨龄测量的效率,减少误差,辅助临床医生更好地评估脊柱侧弯的进展风险。早期THODBERG等[80]研究开发了一种机器学习的模型BoneXpert,能够自动根据手部X射线片评估骨龄,该模型通过算法精确定位手和腕部的每块骨头,并据此计算骨龄,该模型的结果与人工测量结果之间的误差范围在0.52-0.68年之间,均方根误差为0.62年。ZHOU等[81]建立并验证了基于卷积神经网络的Tanner-Whitehouse 3(TW3-AI)骨骼年龄评估系统,同样利用手部X射线片评估骨龄,但其结果更优:均方根误差为0.50年,平均图像处理时间为(1.5±0.2) s。与前面2个研究不同的是XIE等[82]基于深度学习直接在双平面全长脊柱 EOS图像中自动评估Risser征和脊柱生长潜力,使用了3 383个案例用于算法的训练、440个案例用于临床验证,结果显示人工智能自动测量的准确率更高,测量时间更短,是一种值得研究并投入临床使用的方法。

| [1] PÉREZ-MACHADO G, BERENGUER-PASCUAL E, BOVEA-MARCO M, et al. From genetics to epigenetics to unravel the etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Bone. 2020; 140:115563. [2] DE KLEUVER M, FARAJ SS, HAANSTRA TM, et al. The Scoliosis Research Society adult spinal deformity standard outcome set. Spine Deform. 2021;9(5):1211-1221. [3] ZHANG H, HUANG C, WANG D, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Scoliosis: Current Applications and Future Directions. J Clin Med. 2023;12(23):7382. [4] NEGRINI S, YASKINA M, DONZELLI S, et al. Puberty changes the natural history of idiopathic scoliosis: three prediction models for future radiographic curve severity from 1563 consecutive patients. Eur Spine J. 2024;33(10):3767-3775. [5] DE MENDONÇA RGM, SAWYER JR, KELLY DM. Complications after surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47(2):395-403. [6] DUNN J, HENRIKSON NB, MORRISON CC, et al. Screening for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA. 2018;319(2):173-187. [7] BUNNELL WP. The natural history of idiopathic scoliosis before skeletal maturity. Spine. 1986;11(8):773-776. [8] 王海星, 田雪晴, 游茂, 等. 人工智能在医疗领域应用现状、问题及建议[J]. 卫生软科学,2018,32(5):3-5+9. [9] 张婕. 人工智能在医学中的应用现状与展望[J]. 数字通信世界,2022(12):172-174. [10] CHEN W, KHODAEI M, REFORMAT M, et al. Validity of a fast automated 3d spine reconstruction measurements for biplanar radiographs: SOSORT 2024 award winner. Eur Spine J. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08375-7. [11] CHOI RY, COYNER AS, KALPATHY-CRAMER J, et al. Introduction to machine learning, neural networks, and deep learning. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2020;9(2):14. [12] ALTAF F, DRINKWATER J, PHAN K, et al. Systematic review of school scoliosis screening. Spine Deform. 2017;5(5): 303-309. [13] MONTGOMERY F, WILLNER S. Screening for idiopathic scoliosis: Comparison of 90 cases shows less surgery by early diagnosis. Acta Orthop Scand. 1993;64(4):456-458. [14] CUNDY TP, ANTONIOU G, SUTHERLAND LM, et al. Serum titanium, niobium, and aluminum levels after instrumented spinal arthrodesis in children. Spine. 2013;38(7): 564-570. [15] ZHANG T, ZHU C, ZHAO Y, et al. Deep learning model to classify and monitor idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents using a single smartphone photograph. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(8):e2330617-e. [16] JAREMKO J, DELORME S, DANSEREAU J, et al. Use of neural networks to correlate spine and rib deformity in scoliosis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2000; 3(3):203-213. [17] RAMIREZ L, DURDLE NG, RASO VJ, et al. A support vector machines classifier to assess the severity of idiopathic scoliosis from surface topography. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2006;10(1):84-91. [18] YANG J, ZHANG K, FAN H, et al. Development and validation of deep learning algorithms for scoliosis screening using back images. Commun Biol. 2019;2(1):390. [19] WATANABE K, AOKI Y, MATSUMOTO M. An application of artificial intelligence to diagnostic imaging of spine disease: estimating spinal alignment from Moiré images. Neurospine. 