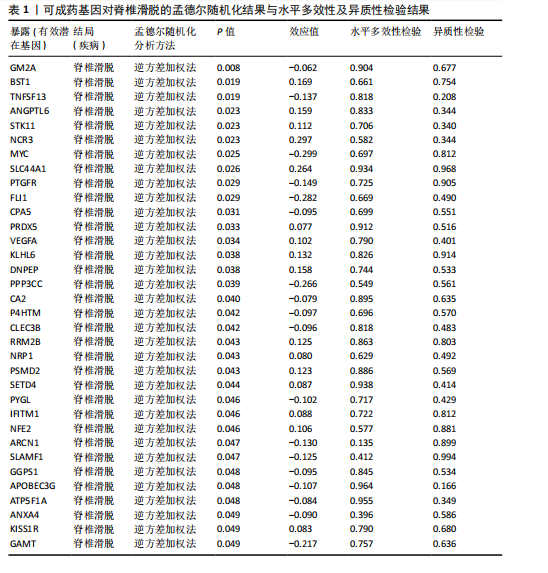
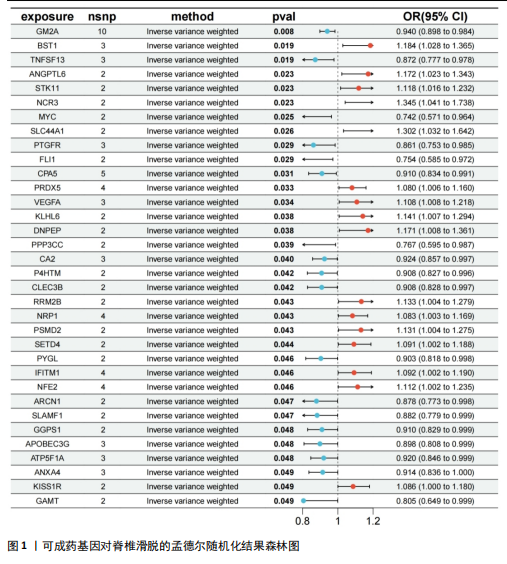
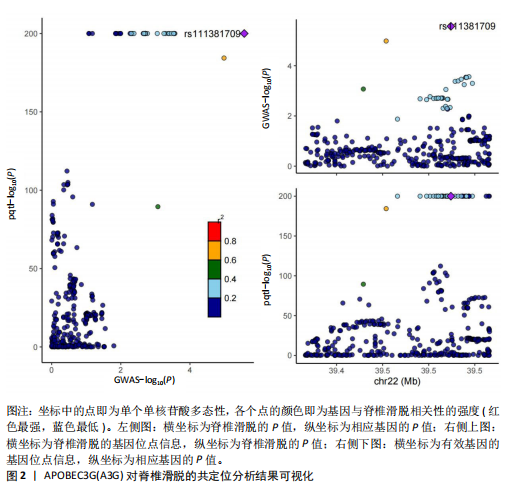
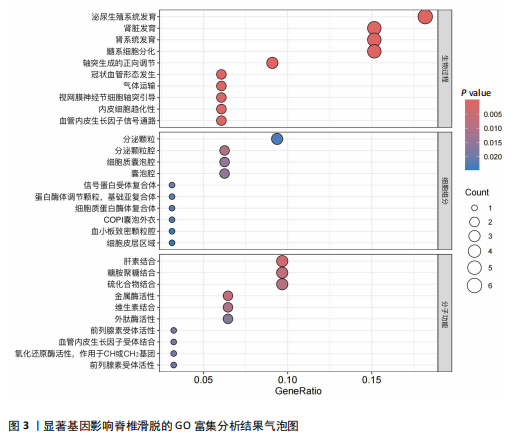
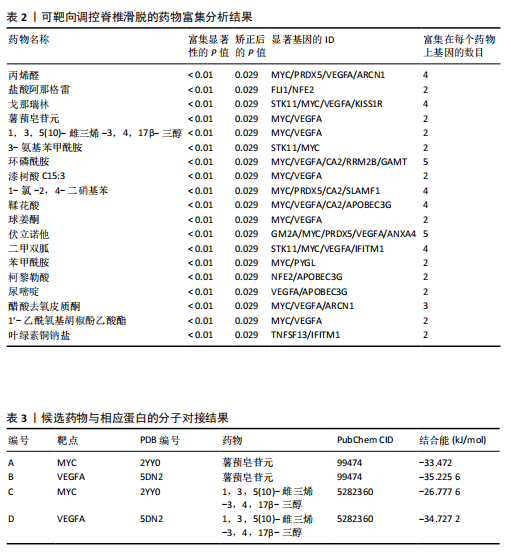
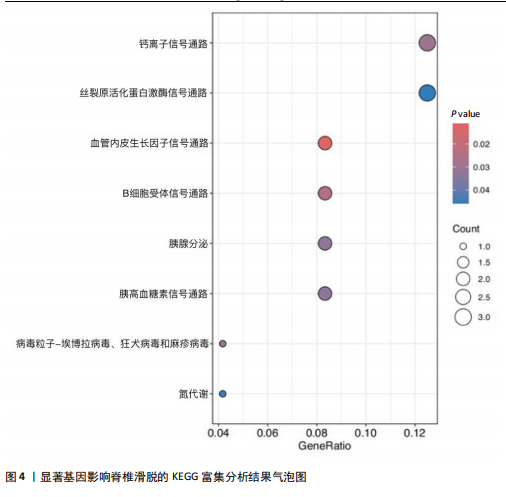
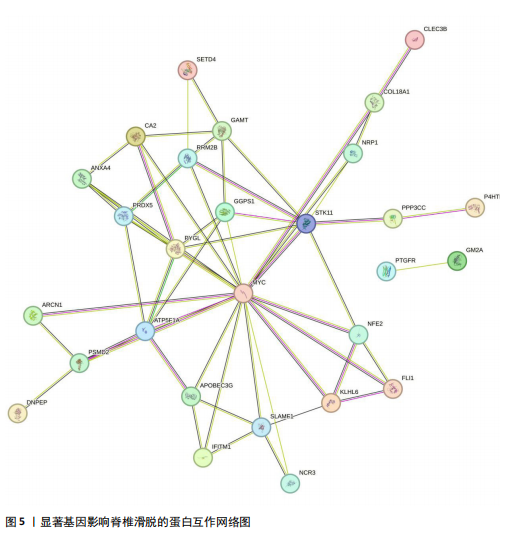
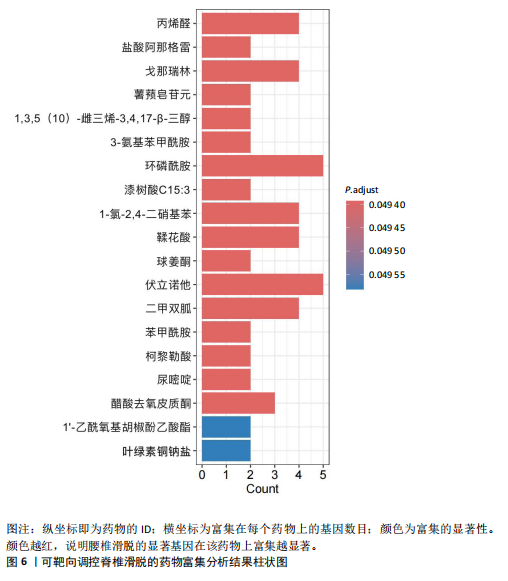
[1] KONIECZNY MR, JÄGER M. Spondylolisthesis. Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2023;52(11):931-940.
[2] POLLY DW JR, HASELHUHN JJ, SORIANO PBO, et al. Management of High-Grade Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2023;34(4):567-572.
[3] KONIECZNY MR, JÄGER M. Spondylolisthesis. Schmerz. 2024;38(2):157-166.
[4] ALOMARI S, JUDY B, SACINO AN, et al. Isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults… A review of the current literature. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;101:124-130.
[5] BERNARD F, MAZERAND E, GALLET C, et al. History of degenerative spondylolisthesis: From anatomical description to surgical management. Neurochirurgie. 2019;65(2-3):75-82.
[6] KANG WY, LEE JW, LEE E, et al. Efficacy and outcome predictors of fluoroscopy-guided facet joint injection for spondylolysis. Skeletal Radiol. 2018;47(8):1137-1144.
[7] JOELSON A. Surgery for spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. BMJ. 2024;386:q1628.
