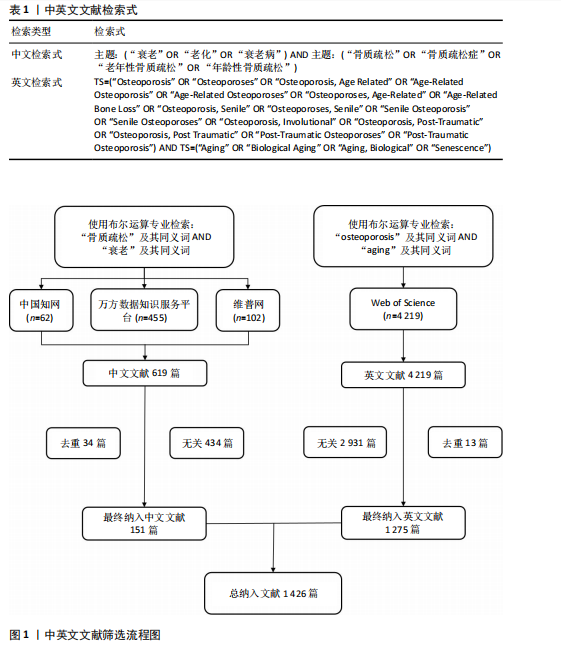
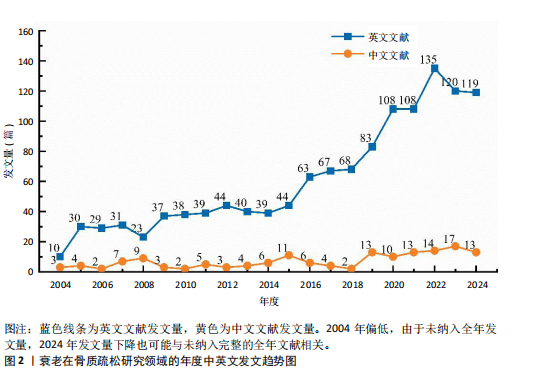
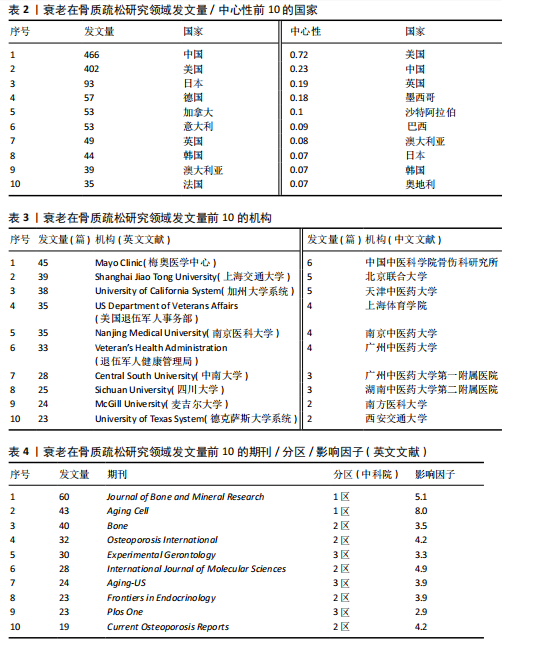
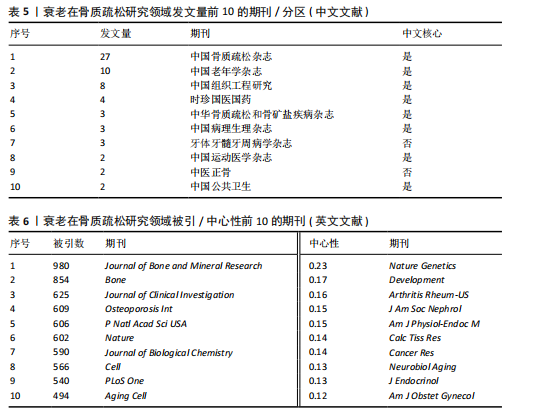
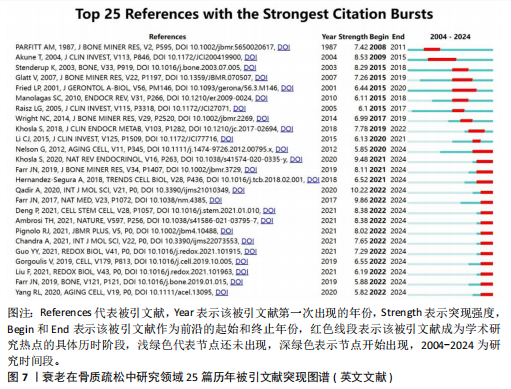
[1] HUO R, WEI C, HUANG X, et al. Mortality associated with osteoporosis and pathological fractures in the United States (1999-2020): a multiple-cause-of-death study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):568.
[2] XIAO PL, CUI AY, HSU CJ, et al. Global, regional prevalence, and risk factors of osteoporosis according to the World Health Organization diagnostic criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(10):2137-2153.