2019;16(4):697. [20] NEGRINI F, CINA A, FERRARIO I, et al. Developing a new tool for scoliosis screening in a tertiary specialistic setting using artificial intelligence: a retrospective study on 10,813 patients: 2023 SOSORT award winner. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(11): 3836-3845. [21] PELC M, VILIMKOVA KAHANKOVA R, BLASZCZYSZYN M, et al. Initial study on an expert system for spine diseases screening using inertial measurement unit. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):10440. [22] 郝子强, 唐颖, 田芳, 等. 轻量化的多尺度注意力脊柱侧弯筛查方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2025,61(3):286-294. [23] 赵凯宇, 李焕国, 宣伟玲, 等 健康体检人群中胸部X线检查结果分析[J]. 医疗卫生装备,2014,35(9):84-86. [24] XIE L, ZHANG Q, HE D, et al. Automatically measuring the Cobb angle and screening for scoliosis on chest radiograph with a novel artificial intelligence method. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(11):7880. [25] ASHWORTH M, HANCOCK JA, ASHWORTH L, et al. Scoliosis screening an approach to cost/benefit analysis. Spine. 1988;13(10): 1187-1188. [26] LEE W, SHIN K, LEE J, et al. Diagnosis of scoliosis using chest radiographs with a semi-supervised generative adversarial network. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2022;83(6): 1298. [27] LEE JS, SHIN K, RYU SM, et al. Screening of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using generative adversarial network (GAN) inversion method in chest radiographs. PLoS One. 2023;18(5):e0285489. [28] VAN WEST H, HERFKENS J, RUTGES J, et al. The smartphone as a tool to screen for scoliosis, applicable by everyone. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(4):990-995. [29] QIAO J, XU L, ZHU Z, et al. Inter-and intraobserver reliability assessment of the axial trunk rotation: manual versus smartphone-aided measurement tools. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:1-4. [30] BALG F, JUTEAU M, THEORET C, et al. Validity and reliability of the iPhone to measure rib hump in scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(8):774-779. [31] DRISCOLL M, FORTIER-TOUGAS C, LABELLE H, et al. Evaluation of an apparatus to be combined with a smartphone for the early detection of spinal deformities. Scoliosis. 2014;9:1-5. [32] IZATT MT, BATEMAN GR, ADAM CJ. Evaluation of the iPhone with an acrylic sleeve versus the Scoliometer for rib hump measurement in scoliosis. Scoliosis. 2012; 7:1-8. [33] WANG L, XIE C, LIN Y, et al. Evaluation and comparison of accurate automated spinal curvature estimation algorithms with spinal anterior-posterior X-Ray images: The AASCE2019 challenge. Med Image Anal. 2021;72:102115. [34] KARPIEL I, ZIĘBIŃSKI A, KLUSZCZYŃSKI M, et al. A survey of methods and technologies used for diagnosis of scoliosis. Sensors (Basel). 2021;21(24):10. [35] WU H, BAILEY C, RASOULINEJAD P, et al. Automated comprehensive adolescent idiopathic scoliosis assessment using MVC-Net. Med Image Anal. 2018;48:1-11. [36] WU H, BAILEY C, RASOULINEJAD P, et al. Automatic landmark estimation for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis assessment using BoostNet; proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention− MICCAI 2017: 20th International Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, September 11-13, 2017, Proceedings, Part I 20, F, 2017. Springer. [37] WANG L, XU Q, LEUNG S, et al. Accurate automated Cobb angles estimation using multi-view extrapolation net. Med Image Anal. 2019;58:101542. [38] GALBUSERA F, NIEMEYER F, WILKE HJ, et al. Fully automated radiological analysis of spinal disorders and deformities: a deep learning approach. Eur Spine J. 2019;28:951-960. [39] WU C, MENG G, LIAN J, et al. A multi-stage ensemble network system to diagnose adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Radiol. 