[8] QI T, SONG L, GUO Y, et al. From genetic associations to genes: methods, applications, and challenges. Trends Genet. 2024;40(8):642-667.
[9] LARSSON SC, BUTTERWORTH AS, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization for cardiovascular diseases: principles and applications. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(47): 4913-4924.
[10] STORM CS, KIA DA, ALMRAMHI MM, et al. Finding genetically-supported drug targets for Parkinson’s disease using Mendelian randomization of the druggable genome. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):7342.
[11] SCHMIDT AF, FINAN C, GORDILLO-MARAÑÓN M, et al. Genetic drug target validation using Mendelian randomisation. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3255.
[12] SU WM, GU XJ, DOU M, et al. Systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomisation identifies therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023;94(11):954-961.
[13] YIN KF, CHEN T, GU XJ, et al. Systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies therapeutic targets for sarcopenia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024;15(4):1324-1334.
[14] GAZIANO L, GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, PEREIRA AC, et al. Actionable druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies repurposing opportunities for COVID-19. Nat Med. 2021;27(4):668-676.
[15] 1000 GENOMES PROJECT CONSORTIUM,AUTON A, BROOKS LD, et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526(7571):68-74.
[16] FINAN C, GAULTON A, KRUGER FA, et al. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci Transl Med. 2017; 9(383):eaag1166.
[17] STALEY JR, BLACKSHAW J, KAMAT MA, et al. PhenoScanner: a database of human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(20):3207-3209.
[18] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525.
[19] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014; 10(5):e1004383.
[20] KANEHISA M, FURUMICHI M, SATO Y, et al. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D587-D592.
[21] RASOOLY D, PELOSO GM, PEREIRA AC, et al. Genome-wide association analysis and Mendelian randomization proteomics identify drug targets for heart failure. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):3826.
[22] YOO M, SHIN J, KIM J, et al. DSigDB: drug signatures database for gene set analysis. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(18):3069-3071.
[23] KIM S, CHEN J, CHENG T, et al. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023; 51(D1):D1373-D1380.
[24] DONG Y, TAO B, XUE X, et al. Molecular mechanism of Epicedium treatment for depression based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021;21(1):222.
[25] SHICHIJO T, YASUNAGA JI, SATO K, et al. Vulnerability to APOBEC3G linked to the pathogenicity of deltaretroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024;121(13):e2309925121.
[26] TALLURI S, SAMUR MK, BUON L, et al. Dysregulated APOBEC3G causes DNA damage and promotes genomic instability in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2021; 11(10):166.
[27] WANG Y, WU S, ZHENG S, et al. APOBEC3G acts as a therapeutic target in mesenchymal gliomas by sensitizing cells to radiation-induced cell death. Oncotarget. 2017;8(33): 54285-54296.
[28] PRABHU P, SHANDILYA SM, BRITAN-ROSICH E, et al. Inhibition of APOBEC3G activity impedes double-stranded DNA repair. FEBS J. 2016;283(1):112-129.
[29] KOMOHARA Y, SUEKANE S, NOGUCHI M, et al. Expression of APOBEC3G in kidney cells. Tissue Antigens. 2007;69(1):95-98.
[30] GARCÍA-RAMOS CL, VALENZUELA-GONZÁLEZ J, BAEZA-ÁLVAREZ VB, et al. Degenerative spondylolisthesis I: general principles. Acta Ortop Mex. 2020;34(5):324-328.
[31] KANG L, ZHANG H, JIA C, et al. Epigenetic modifications of inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;87:101902.
[32] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):47-60.
[33] LI H, WANG C, HE T, et al. Mitochondrial Transfer from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Motor Neurons in Spinal Cord Injury Rats via Gap Junction. Theranostics. 2019;9(7):2017-2035.
[34] XU M, FENG T, LIU B, et al. Engineered exosomes: desirable target-tracking characteristics for cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disease therapies. Theranostics. 2021;11(18):8926-8944.
[35] VIÑAS JL, BURGER D, ZIMPELMANN J, et al. Transfer of microRNA-486-5p from human endothelial colony forming cell-derived exosomes reduces ischemic kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2016;90(6):1238-1250.
[36] ZHANG S, TEO KYW, CHUAH SJ, et al. MSC exosomes alleviate temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation and restoring matrix homeostasis. Biomaterials. 2019;200:35-47.