[3] LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO MA, PARTRIDGE L, et al. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013; 153(6):1194-1217.
[4] KENNEDY BK, BERGER SL, BRUNET A, et al. Geroscience: linking aging to chronic disease. Cell. 2014;159(4):709-713.
[5] DOBSON PF, DENNIS EP, HIPPS D, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction impairs osteogenesis, increases osteoclast activity, and accelerates age related bone loss. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):11643.
[6] MANSOUR A, MEZOUR MA, BADRAN Z, et al. Extracellular Matrices for Bone Regeneration: A Literature Review. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(23-24):1436-1451.
[7] SINGH L, BRENNAN TA, RUSSELL E, et al. Aging alters bone-fat reciprocity by shifting in vivo mesenchymal precursor cell fate towards an adipogenic lineage. Bone. 2016; 85:29-36.
[8] MA Y, QI M, AN Y, et al. Autophagy controls mesenchymal stem cell properties and senescence during bone aging. Aging Cell. 2018;17(1):e12709.
[9] KIRKLAND JL, TCHKONIA T, ZHU Y, et al. The Clinical Potential of Senolytic Drugs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(10):2297-2301.
[10] HAMBRIGHT WS, MU X, GAO X, et al. The Senolytic Drug Fisetin Attenuates Bone Degeneration in the Zmpste24-/- Progeria Mouse Model. J Osteoporos. 2023;2023:5572754.
[11] KOKOL P, BLAŽUN VOŠNER H, ZAVRŠNIK J. Application of bibliometrics in medicine: a historical bibliometrics analysis. Health Info Libr J. 2021;38(2):125-138.
[12] 牛奔,朱晓倩,杨辰,等.基于CiteSpace的国内外医疗大语言模型研究热点演进及趋势分析[J/OL].中国全科医学,1-9[2025-02-10].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/13.1222.R.20240912.1606.003.html.
[13] 宋浩然,张玉强,谷娜,等.基于Citespace对人工智能在骨创伤研究的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(3):493-502.
[14] 杨泽雨,支亮,王佳,等.高频重复经颅磁刺激研究热点宏观角度的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2026,30(5):1320-1330.
[15] DE SOLLA PRICE DJ. Little Science, Big Science and beyond. New York: Columbia University Press,1963.
[16] JIA HF, LI HZ, RONG YF, et al. Knowledge Mapping of Macrophages in Osteoporosis: A Bibliometric Analysis (1999-2023). Orthop Surg. 2024;16(10):2326-2343.
[17] LÓPEZ-MUÑOZ F, WEINREB RN, MOGHIMI S, et al. A Bibliometric and Mapping Analysis of Glaucoma Research between 1900 and 2019. Ophthalmol Glaucoma. 2022;5(1):16-25.
[18] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(5):593-608.
[19] KAUR J, FARR JN. Cellular senescence in age-related disorders. Transl Res. 2020;226:96-104.
[20] MANOLAGAS SC. From estrogen-centric to aging and oxidative stress: a revised perspective of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2010;31(3):266-300.
[21] ALMEIDA M, O’BRIEN CA. Basic biology of skeletal aging: role of stress response pathways. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013;68(10):1197-1208.
[22] WANG T, HUANG S, HE C. Senescent cells: A therapeutic target for osteoporosis. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(12):e13323.
[23] MANOLAGAS SC, PARFITT AM. What old means to bone. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010;21(6):369-374.
[24] LI Q, CHENG JC, JIANG Q, et al. Role of sirtuins in bone biology: Potential implications for novel therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Aging Cell. 2021;20(2): e13301.
[25] CHEN C. Science Mapping: A Systematic Review of the Literature. JDIS. 2017;2(2):1-40.
[26] 彭皓,陈奇刚,申震.H型血管在不同骨骼疾病中研究热点的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2026,30(3):760-769.
[27] ZHU Y, TCHKONIA T, PIRTSKHALAVA T, et al. The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: from transcriptome to senolytic drugs. Aging Cell. 2015;14(4):644-658.
[28] FARR JN, XU M, WEIVODA MM, et al. Targeting cellular senescence prevents age-related bone loss in mice. Nat Med. 2017;23(9):1072-1079.
[29] 裴凌鹏,董福慧,惠伯棣.D-半乳糖致衰老作用对大鼠骨质的影响[J].中医正骨, 2007,19(3):1-3.
[30] 裴凌鹏,董福慧,惠伯棣.虾青素对D-半乳糖老龄大鼠骨质影响[J].中国公共卫生,2007,23(3):297-299.
[31] 裴凌鹏,惠伯棣,董福慧.角黄素对D-半乳糖致衰老大鼠抗氧化功能影响[J].中国公共卫生,2007,23(4):453-454.
[32] 裴凌鹏,惠伯棣,王东晖,等.反式白藜芦醇对D-半乳糖致老大鼠骨质影响研究[J].北京中医药大学学报,2007,30(5):317-322.