2022;32(9):5880-5889. [40] ZOU L, GUO L, ZHANG R, et al. VLTENet: a deep-learning-based vertebra localization and tilt estimation network for automatic Cobb angle estimation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2023;27(6):3002-3013. [41] RAHMANIAR W, SUZUKI K, LIN TL. Auto-CA: automated Cobb angle measurement based on vertebrae detection for assessment of spinal curvature deformity. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2024;71(2):640-649. [42] CHEN K, LEPENIK C, HUMMER A, et al. Fully automated measurement of Cobb angles in coronal plane spine radiographs. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024;32:S78-S79. [43] ANITHA H, KARUNAKAR A, DINESH K. Automatic extraction of vertebral endplates from scoliotic radiographs using customized filter. Biomed Eng Lett. 2014;4:158-165. [44] PRABHU G. Automatic quantification of spinal curvature in scoliotic radiograph using image processing. J Med Syst. 2012; 36(3):1943-1951. [45] SARDJONO TA, WILKINSON MH, VELDHUIZEN AG, et al. Automatic Cobb angle determination from radiographic images. Spine. 2013;38(20):E1256-E1262. [46] ZHAO Y, ZHANG J, LI H, et al. Automatic Cobb angle measurement method based on vertebra segmentation by deep learning. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022;60(8):2257-2269. [47] MAEDA Y, NAGURA T, NAKAMURA M, et al. Automatic measurement of the Cobb angle for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using convolutional neural network. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):14576. [48] MAALIW III RR. SCOLIONET: An Automated Scoliosis Cobb Angle Quantification Using Enhanced X-ray Images and Deep Learning Models. J Imaging. 2023;9(12):265. [49] WONG JC, REFORMAT MZ, PARENT EC, et al. Validation of an artificial intelligence-based method to automate Cobb angle measurement on spinal radiographs of children with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2023;54(4):535. [50] BERLIN C, ADOMEIT S, GROVER P, et al. Novel AI-based algorithm for the automated computation of coronal parameters in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients: a validation study on 100 preoperative full spine X-rays. Global Spine J. 2024;14(6):1728-1737. [51] JAKUBICEK R, CHMELIK J, OUREDNICEK P, et al. Deep-learning-based fully automatic spine centerline detection in CT data; proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), F, 2019 [C]. IEEE. [52] QADRI SF, SHEN L, AHMAD M, et al. OP-convNet: A Patch Classification-Based Framework for CT Vertebrae Segmentation. IEEE Access. 2021;9:158227-158240. [53] LI L, ZHANG T, LIN F, et al. Automated 3D Cobb Angle Measurement Using U-Net in CT Images of Preoperative Scoliosis Patients. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025;38(1):309-317. [54] ANTICO M, LITTLE JP, JENNINGS H, et al. Deep Learning-based automatic segmentation for reconstructing vertebral anatomy of Healthy Adolescents and Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS) Using MRI Data. IEEE Access. 2021;9:86811-86823. [55] VAN DER GRAAF JW, VAN HOOFF ML, VAN GINNEKEN B, et al. Development and validation of AI-based automatic measurement of coronal Cobb angles in degenerative scoliosis using sagittal lumbar MRI. Eur Radiol. 