[37] WANG T, JIAN Z, BASKYS A, et al. MSC-derived exosomes protect against oxidative stress-induced skin injury via adaptive regulation of the NRF2 defense system. Biomaterials. 2020;257:120264.
[38] XING H, ZHANG Z, MAO Q, et al. Injectable exosome-functionalized extracellular matrix hydrogel for metabolism balance and pyroptosis regulation in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):264.
[39] GANDHI NS, MANCERA RL. The structure of glycosaminoglycans and their interactions with proteins. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008; 72(6):455-482.
[40] SALBACH J, RACHNER TD, RAUNER M, et al. Regenerative potential of glycosaminoglycans for skin and bone. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012;90(6):625-635.
[41] LIAN JB, JAVED A, ZAIDI SK, et al. Regulatory controls for osteoblast growth and differentiation: role of Runx/Cbfa/AML factors. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2004; 14(1-2):1-41.
[42] BERRIDGE MJ, BOOTMAN MD, RODERICK HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(7):517-529.
[43] CAO Z, LIU D, ZHANG Q, et al. Aluminum Chloride Induces Osteoblasts Apoptosis via Disrupting Calcium Homeostasis and Activating Ca(2+)/CaMKII Signal Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;169(2):247-253.
[44] HU K, OLSEN BR. Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):509-526.
[45] AOKI Y, TAKAHASHI H, NAKAJIMA A, et al. Prevalence of lumbar spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in patients with degenerative spinal disease. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):6739.
[46] HEPWORTH EMW, HINTON SD. Pseudophosphatases as Regulators of MAPK Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12595.
[47] FALCICCHIA C, TOZZI F, ARANCIO O, et al. Involvement of p38 MAPK in Synaptic Function and Dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5624.
[48] JIA XB, ZHANG Q, XU L, et al. Lotus leaf flavonoids induce apoptosis of human lung cancer A549 cells through the ROS/p38 MAPK pathway. Biol Res. 2021;54(1):7.
[49] WU Z, HE D, ZHAO S, et al. IL-17A/IL-17RA promotes invasion and activates MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression via p38 MAPK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;455(1-2):195-206.
[50] REN Y, OUYANG Z, HOU Z, et al. CIC Is a Mediator of the ERK1/2-DUSP6 Negative Feedback Loop. iScience. 2020;23(11): 101635.
[51] FU B, LIANG J, HU J, et al. GPCR-MAPK signaling pathways underpin fitness trade-offs in whitefly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024;121(28):e2402407121.
[52] WEN X, JIAO L, TAN H. MAPK/ERK Pathway as a Central Regulator in Vertebrate Organ Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3): 1464.
[53] HWANG JH, PARK YS, KIM HS, et al. Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice. J Control Release. 2023;355:184-198.
[54] CONG S, PENG Q, CAO L, et al. Diosgenin prevents periodontitis by inhibiting inflammation and promoting osteogenic differentiation. Oral Dis. 2024;30(4):2497-2510.
[55] TOMÉ-BERMEJO F, PIÑERA AR, ALVAREZ L. Osteoporosis and the Management of Spinal Degenerative Disease (II). Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2017;5(6):363-374.
[56] HASSAN KZ, SHERMAN AL. Epidural Steroids. In: StatPearls[Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2025.
[57] HERNÁNDEZ N, LÓPEZ-MORATÓ M, PERIANES MJ, et al. 4-Hydroxyestradiol improves mouse embryo quality, epidermal growth factor-binding capability in vitro and implantation rates. Mol Hum Reprod. 2021;27(2):gaaa075.
[58] ALANKO J, SIEVI E, LÄHTEENMÄKI T, et al. Catechol estrogens as inhibitors of leukotriene synthesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;55(1):101-104.
[59] CHEN Q, TU Z, AI Y, et al. Forearm bone mineral density predicts screw loosening after lumbar fusion similar to lumbar Hounsfield unit value in patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis. Osteoporos Int. 2024;35(3):543-549.
[60] LANXIANG W, BIN W, GE X, et al. Long-term exposure of 4-hydroxyestradiol induces the cancer cell characteristics via upregulating CYP1B1 in MCF-10A cells. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2019;29(9):686-692.
|