[33] MATSUSHITA M, TSUBOYAMA T, KASAI R, et al. Age-related changes in bone mass in the senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM). SAM-R/3 and SAM-P/6 as new murine models for senile osteoporosis. Am J Pathol. 1986;125(2):276-283.
[34] JILKA RL, WEINSTEIN RS, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Linkage of decreased bone mass with impaired osteoblastogenesis in a murine model of accelerated senescence. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(7):1732-1740.
[35] STENDERUP K, JUSTESEN J, CLAUSEN C, et al. Aging is associated with decreased maximal life span and accelerated senescence of bone marrow stromal cells. Bone. 2003;33(6):919-926.
[36] KHOSLA S, FARR JN, TCHKONIA T, et al. The role of cellular senescence in ageing and endocrine disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(5):263-275.
[37] KHOSLA S. Odanacatib: location and timing are everything. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(3):506-508.
[38] KHOSLA S, FARR JN, KIRKLAND JL. Inhibiting Cellular Senescence: A New Therapeutic Paradigm for Age-Related Osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(4): 1282-1290.
[39] QADIR A, LIANG S, WU Z, et al. Senile Osteoporosis: The Involvement of Differentiation and Senescence of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(1):349.
[40] DI MICCO R, KRIZHANOVSKY V, BAKER D, et al. Cellular senescence in ageing: from mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2):75-95.
[41] FARR JN, FRASER DG, WANG H, et al. Identification of Senescent Cells in the Bone Microenvironment. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(11):1920-1929.
[42] COPPÉ JP, DESPREZ PY, KRTOLICA A, et al. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: the dark side of tumor suppression. Annu Rev Pathol. 2010;5:99-118.
[43] DEMARIA M, OHTANI N, YOUSSEF SA, et al. An essential role for senescent cells in optimal wound healing through secretion of PDGF-AA. Dev Cell. 2014;31(6):722-733.
[44] TAKASUGI M, YOSHIDA Y, HARA E, et al. The role of cellular senescence and SASP in tumour microenvironment. FEBS J. 2023; 290(5):1348-1361.
[45] KIRKLAND JL, TCHKONIA T. Senolytic drugs: from discovery to translation. J Intern Med. 2020;288(5):518-536.
[46] WANG Y, CHE L, CHEN X, et al. Repurpose dasatinib and quercetin: Targeting senescent cells ameliorates postmenopausal osteoporosis and rejuvenates bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2023;25:13-28.
[47] CHAN WL, BUCHER CH, GOLDES J, et al. Targeting TGF-β signaling, oxidative stress, and cellular senescence rescues osteoporosis in gerodermia osteodysplastica. Aging Cell. 2024;23(12): e14322.
[48] SONAR Y. Therapeutic potential of boosting NAD+ levels in aging and age-related bone loss. Queensland University of Technology, 2023.
[49] 吴钰坤,韩杰,温帅波.骨折愈合过程中Runx2基因的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2274-2279.
[50] UNGURIANU A, ZANFIRESCU A, MARGINĂ D. Sirtuins, resveratrol and the intertwining cellular pathways connecting them. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;88:101936.
[51] FALVINO A, CARIATI I, BONANNI R, et al. Cellular senescence as a key factor in osteoporosis:the role of SIRT1. Int J Bone Frag. 2023; 3(3):100-104.
[52] KANG X, CHEN L, YANG S, et al. Zuogui Wan slowed senescence of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;294:115323.
[53] ZENG J, XIAO Q, LI X, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products aggravate age‑related bone loss by increasing sclerostin expression in osteocytes via ROS‑dependent downregulation of Sirt1. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(6):108.
[54] WANG Y, XIE F, HE Z, et al. Senescence-Targeted and NAD+-Dependent SIRT1-Activated Nanoplatform to Counteract Stem Cell Senescence for Promoting Aged Bone Regeneration. Small. 2024;20(12): e2304433.
[55] WU W, FU J, GU Y, et al. JAK2/STAT3 regulates estrogen-related senescence of bone marrow stem cells. J Endocrinol. 2020;245(1):141-153.
[56] ZHANG Y, YU X, ZHOU C, et al. Targeting cellular senescence in senile osteoporosis: therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1288993.
[57] 伍子贤,方志超,林锋,等. 龟板提取物抑制细胞衰老缓解SOP小鼠骨量丢失及海马退变[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2024,30(3):318-326.
[58] 黄勇,董克芳,王凡,等.三种补肾方含药血清对衰老骨髓间充质干细胞中COLⅠ和ALP的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2022,42(7):1082-1086.
[59] 张天驰,李沐哲,牛园园,等.温肾通络止痛方抑制巨噬细胞衰老改善BMSC成骨分化和老年性骨质疏松模型小鼠骨丢失的研究[J].南京中医药大学学报,2024, 40(3):249-260.
[60] 钟培瑞,何晓艳,廖瑛,等.P53/P21通路在电针抑制骨质疏松大鼠模型成骨细胞衰老中的机制[J].实用医学杂志,2023, 39(2):192-197.
|