2024;34(9):5748-5757. [56] AUBERT B, VAZQUEZ C, CRESSON T, et al. Automatic spine and pelvis detection in frontal X-rays using deep neural networks for patch displacement learning; proceedings of the 2016 ieee 13th international symposium on biomedical imaging (isbi), F, 2016 [C]. IEEE. [57] BAKHOUS C, AUBERT B, VAZQUEZ C, et al. Automatic pedicles detection using convolutional neural network in a 3D spine reconstruction from biplanar radiographs; proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2018: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, F, 2018 [C]. SPIE. [58] AUBERT B, VAZQUEZ C, CRESSON T, et al. Toward automated 3D spine reconstruction from biplanar radiographs using CNN for statistical spine model fitting. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019;38(12):2796-2806. [59] JIANG W, MEI F, XIE Q. Novel automated spinal ultrasound segmentation approach for scoliosis visualization. Front Physiol. 2022;13:1051808. [60] HUANG Y, JIAO J, YU J, et al. Si-MSPDNet: A multiscale Siamese network with parallel partial decoders for the 3-D measurement of spines in 3D ultrasonic images. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2023;108:102262. [61] RAN QY, MIAO J, ZHOU SP, et al. Automatic 3-D spine curve measurement in freehand ultrasound via structure-aware reinforcement learning spinous process localization. Ultrasonics. 2023;132:107012. [62] DAESCHLER SC, BOURGET MH, DERAKHSHAN D, et al. Rapid, automated nerve histomorphometry through open-source artificial intelligence. Sci Rep. 2022; 12(1):5975. [63] HENTSCHEL S, KOBS K, HOTHO A. CLIP knows image aesthetics. Front Artif Intell. 2022;5:976235. [64] TAJDARI M, MAQSOOD A, LI H, et al. Artificial intelligence data-driven 3D model for AIS. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2021;280:141-145. [65] FABIJAN A, POLIS B, FABIJAN R, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Scoliosis Classification: An Investigation of Language-Based Models. J Pers Med. 2023;13(12): 1695. [66] FABIJAN A, ZAWADZKA-FABIJAN A, FABIJAN R, et al. Assessing the Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Models in Scoliosis Classification and Suggested Therapeutic Approaches. J Clin Med. 2024;13(14):4013. [67] FABIJAN A, ZAWADZKA-FABIJAN A, FABIJAN R, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging: Analyzing the Performance of ChatGPT and Microsoft Bing in Scoliosis Detection and Cobb Angle Assessment. Diagnostics. 2024;14(7):773. [68] CHALHOUB R, MOUAWAD A, AOUN M, et al. Will ChatGPT be able to replace a spine surgeon in the clinical setting?. World Neurosurg. 2024;185:e648-e652. [69] LENKE LG, BETZ RR, HARMS J, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83(8):1169-1181. [70] HOSSEINPOUR-FEIZI H, SOLEIMANPOUR J, SALES JG, et al. Lenke and King classification systems for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: interobserver agreement and postoperative results. Int J Gen Med. 2011:4:821-825. [71] ZHUANG Q, QIU G, LI Q, et al. Modified PUMC classification for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J. 2019;19(9): 1518-1528. [72] THONG W, PARENT S, WU J, et al. Three-dimensional morphology study of surgical adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patient from encoded geometric models. Eur Spine J. 2016;25:3104-3113. [73] TINGSHENG L, CHUNSHAN L, SHUDAN Y, et al. Validation of artificial intelligence in the classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and the compairment to clinical manual handling. Orthop Surg. 2024;16(8): 2040-2051. [74] MANZETTI M, RUFFILLI A, BARILE F, et al. Is there a skeletal age index that can predict accurate curve progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? A systematic review. Pediatr Radiol. 2024;54(2):299-315. [75] NAULT ML, BEAUSÉJOUR M, ROY-BEAUDRY M, et al. A predictive model of progression for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis based on 3D spine parameters at first visit. Spine. 2020;45(9):605-611. [76] YAHARA Y, TAMURA M, SEKI S, et al. A deep convolutional neural network to predict the curve progression of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):610. [77] KIM YG, KIM S, PARK JH, et al. Explainable Deep-Learning-Based Gait Analysis of Hip–Knee Cyclogram for the Prediction of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Progression. Sensors. 2024;24(14):4504. [78] SMITH JS, SHAFFREY CI, BESS S, et al. Recent and emerging advances in spinal deformity. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S70-S85. [79] SHEEHAN DD, GRAYHACK J. Pediatric scoliosis and kyphosis: an overview of diagnosis, management, and surgical treatment. Pediatr Ann. 2017;46(12): e472-e480. [80] THODBERG HH, KREIBORG S, JUUL A, et al. The BoneXpert method for automated determination of skeletal maturity. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2008;28(1):52-66. [81] ZHOU XL, WANG EG, LIN Q, et al. Diagnostic performance of convolutional neural network-based Tanner-Whitehouse 3 bone age assessment system. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020;10(3):657. [82] XIE LZ, DOU XY, GE TH, et al. Deep learning–based identification of spine growth potential on EOS radiographs. Eur Radiol. 2024;34(5):2849-2860. [83] 吴南, 仉建国, 朱源棚, 等. 人工智能在脊柱畸形诊疗中的应用[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版),2023,61(3):14-20. |
| [1] | 刘可新, 郝凯敏, 庄文越, 李正祎. 自噬相关基因在肺纤维化模型中的表达:生物信息学分析及实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1129-1138. |
| [2] | 张 迪, 赵 君, 马广悦, 孙 晖, 蒋 蓉. 基于高通量测序技术分析慢性社会挫败应激小鼠抑郁样行为的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [3] | 胡 静, 朱 伶, 谢 娟, 孔德营, 刘豆豆. 自噬影响组蛋白修饰标记H3K4me3调控小鼠早期胚胎发育[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1147-1155. |
| [4] | 李郝静, 王 新, 宋成林, 张胜男, 陈云昕. 上斜方肌处体外冲击波与运动控制训练治疗慢性非特异性颈痛[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [5] | 刘 煜, 雷森林, 周锦涛, 刘 辉, 李先辉. 有氧和抗阻运动改善肥胖相关认知障碍的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [6] | 陶云飞, 彭 莉. 血流限制在急性抗阻运动中对内皮功能相关炎性因子的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1184-1195. |
| [7] | 王正业, 刘万林, 赵振群. miRNA在激素诱导股骨头坏死机制中的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [8] | 部洋洋, 宁新丽, 赵 琛. 关节腔注射治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎:不同药物与多种联合治疗方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [9] | 文 凡, 向 阳, 朱 欢, 庹艳芳, 李 锋. 运动干预改善2型糖尿病患者的微血管功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [10] | 傅振燚, 李俊豪, 张雅婷, 何昀锴, 刘俊妤, 魏云昊, 刘佳鑫. 施万细胞促进外周神经再生:回顾与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1236-1246. |
| [11] | 刘新月, 李春年, 李一卓, 徐世芳. 口腔牙槽骨缺损的再生修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [12] | 郑 银, 吴振桦, 张 成, 阮可馨, 刚骁琳, 汲 泓. 免疫吸附治疗类风湿关节炎的安全性和有效性:网状Meta分析和系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [13] | 陈 强, 伍文娟, 江舒华, 黄 达. 体育锻炼改善烧伤患者身体功能的系统评价与Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1269-1281. |
| [14] | 冷晓轩, 赵玉欣, 刘西花. 不同神经调控刺激方式改善帕金森病患者非运动症状的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [15] | 温小龙, 翁锡全, 冯 瑶, 曹文燕, 刘玉倩, 王海涛, . 炎症对2型糖尿病患者血清抗菌多肽及铁代谢相关参数影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
人工智能是人类智能的延伸,通过模拟人类的思维方式和思考过程,做出与人类智能相似的行为反应。人工智能作为一项新兴的技术应用于医学的各个领域如:医学图像识别、疾病辅助诊断、健康管理、疾病预测、药物研发等,帮助医疗人员开展更准确更科学更高效的诊疗分析[8-9]。目前,人工智能在脊柱侧弯的应用展示出很大的潜力,机器学习和深度学习是人工智能应用于脊柱侧弯诊治的两项技术[3],其关系如图1所示。机器学习是人工智能的高级分支,通过使用算法和数据来模拟人类学习。医学影像中最常见的机器学习技术是卷积神经网络,它可以有效地完成影像分析、参数测量、三维重建等[10]。深度学习旨在模拟人脑的神经网络和分析处理能力,已经成为机器学习和神经网络研究的新方向[11],它可以提高脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断效率,帮助医生完成更准确的判断。
通过临床观察及文献回顾,此次研究发现人工智能技术,尤其机器学习和深度学习,在脊柱侧弯筛查与诊断中的应用不断增加。这些技术的自动化处理显著减轻了临床医生的工作负担,智能化算法大幅缩短了测量时间,持续优化的模型显著提升了测量的精确度。人工智能技术在脊柱侧弯的早期发现、病情严重程度评估以及进展风险预测方面展现出显著优势,未来有望在临床实践中为医生提供有力支持。此文综合分析了相关研究文献,从多角度概述了人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查与诊断领域的最新进展,并对未来的发展方向进行了展望,旨在为临床完善和应用提供参考。人工智能辅助脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断的工作流程见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024-08-16进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 2012年1月至2024年8月,同时纳入少量的远期相关文献进行综述。
1.1.3 检索数据库 检索中国知网、万方数据库、PubMed、IEEE Xplore数据库收录的相关文章。
1.1.4 检索文献类型 研究性论文、综述和荟萃分析。
1.1.5 检索词 英文数据库检索词为“scoliosis,artificial intelligence,machine learning,screen,diagnosis”等,中文数据库检索词为“脊柱侧弯、人工智能、机器学习、筛查、诊断”等。运用布尔逻辑运算符“OR”和“AND”分别将检索词连接进行检索。
1.1.6 检索策略 以中国知网、万方数据库、IEEE Xplore、PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图3。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步得到文献 1 623 篇,其中中文文献 137 篇、英文文献1 486 篇。
1.2 纳入与排除标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①纳入文献聚焦于人工智能合理高效地应用于脊柱侧弯筛查、诊断领域,内容覆盖模型简述、应用领域、成果效果、创新优势等;②研究内容前沿、过程清晰、论点论据可靠、结果客观的文献;③同一领域的文献选择近期或权威杂志发表的文献;④研究成果有推广应用的潜力且对未来进一步研究具有指导意义的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与此次研究主题关联性差且不具有创新性和临床意义的文献;②实验设计不严谨、数据质量低、可信度差的文献;③无法获取全文的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 共检索文献 1 623 篇,根据纳入及排除标准筛选后,排除重复性研究及内容不相关的文献,最终纳入83篇符合标准的文献进行综述,见图4。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 目前已有的综述主要分析了人工智能在脊柱侧弯诊治中的应用[83],然而在筛查和诊断中应用的介绍并不详细,特别是缺少应用于筛查领域的文章。此文不仅详细回顾了人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断领域的最新应用进展,还详细介绍了各类人工智能模型的功效、创新和意义。
3.3 综述的局限性 由于近年来该领域的中文文献数量较少,且质量不高,所以纳入分析的主要为英文文献,对国内近年来的现状和发展可能存在误差。此文纳入的文献大多数以特发性脊柱侧弯为研究对象,对于人工智能在其他类型脊柱侧弯应用的研究文献较少且没有确切的证据证明其疗效,所以文中没有多加赘述。此外,此文在展望未来时,未能充分考虑到大范围临床应用的潜在伦理问题。未来的研究应该纳入伦理问题并结合更广泛的文献分析,更全面地展示人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用进展。
3.4 综述的重要意义 此文首次单独综述了人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用,通过严格的筛选纳入了相关高质量文献,对目前该领域的研究进展、发展方向、优势和创新等进行总结。这对于推动该领域的临床应用和技术进步具有重要的指导意义,同时也可以让研究者们短时间了解该领域的研究进展,发现研究新思路。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 对于人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断领域的未来发展,提出以下几点建议:①伦理与法规:制订相关的法律法规,确保人工智能在医学领域应用过程中的隐私保护和数据安全。建立健全审查和监督机制,确保其安全性和有效性。②技术的精进与创新:鼓励研究者对现有的人工智能模型进行优化,改善模型的稳定性不足和泛化能力有限问题,提高脊柱侧弯筛查诊断的效率和准确性,并进一步探索新技术。③多学科交叉融合:工程师在设计模型时应该结合医生临床经验切实解决临床问题,医生要做多中心的临床验证帮助工程师优化模型,共同努力将人工智能技术有机应用到脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中去,促进医工结合的发展。④以人类决策为中心:人工智能作为辅助工具并不能代替医生成为最终的医疗决策者,要保证医生在医疗过程中的主导权,人工智能不能代替人类智能。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
文题释义:
脊柱侧弯:是一种常见的脊柱疾病,主要表现为脊柱三维方向的畸形,使背部呈现C形或S形曲线,其发病原因复杂,各类型脊柱侧弯的病因各异,并随年龄增加症状逐渐加剧,严重者影响呼吸、心脏功能,甚至出现脊髓压迫及瘫痪现象。人工智能:一个以计算机科学为基础,通过模拟人类的思维方式和思考过程,做出与人类智能相似的行为反应,目前正应用于医学的各个领域。#br# #br#
本文综述了人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中的应用并展望未来的发展,对目前该领域的研究进展、发展方向、优势和创新等进行总结。内容尽可能全面地覆盖了人工智能在脊柱侧弯的初期筛查、胸片筛查、智能手机筛查、X射线片诊断、CT和MRI诊断、三维图像重建、开源人工智能诊断、辅助分型、预测进展风险领域的应用。这对于促进脊柱侧弯领域的临床应用和技术进步具有显著的指导作用,并为研究者们提供了一个快速了解该领域进展和探索新研究方向的窗口。#br#
回顾过往的研究,学者们主要分析了人工智能在脊柱侧弯诊治中的应用,在筛查和诊断中应用介绍并不详细,而本文不仅详细介绍了人工智能在脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断领域的最新应用进展,还详细介绍了各类人工智能模型的功效并深入探讨了不同人工智能模型的创新性和意义。#br# 值得注意的是,以往研究脊柱侧弯问题多是在医学学科框架下开展研究的,而本文多学科交叉融合提出工程师在设计模型时应该结合医生临床经验切实解决临床问题,医生要做多中心的临床验证帮助工程师优化模型,共同努力将人工智能技术有机应用到脊柱侧弯筛查和诊断中去,促进医工结合的发展。#br# 综上所述,本文创新性地综述了人工智能在脊柱侧弯领域的应用潜力,并展望了未来的发展方向。期望未来人工智能技术能够合理且高效地应用于脊柱侧弯领域,从而提升医疗服务质量,惠及广大患者。 #br# #br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||